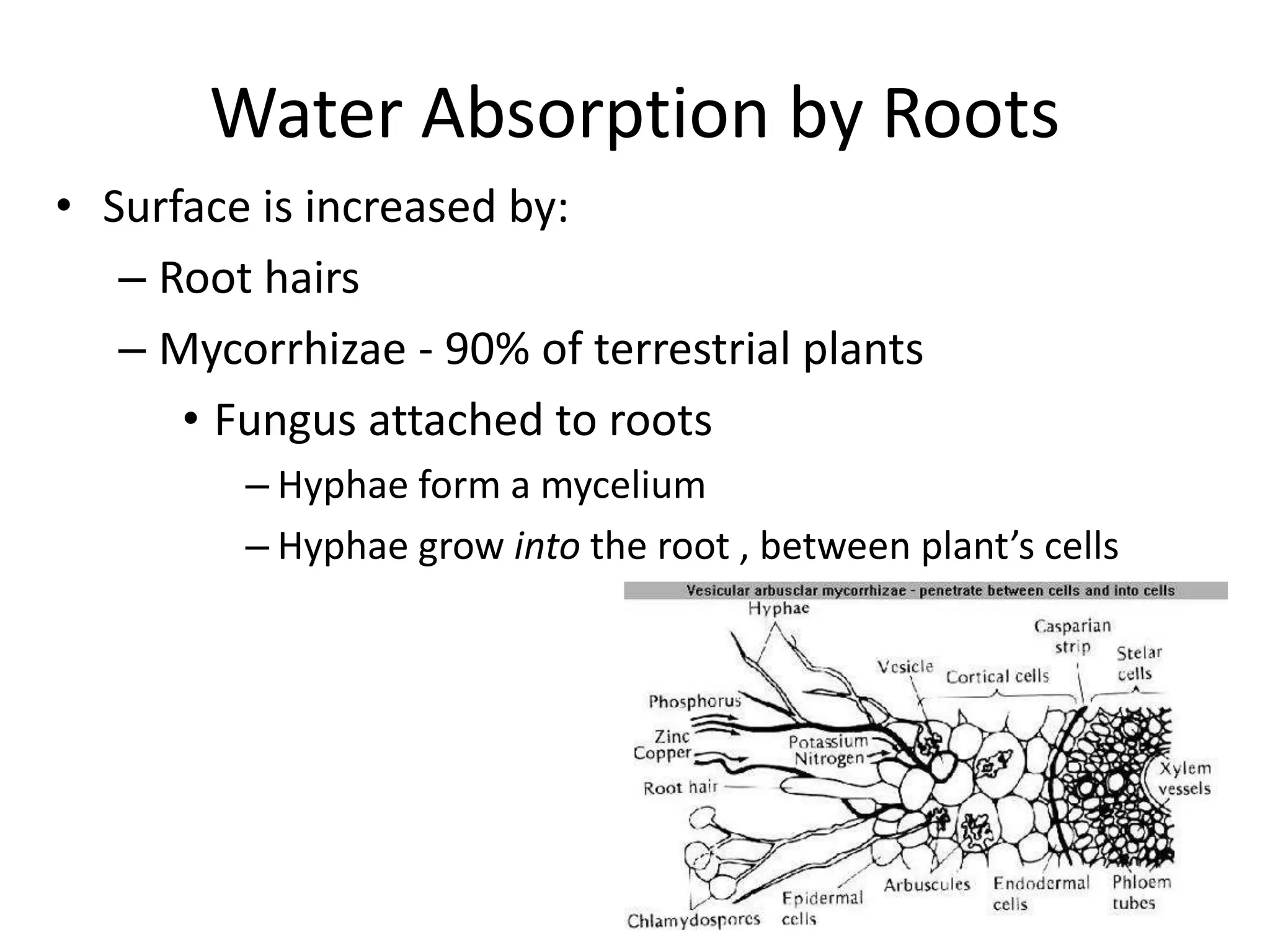
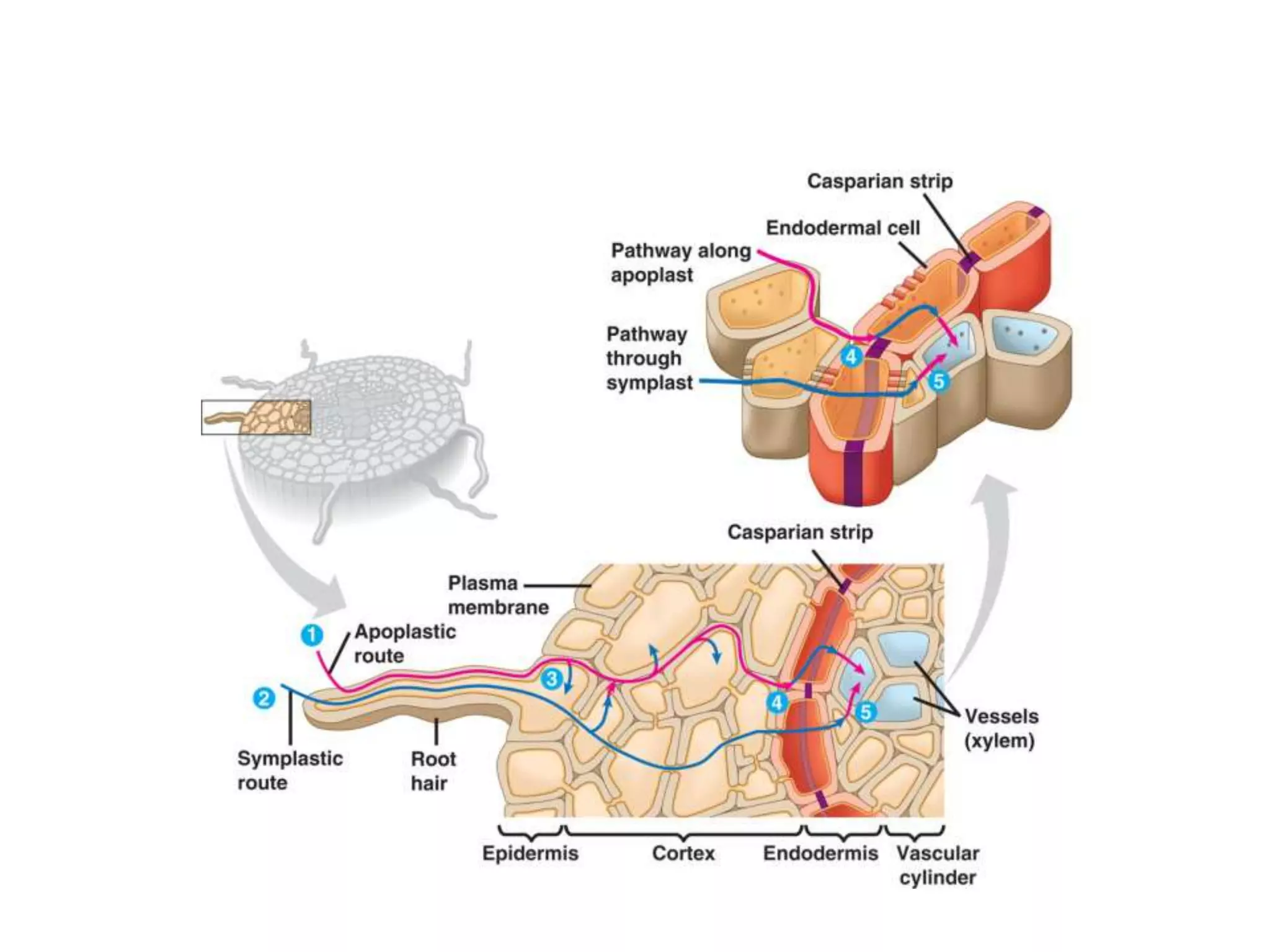
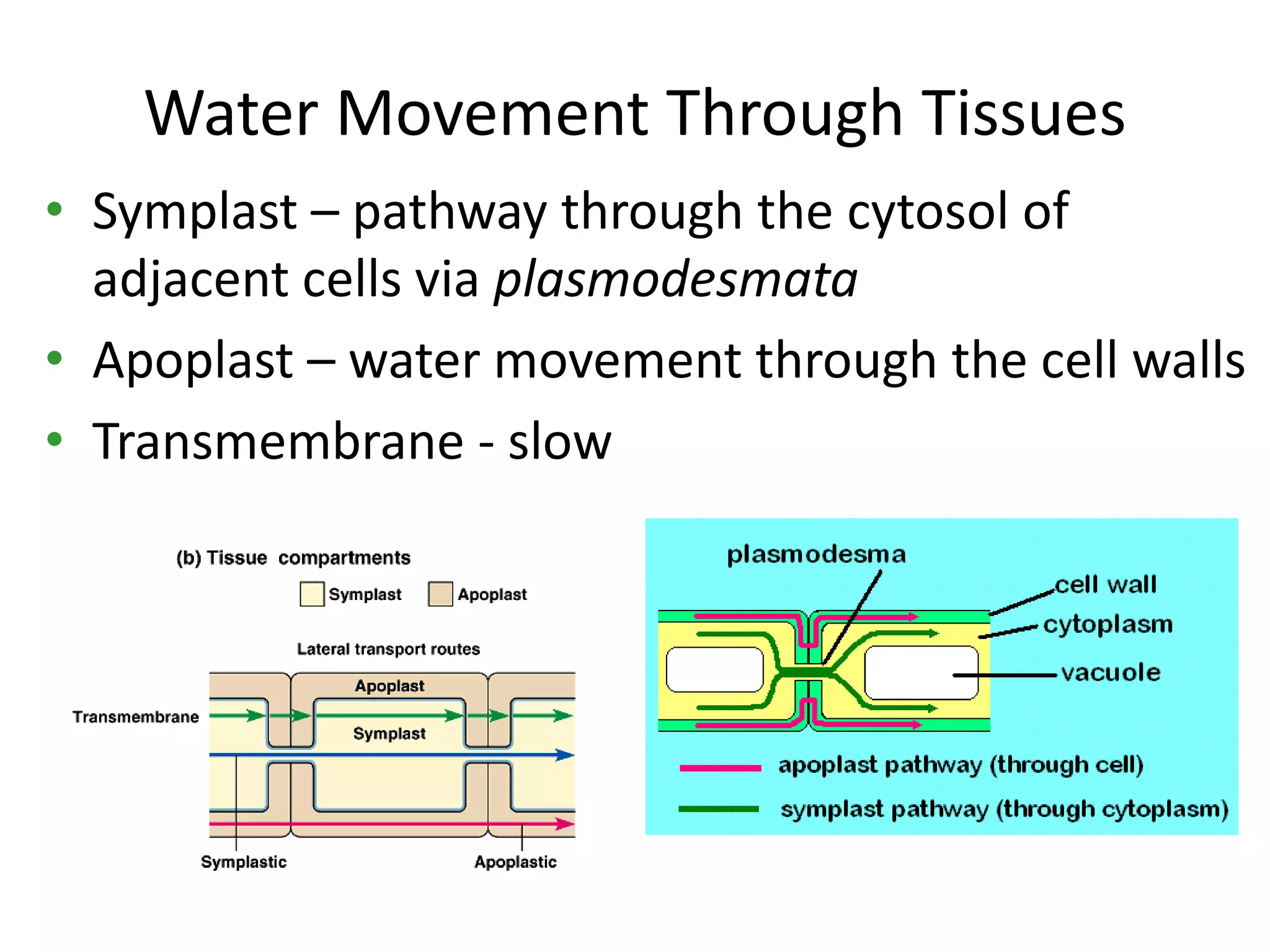
