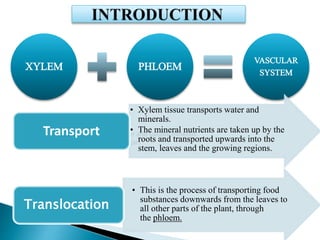
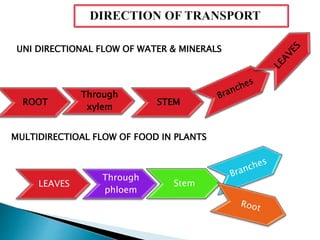
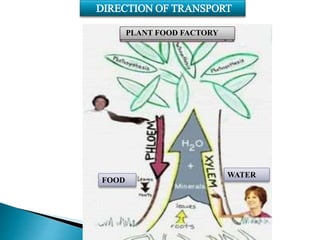
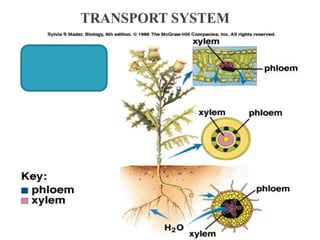
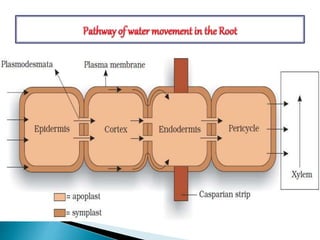
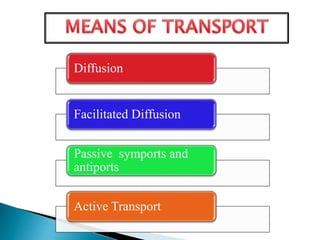
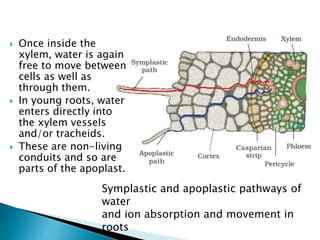
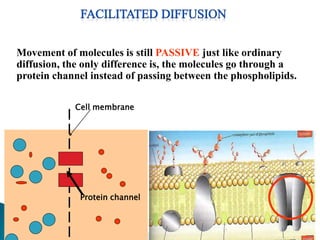
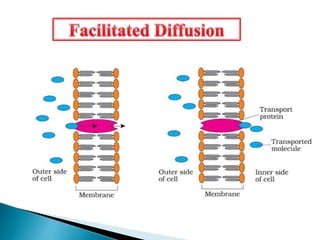
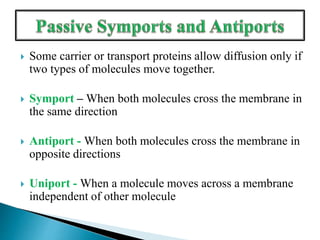
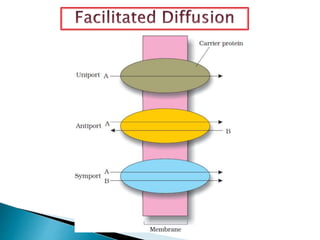
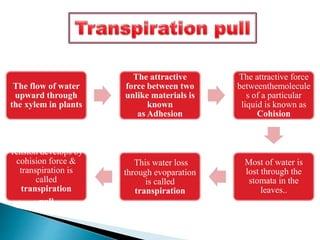
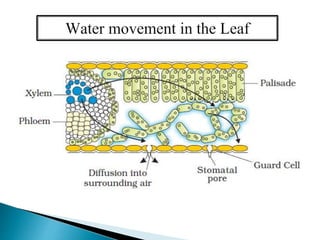
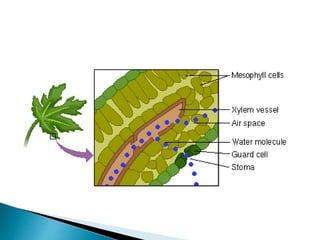
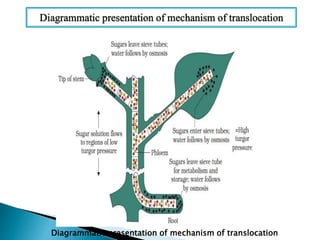
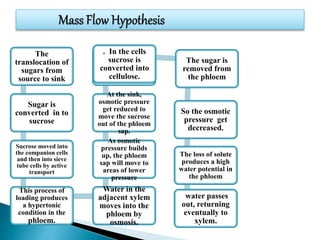
Plants require a transport system to facilitate the movement of nutrients, particularly water and sugars, between their roots and leaves. This transport occurs through xylem tissue, which carries water and minerals, and phloem tissue, which distributes sugars throughout the plant. Various mechanisms, including diffusion, active transport, and osmosis, play critical roles in nutrient absorption and translocation within the plant.