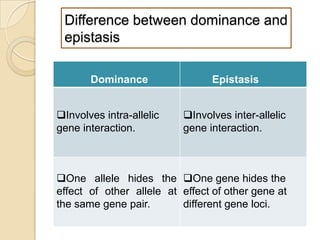
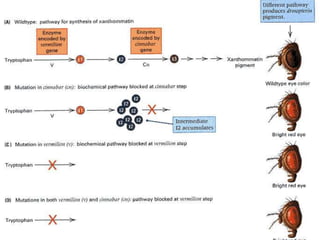
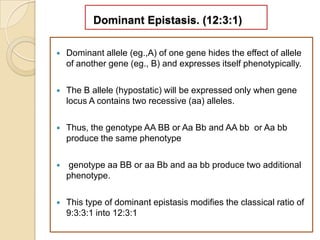
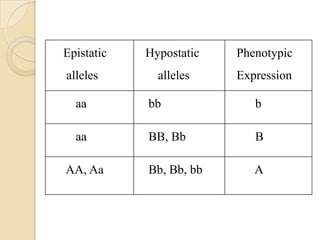
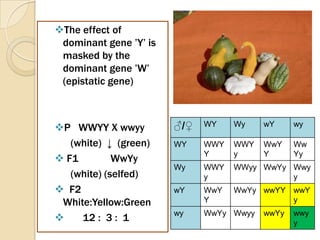
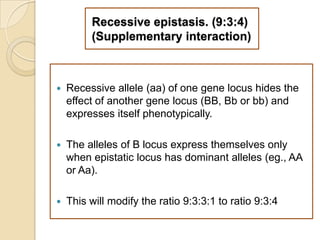
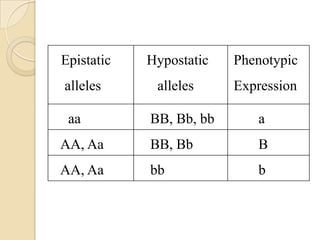
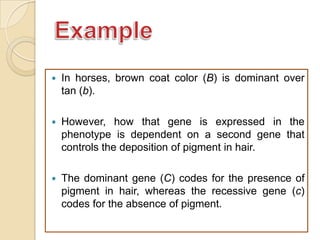
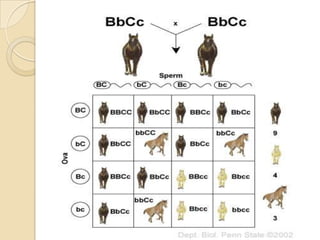
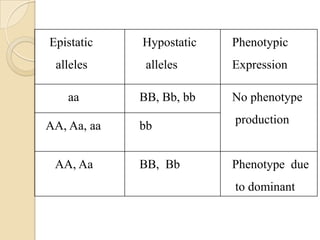
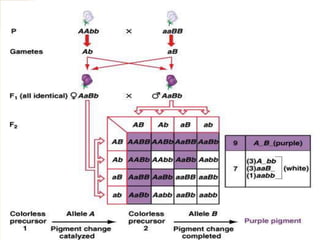
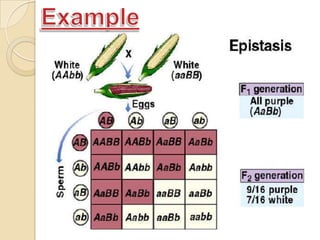
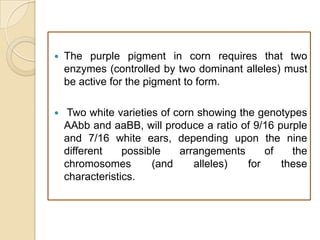
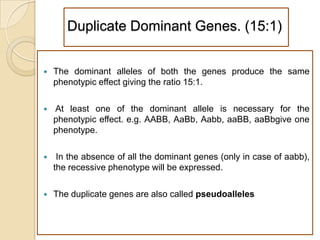
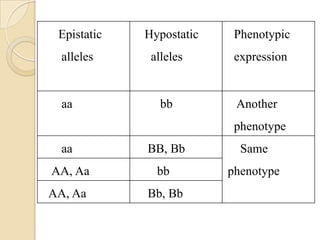
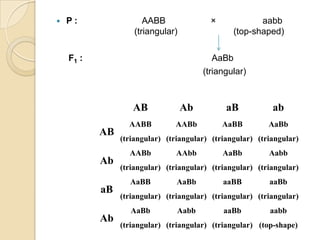
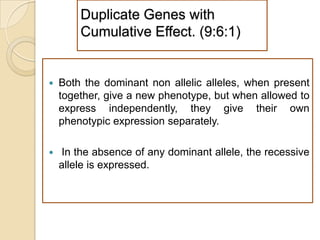
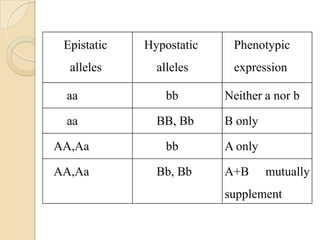
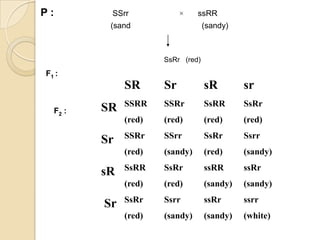
