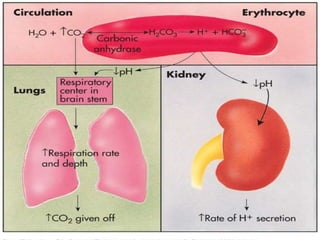
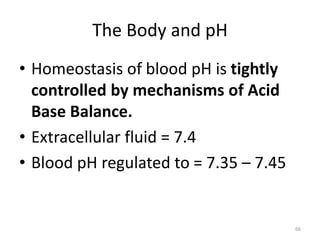
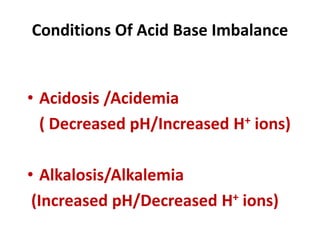
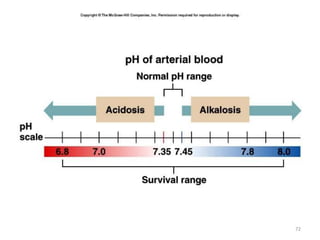
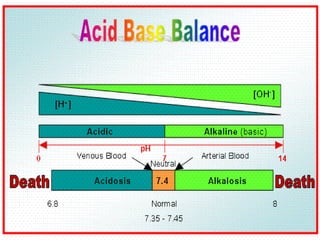
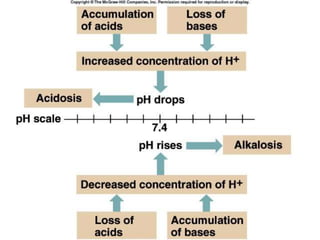
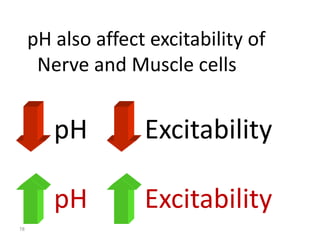
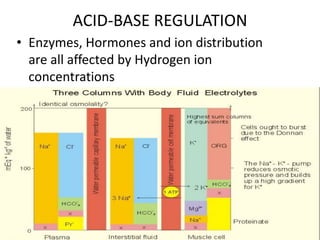
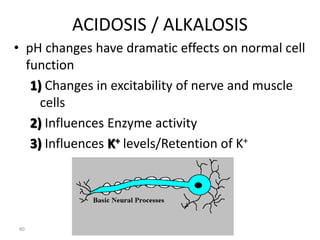
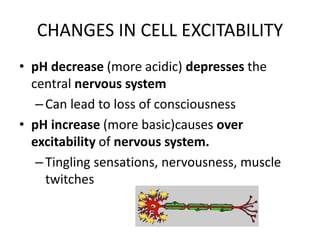
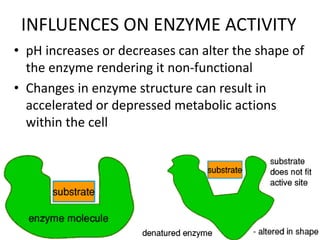
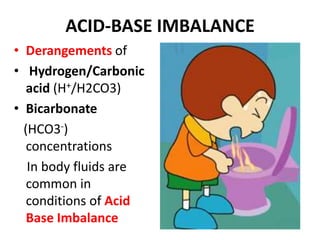
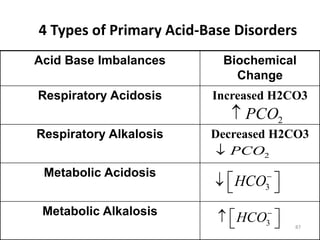
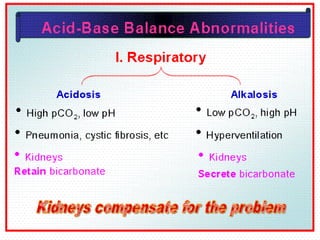
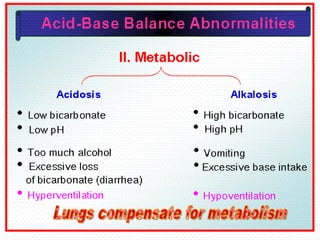
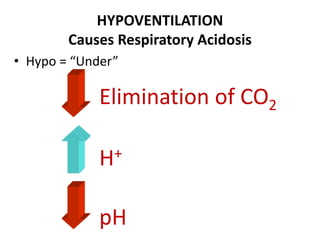
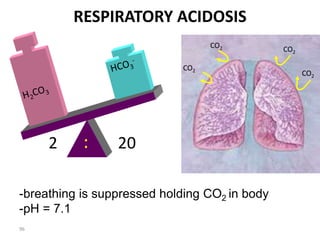
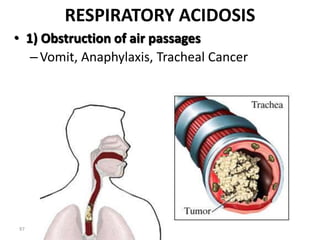
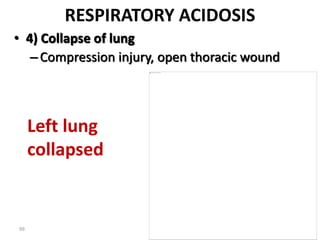
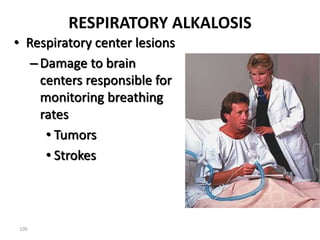
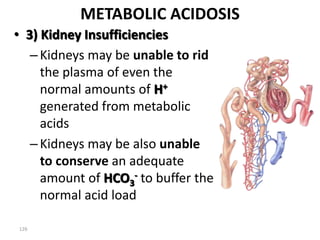
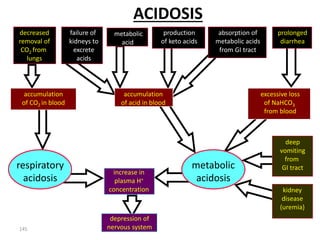
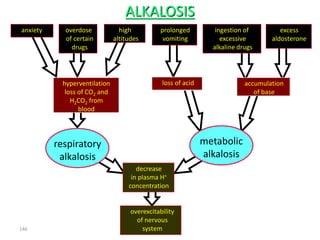
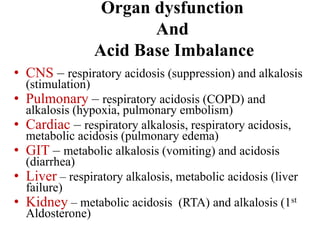
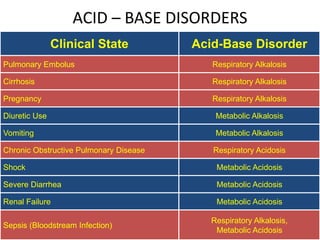
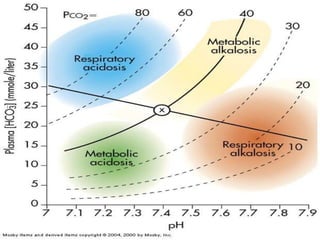
This document discusses acid-base balance and the mechanisms that regulate blood pH homeostasis. It begins by defining pH and explaining why blood pH is tightly regulated. It then describes the various sources of acids and bases in the body from metabolic processes. The key mechanisms that regulate blood pH include buffer systems, respiratory regulation, and renal regulation. Buffers act quickly, respiration provides short-term regulation, and the kidneys provide long-term regulation. Imbalances can occur if these regulatory mechanisms fail, leading to acidosis or alkalosis conditions.



