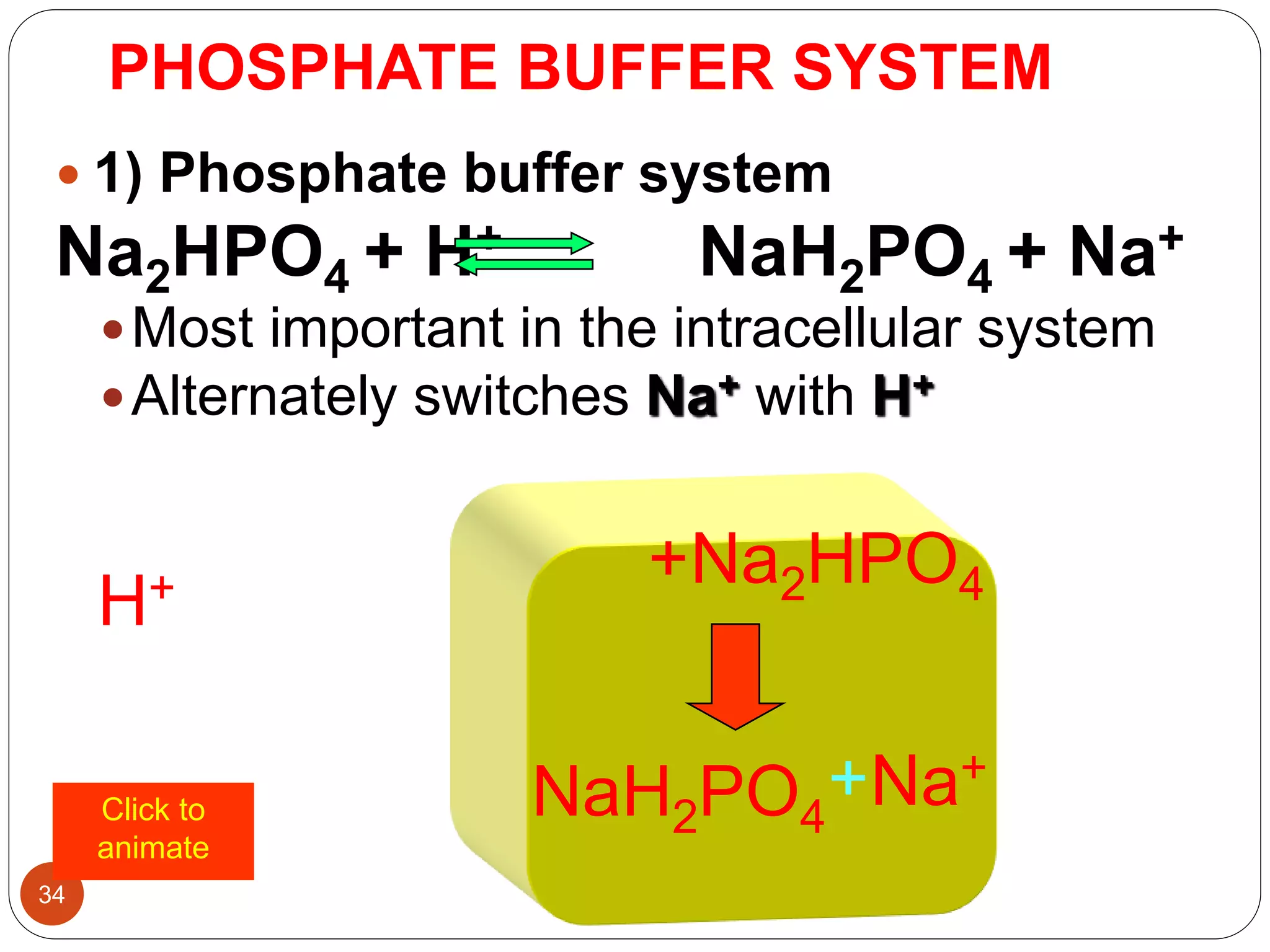
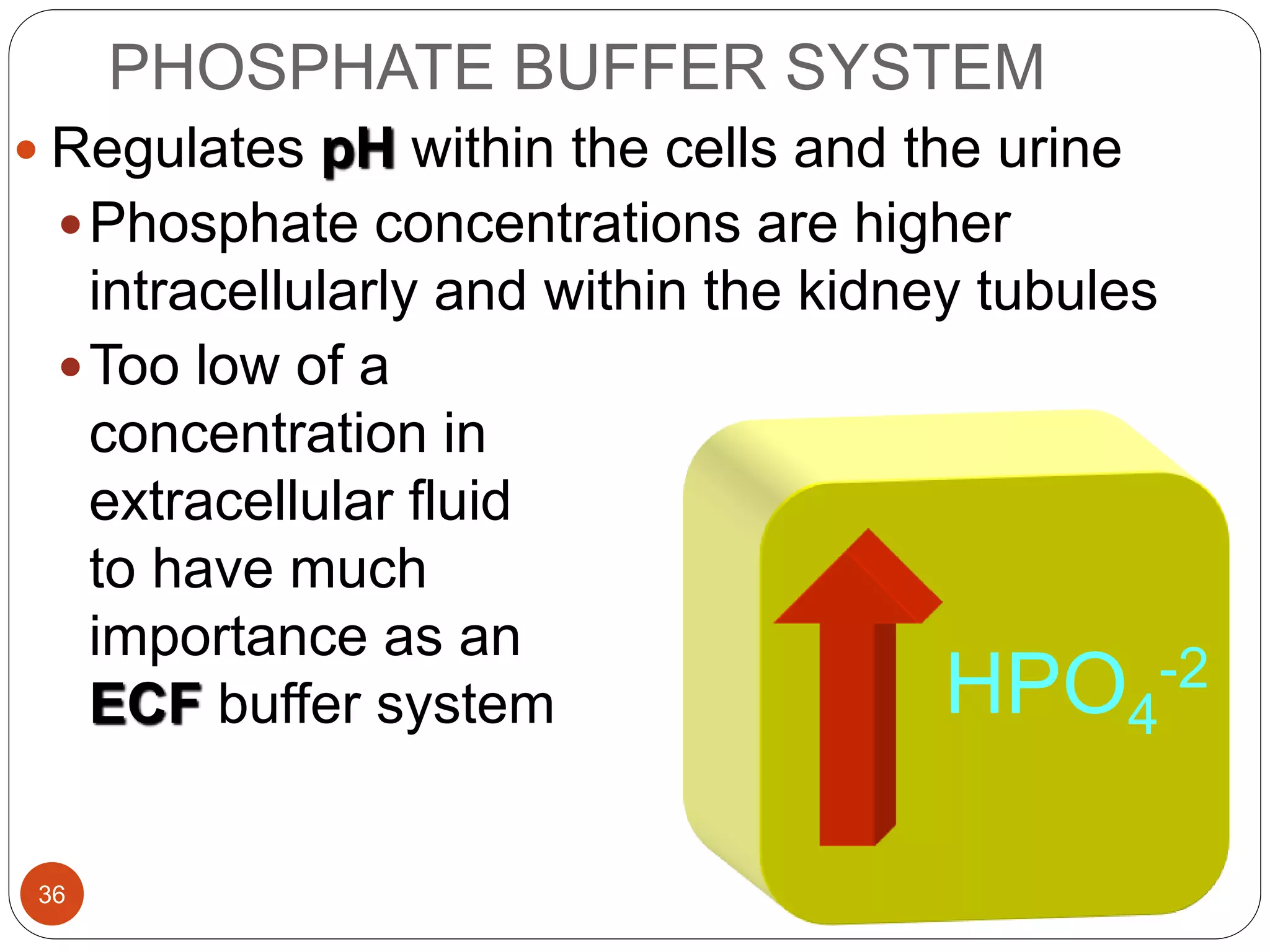
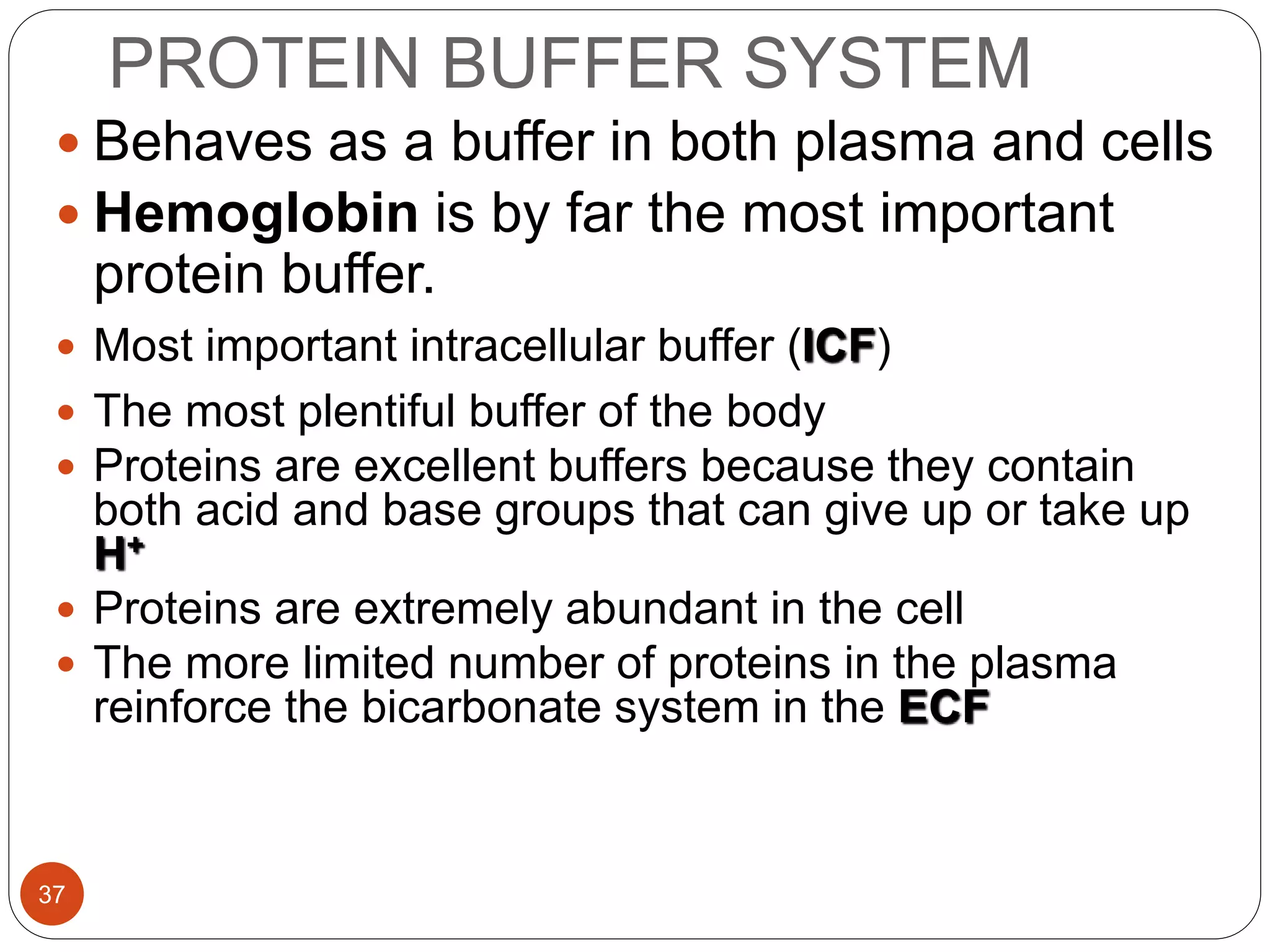
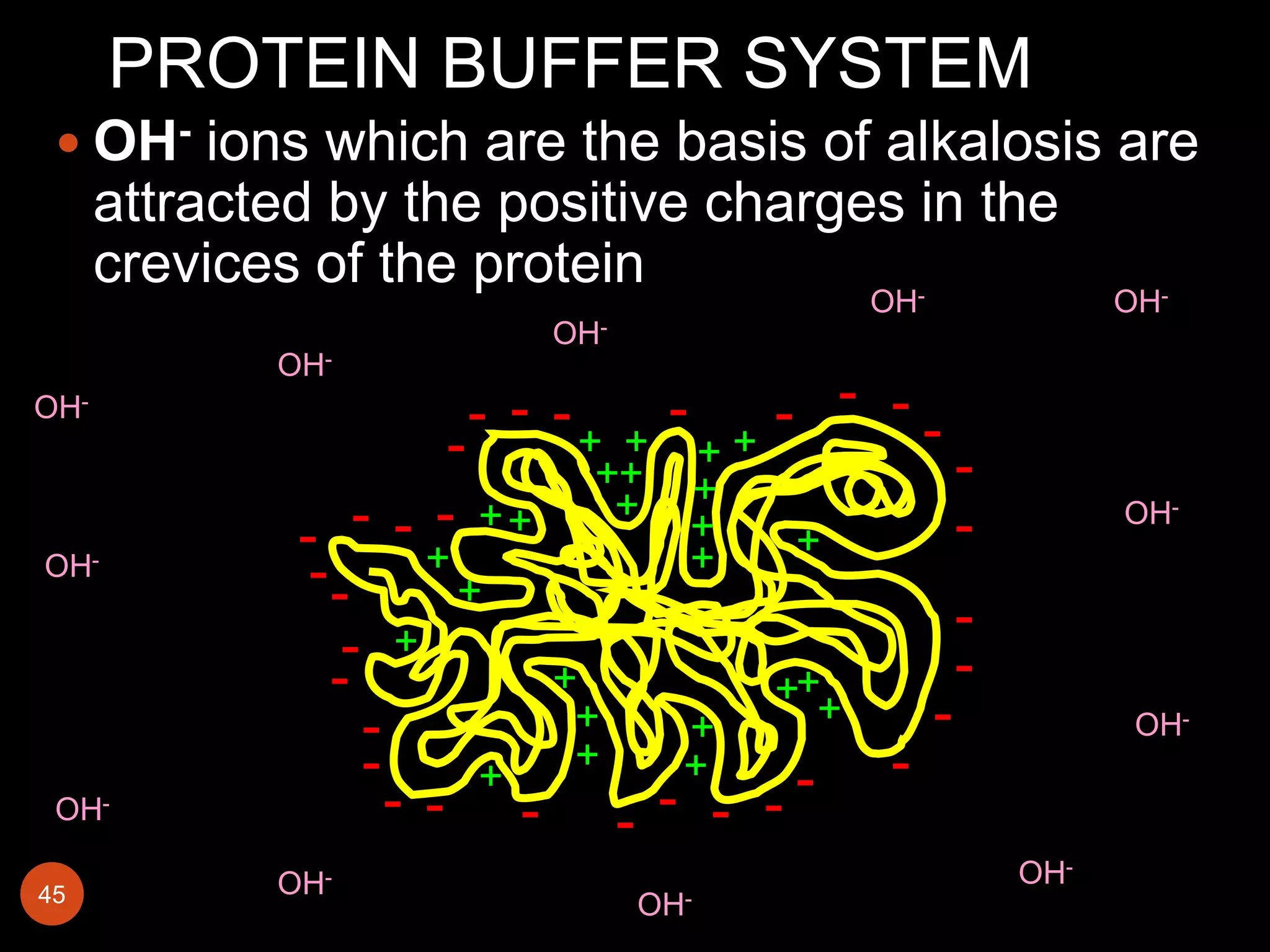
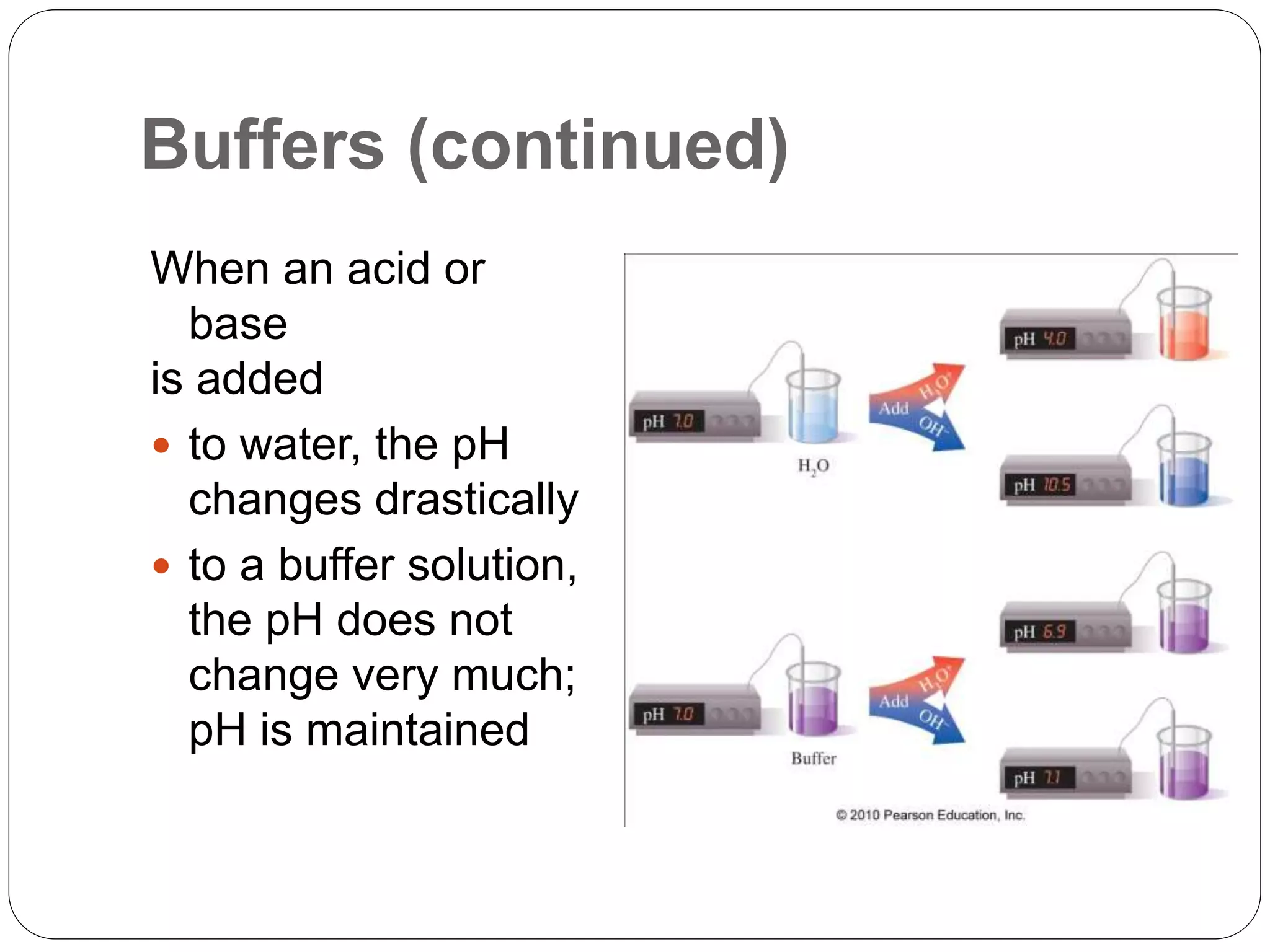
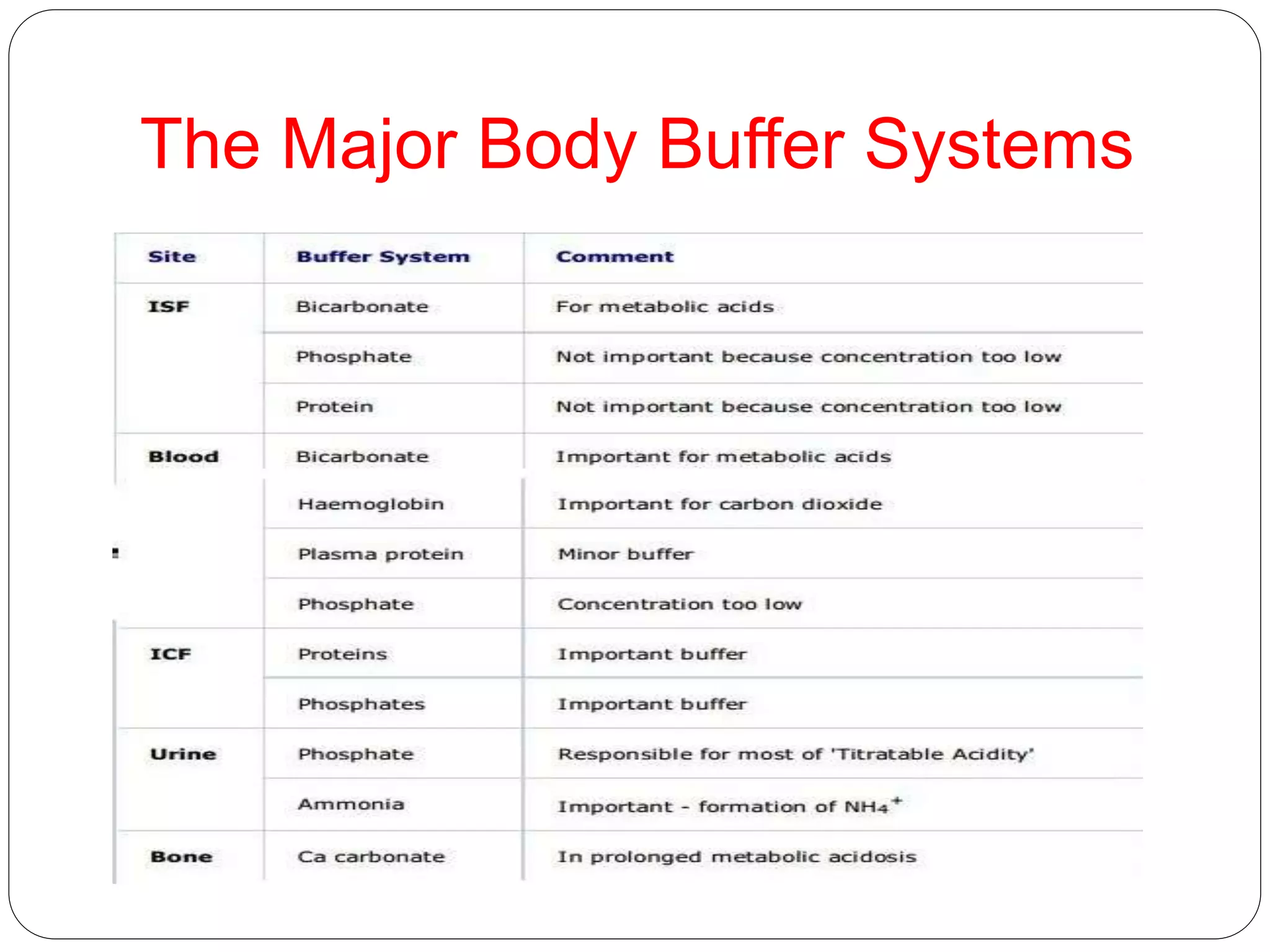
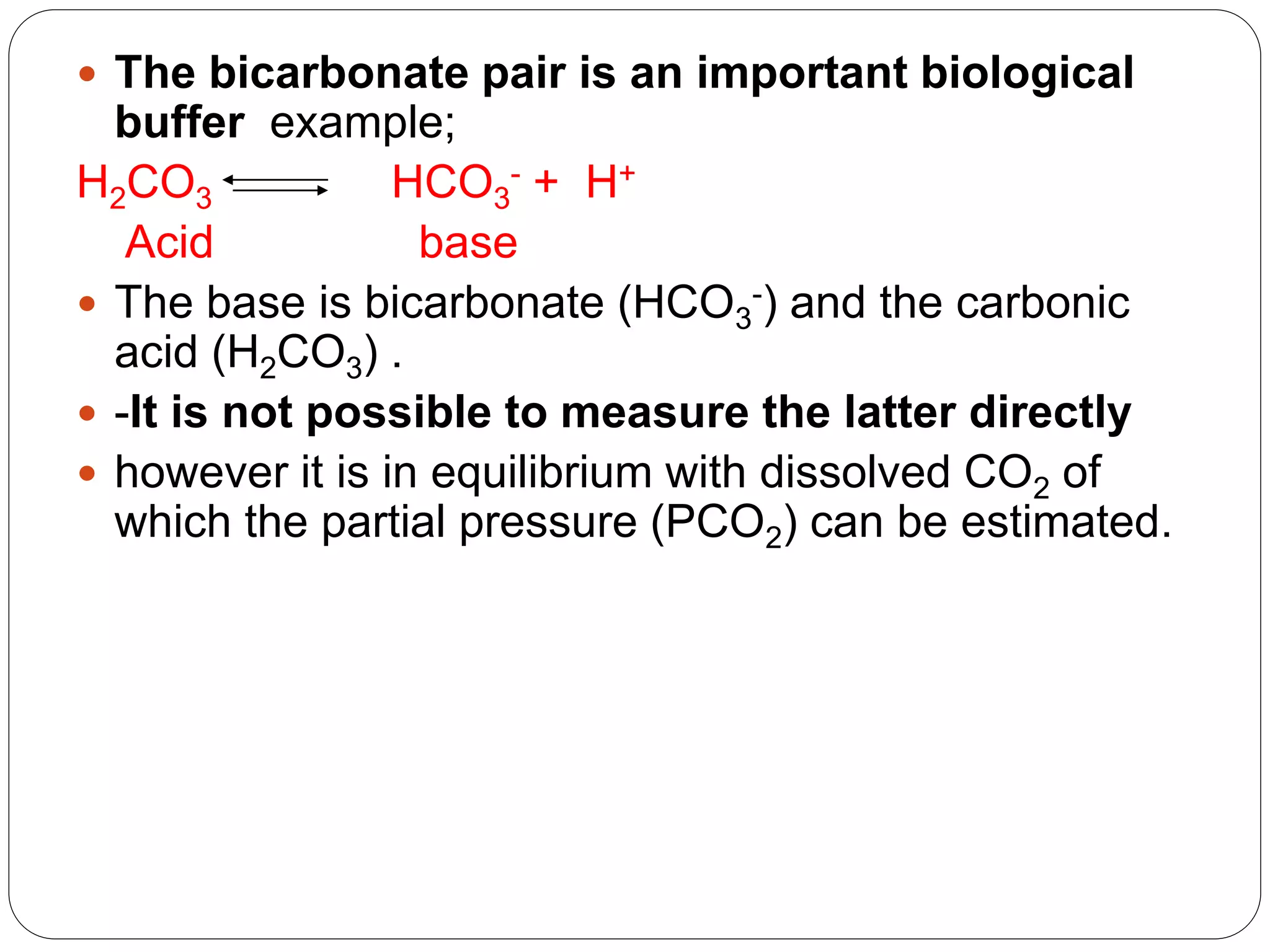
