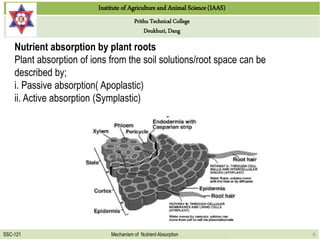
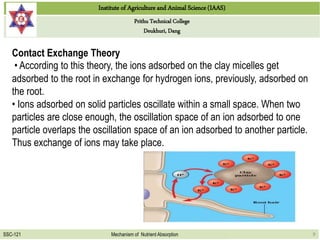
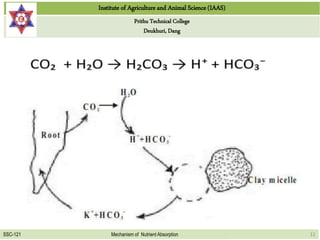
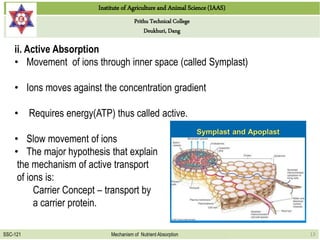
This document discusses the mechanisms by which nutrients are absorbed by plant roots from soil. It explains that nutrients come into contact with roots through root interception, mass flow, or diffusion. Root interception occurs when nutrients physically contact roots, while mass flow transports nutrients to roots via water movement. Diffusion moves nutrients along a concentration gradient from high to low. Nutrients are then absorbed passively through the root cell walls or actively through the cells with energy usage. Passive absorption follows concentration gradients, while active transport moves nutrients against gradients with carrier proteins.