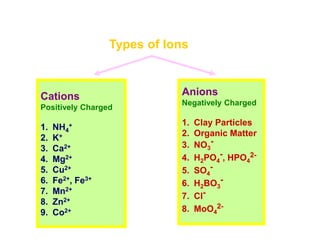
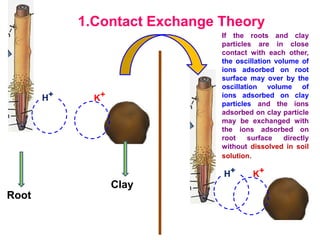
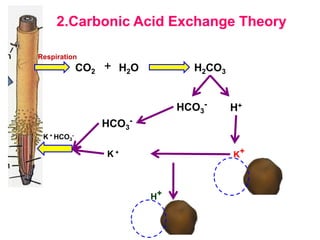
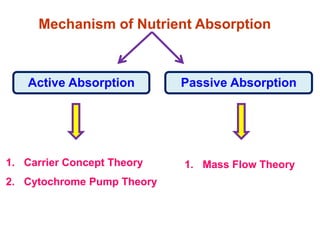
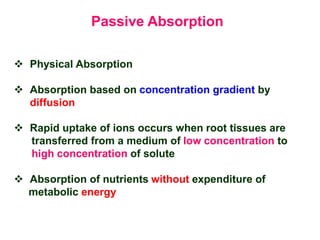
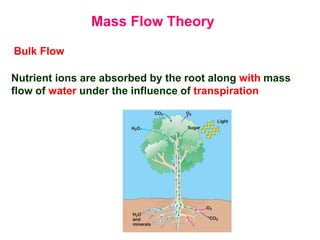
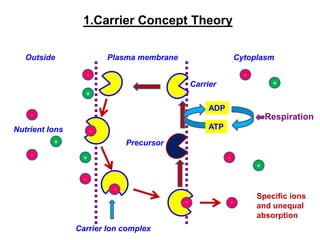
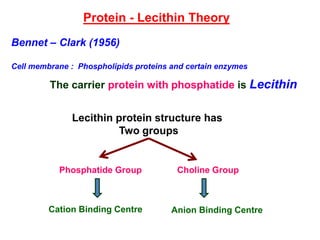
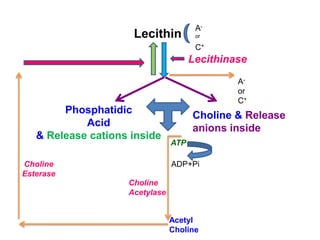
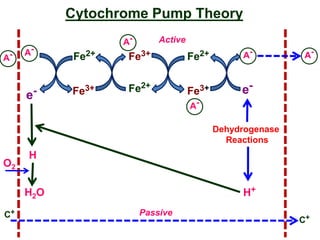
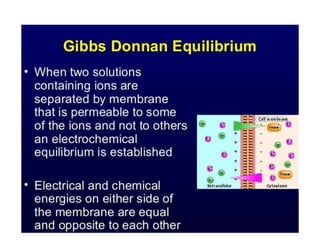
The document discusses nutrient uptake by plant roots. Ions are absorbed through the meristematic region of roots either actively, through carrier proteins and cytochrome pumps, or passively through diffusion or mass flow. Active transport requires energy and moves ions against their concentration gradient, while passive transport relies on gradients. Once inside root cells, ions move between cells through apoplastic or symplastic pathways and eventually load into the xylem for long-distance transport.