Buffers in the body resist changes in pH and maintain it within a narrow range. The major buffer systems are bicarbonate, phosphate, and proteins. Bicarbonate buffers work by absorbing excess hydrogen ions in the blood and tissues. The kidneys and lungs work together to control bicarbonate and carbon dioxide levels to regulate pH. When an acid is added, buffers prevent a large change in pH by neutralizing the hydrogen ions.




![Body Buffer system
• Hydrogen Ion Homeostasis
About 50 to100 m mol of hydrogen ions are
released from cells into extracellular fluid each
day
• Hydrogen ion concentration [H+] is
maintained between about 35 and 45 nano
molL. (40nmol/L=pH 7.4)
• Control of hydrogen ion balance depends
on the secretion of H+ from the body, mainly
into the urine therefore Renal impairment
causes acidosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-8-2048.jpg)



![PH is a measure of hydrogen ion
activity
Log 100 =log 102=2
Log 107=7
If [H+] is 10-7 (0.000 0001)
Then log [H+] =-7
The Henderson –hasselbalch equation
PH=PK+log [base] /[acid]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-12-2048.jpg)
![The conc. of H2CO3 is derived by multiplying this
measured value by the solubility co efficient (s) for
CO2 therefore
PH =PK-log [HCO3
-]/PCO2 XS (0.03 )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-14-2048.jpg)




![ the rate of respiration, and then therefore the rate of
CO2 elemination is controlled by chemoreceptor in
the respiratory centre in the medulla of the brain.
The receptors respond to changes in the [CO2]or[H+]
of plasma or of the cerebrospinal fluid .
1. the PCO2 rises much above 40 mm of Hg
2. the PH falls, the rate of respiration increases .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-19-2048.jpg)
![ Normal lungs have a very large reserve capacity for CO2
elimination
The normal respiratory centre and lungs can control CO2
conc. Within norrow limits by responding to changes in
the [H+] and therefore compensate for changes in acid-
base disturbances .