![What Is pH?
• pH is a Hydrogen ion concentration.
• pH = - log [H+]
• Different compartment of human
body has specific pH.
• pH has role in Enzyme activity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalacidbasebalane-221122035856-3d7b41f5/85/final_acid_base_balane-pptx-4-320.jpg)








































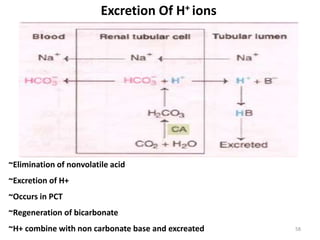
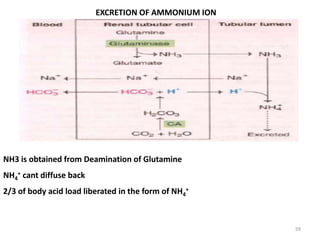

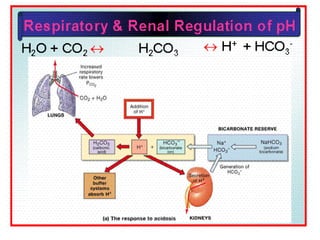
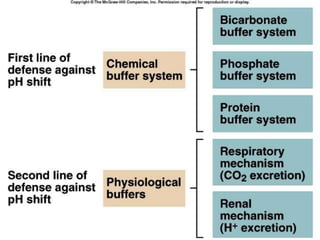

























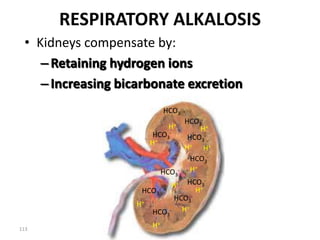
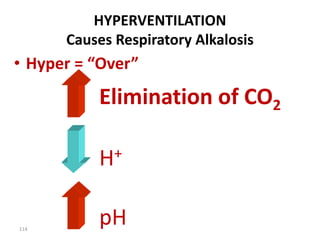




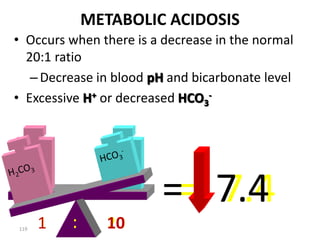































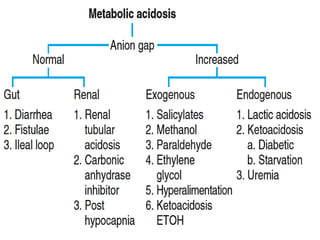

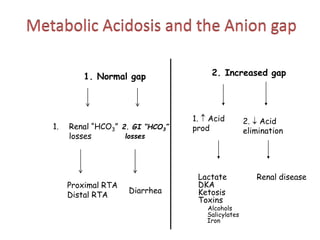
![Anion Gap Acidosis:
• Anion gap >12 mmol/L; caused by a decrease
in [HCO3 -]
• Balanced by an increase in an unmeasured
acid ion from either endogenous production
or exogenous ingestion (normochloremic
acidosis).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalacidbasebalane-221122035856-3d7b41f5/85/final_acid_base_balane-pptx-161-320.jpg)

![Henderson Hasselbalch Equation
• pH= pka +log [HCO3-]/[H2CO3]
• At pH 7.4 the ratio of HCO3-/H2CO3
is 1:20.
• A buffer is most effective when
pH=pKa
• When concentration of salt and acid
are equal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalacidbasebalane-221122035856-3d7b41f5/85/final_acid_base_balane-pptx-164-320.jpg)