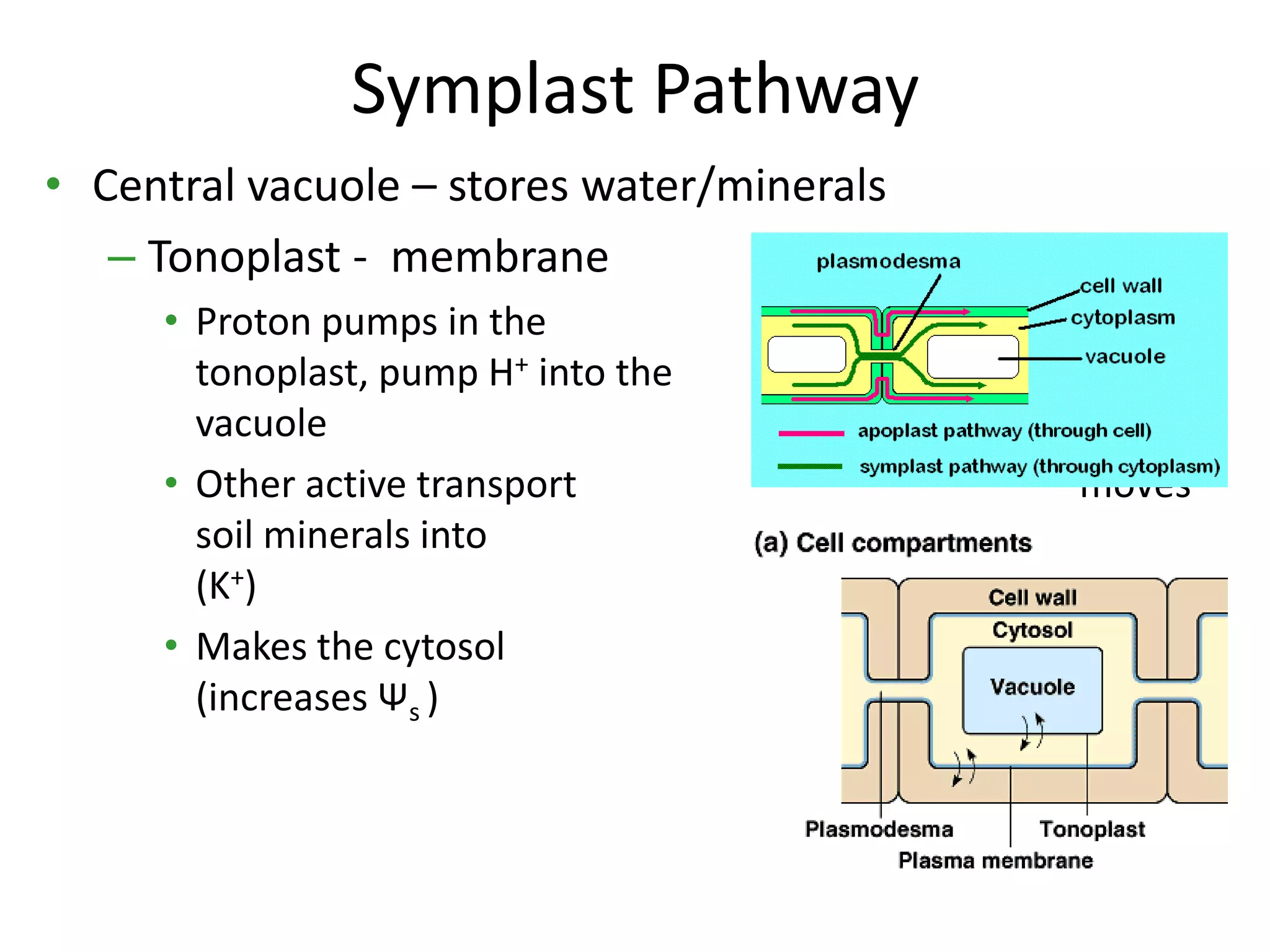
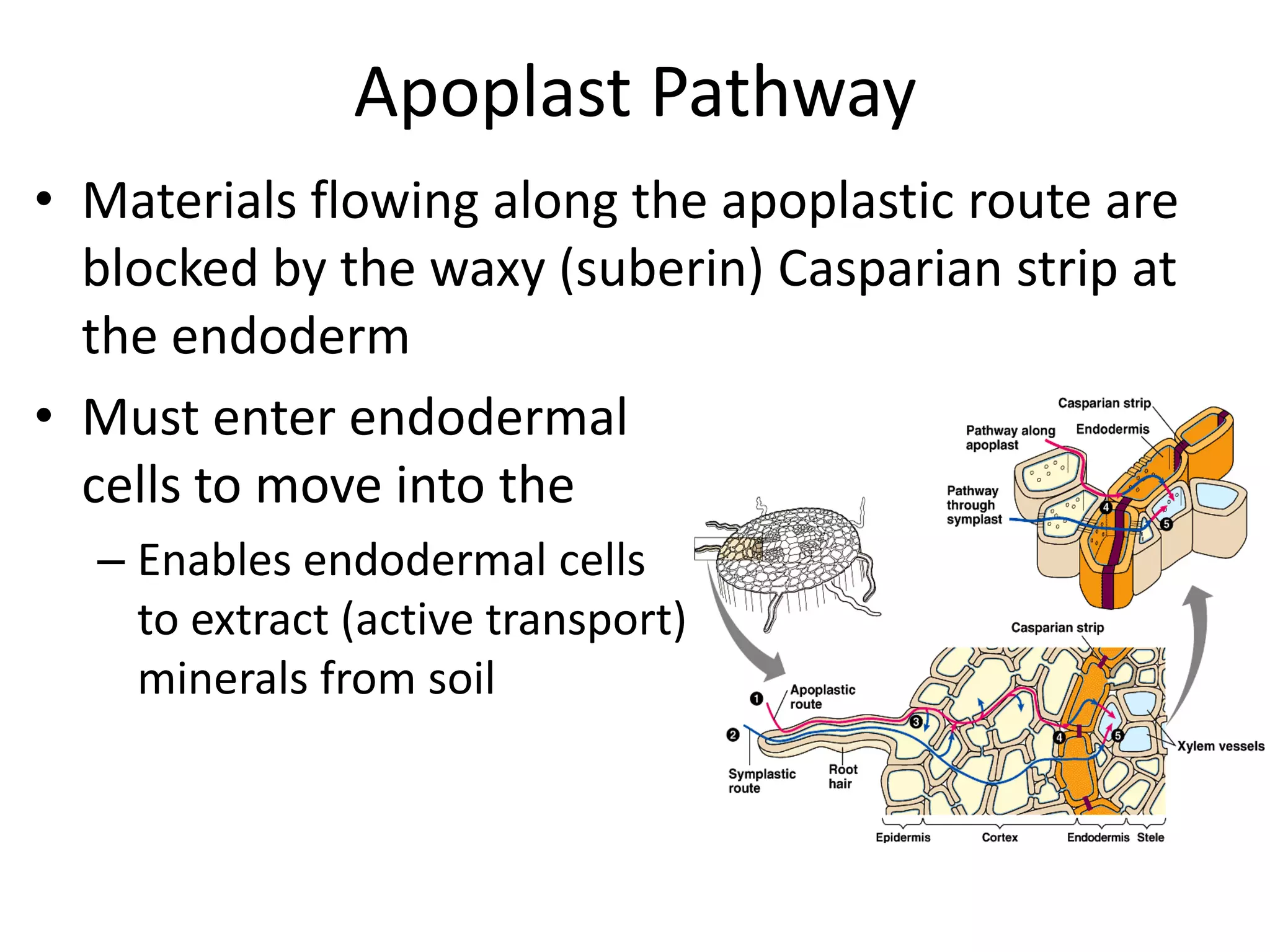
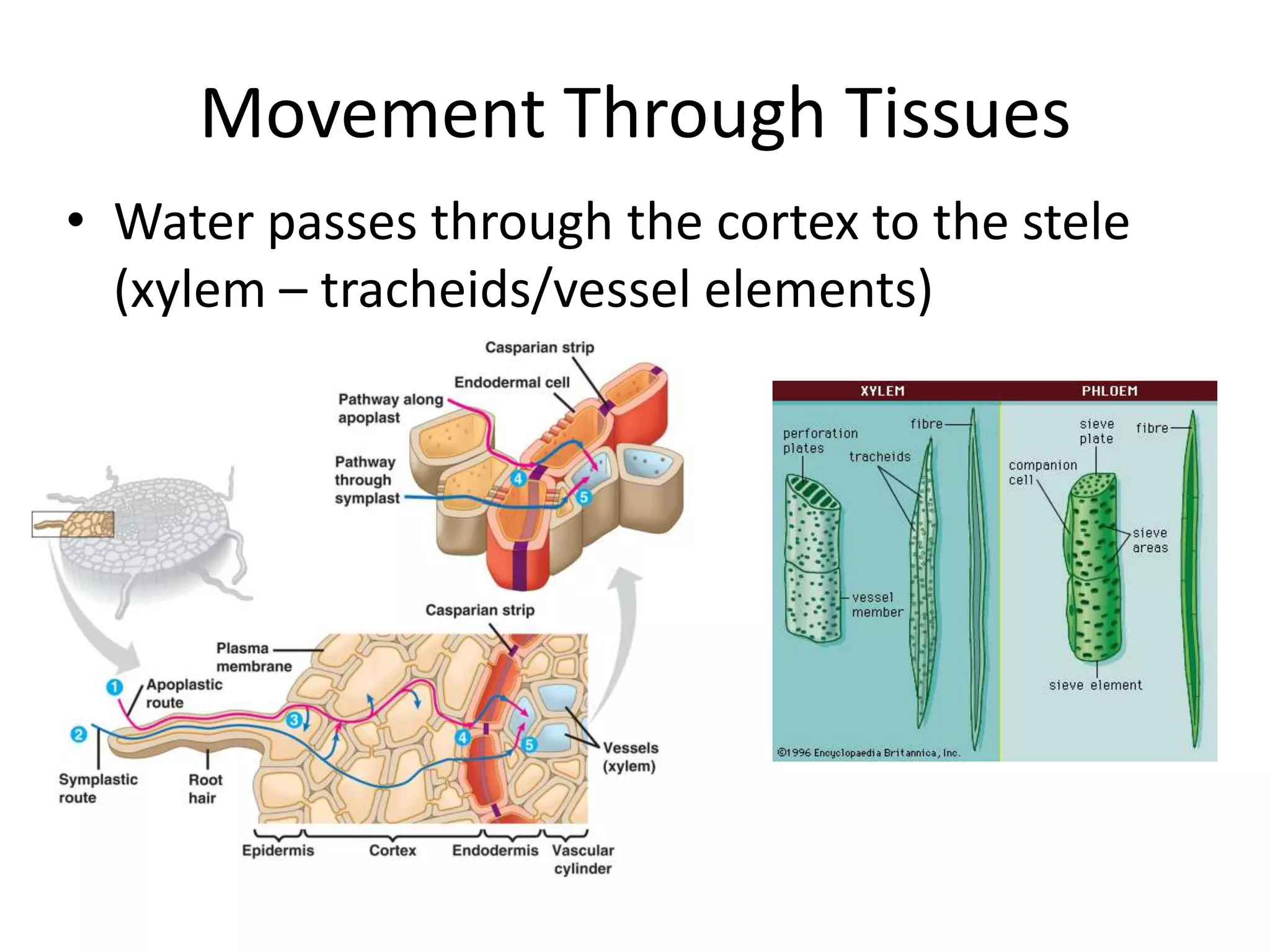
This document discusses the movement of water at the tissue and organ level in plants. It describes how water is absorbed by roots through root hairs and mycorrhizal fungi, then passed through the root cortex to the stele via the apoplast or symplast pathways. The symplast involves movement through plasmodesmata connecting cell cytosols, while the apoplast involves movement through cell walls. Water then moves up through the xylem tracheids and vessel elements to the stem.