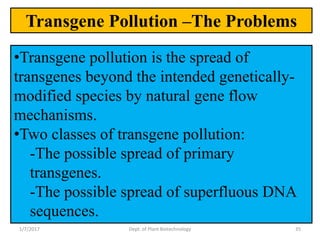
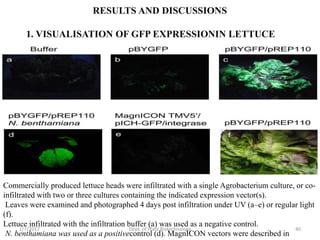
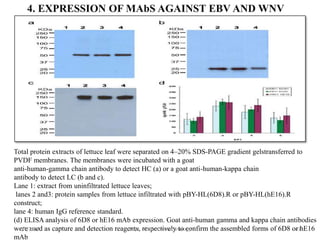
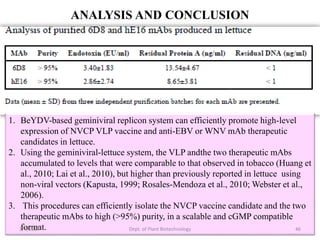
This document discusses plant molecular pharming (PMP), which uses plants as bioreactors for producing recombinant pharmaceutical proteins. It covers the definition, history, strategies, host systems, production of antibiotics/enzymes/vaccines in plants, advantages/disadvantages of plant systems, and issues of transgene pollution. Key points include:
- PMP uses whole plants, plant cells or tissues to produce commercially valuable proteins like vaccines via recombinant DNA.
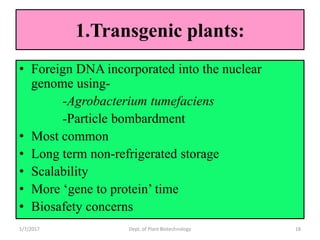
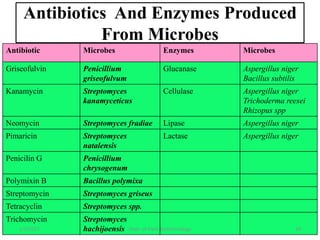
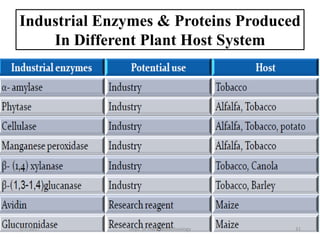
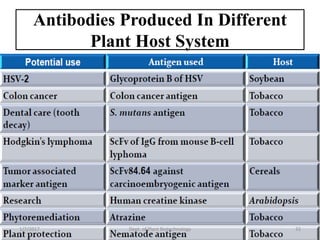
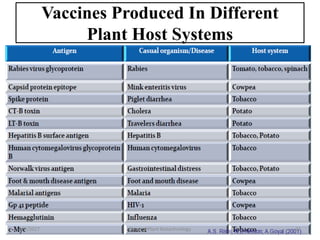
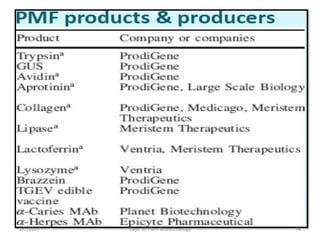
- Early work in 1986 produced human growth hormone in tobacco and sunflower. Commercial production of various proteins in plants has occurred.
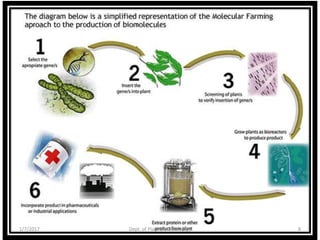
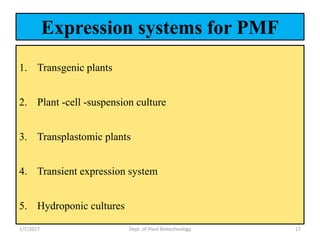
- Strategies include transforming host plants, growing biomass, processing/purifying the product of interest.
- Plants,