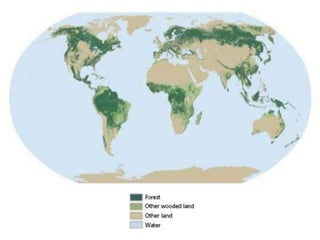
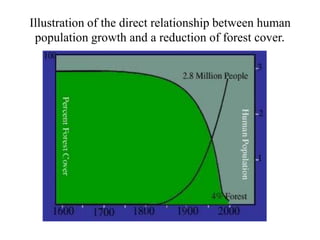
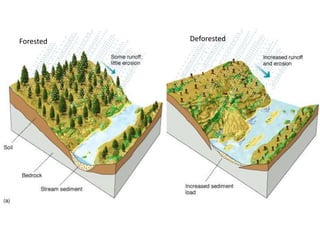
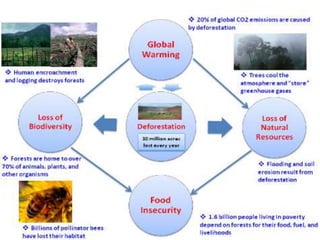
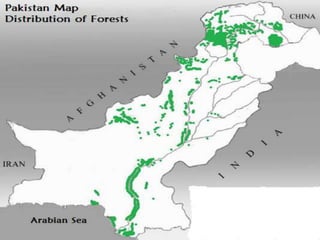
Deforestation is the removal of forests to make room for human development. It has increased due to population growth, urbanization, and industrialization. Deforestation leads to soil erosion, flooding, loss of wildlife, increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, and other environmental issues. Pakistan has one of the highest deforestation rates in Asia due to unsustainable logging and lack of enforcement of forestry laws. Reforestation efforts and use of alternative energy are needed to address deforestation.