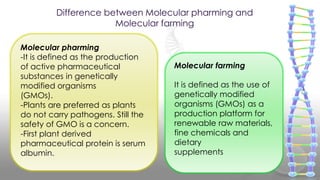
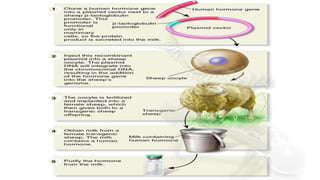
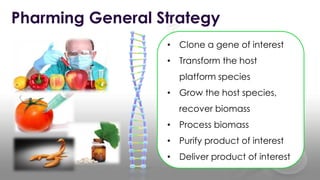
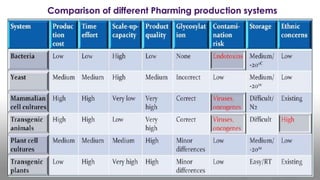
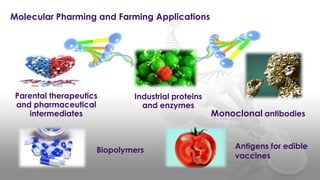
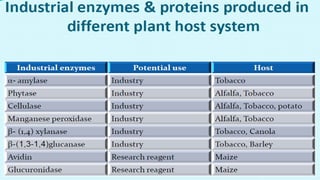
This document discusses molecular pharming, which uses plants or other organisms as bioreactors for producing commercially valuable products through recombinant DNA techniques. It defines molecular pharming and farming and describes the process of transforming organisms with genes for a target product and extracting the product. The history of major developments is reviewed. Advantages include low cost large-scale production, but biosafety issues include gene pollution and ensuring product safety. Containment strategies and alternative production methods aim to address these risks. Overall, molecular farming provides opportunities for economical mass production if risks to health and environment can be adequately managed.