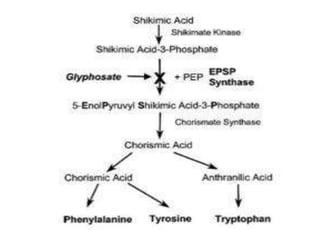
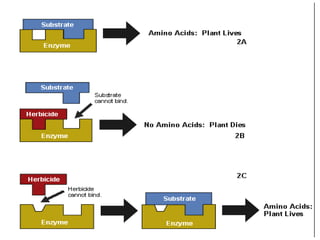
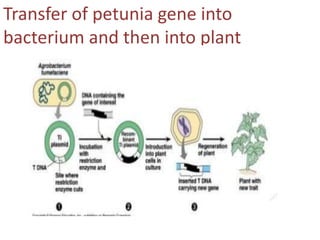
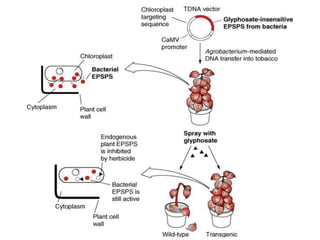
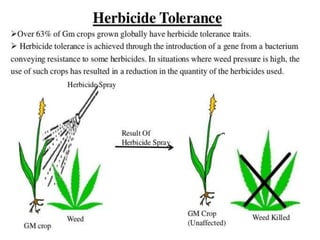
Weeds reduce crop yields by 10-15% by competing for resources. Herbicides were developed to control weeds, but can also damage crops. Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum herbicide that inhibits the shikimic acid pathway in plants, blocking growth. To develop resistant crops, scientists have introduced the petunia EPSPS gene to overexpress the enzyme, used a mutant version of EPSPS that cannot bind glyphosate, and introduced bacterial genes that detoxify glyphosate. Combining these strategies provides high levels of herbicide resistance.