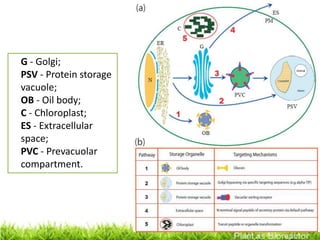
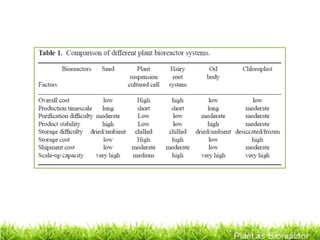
Plants can be used as bioreactors to produce valuable proteins and chemicals. There are several types of plant bioreactors, including seed-based systems, plant suspension cultures, hairy root cultures, and chloroplast bioreactors. Plants offer advantages over traditional fermentation systems as they are inexpensive to culture and scale up, can produce properly folded and assembled proteins, and do not harbor human pathogens. However, some safety and environmental concerns must be addressed when using genetically modified plants as bioreactors.