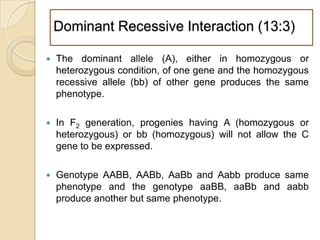
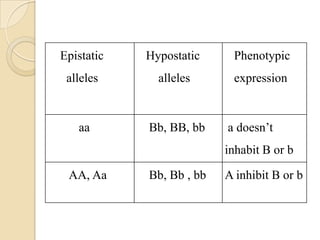
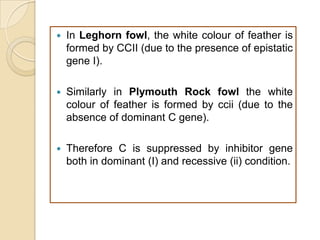
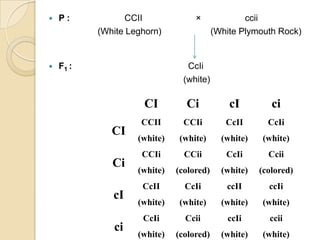
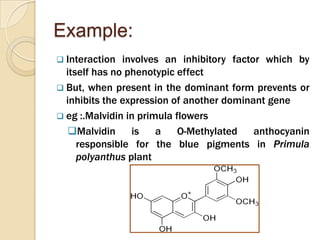
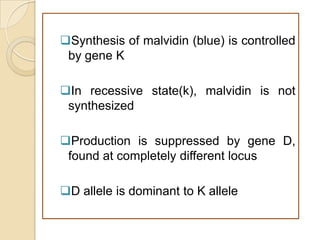
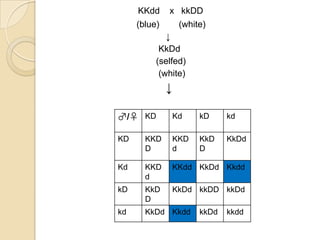
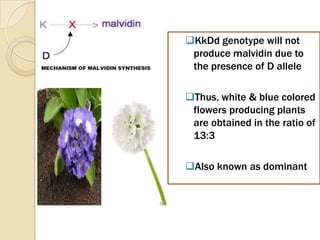
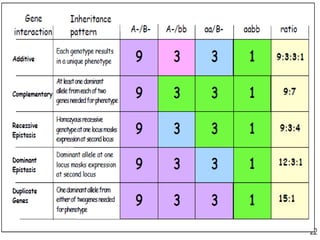
The document discusses different types of epistatic interactions, including dominant and recessive epistasis where one gene hides the effects of another gene. It provides examples of different epistatic ratios seen in traits like eye color in Drosophila and fruit shape in plants. The types of epistasis covered include dominant, recessive, duplicate recessive genes, and genes with cumulative effects.