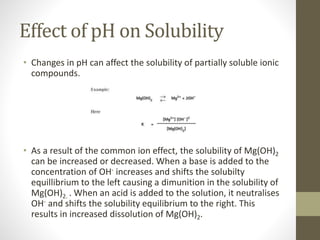
Biological buffers are organic substances that neutralize hydrogen ions to maintain optimal pH for biochemical processes, comprising weak acids and their conjugate bases. They play crucial roles in homeostasis, enzymatic regulation, and pH control in biological systems, with examples including bicarbonate, phosphate, and protein buffers. The effectiveness of these buffers is influenced by their concentration and the presence of other chemicals that may affect enzymatic activity and solubility.




![Handerson-Hasselbalch Equation
• The pH of a solution containing a weak acid is related to its
acid dissociation constant. The relationship can be stated in
the convenient form of the “ Handerson- Hasselbalch
equation”
pH = Pka+ log10 [A-]
[HA]
• The Handerson- Hasselbalch equation is an expression of
great predictive value in protonic equilibria.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffersinbiologicalsystems-240430150229-de5130ac/85/buffers_in_biological_systems_acid_base-5-320.jpg)









![Buffering in Cells and Tissues
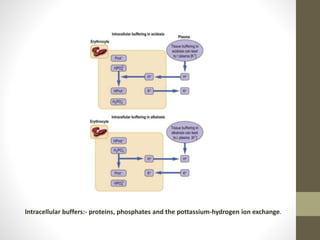
• Amino acids present in proteins in cells and tissues contain
functional groups that act as weak acid and bases.
• The phosphate and bicarbonate buffer systems are most
predominant in biological systems.
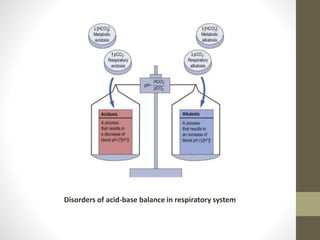
• The bicarbonate buffer system plays an important role in
buffering the blood system where in carbonic acid acts as a
weak acid (proton donor) and bicarbonate act as a conjugate
base (proton acceptor). Their relationship can be expressed as
follows:-
K1 = [H+] [HCO3
-]
[H2CO3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffersinbiologicalsystems-240430150229-de5130ac/85/buffers_in_biological_systems_acid_base-17-320.jpg)