diseases of the lungs, or abnormalities of respiratory
control, primarily affect the PCO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-20-2048.jpg)




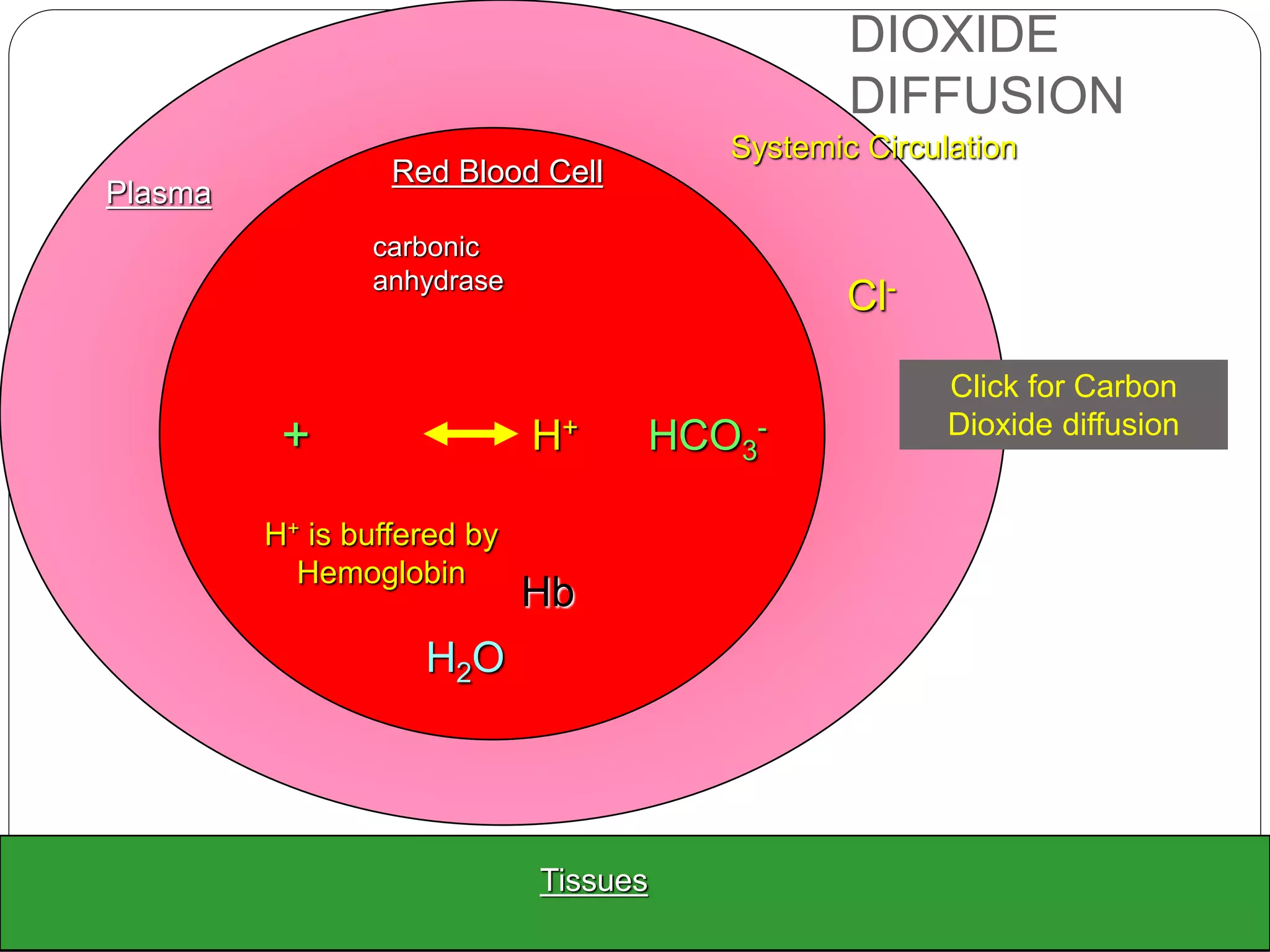
![ HCO3
- generation is therefore accelerated if the
conc.of
1. CO2 rises
2. HCO3
- falls.
3. H+ falls because it is either buffered by
erythrocytes or excreted from the body by
renal tubular cells.
Therefore an increase of intracellular P CO2 or
decrease in intracellular [HCO3
-] in the
erythrocytes and renal tubular cells maintain the
extracellular bicarbonate conc. by accelerating
the production of HCO3
-.
This minimizes changes in the ratio of [HCO3
-] to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-25-2048.jpg)
![In normal subject, at a plasma ;
1. PCO2 of 40mm of hg (a CO2 of about 1.2
mmolL)
2. Erythrocytes and renal tubular cells keep the
extracellular bicarbonate at about 25 mmolL
3. The extracellular ratio of [HCO3
-] to [CO2] (both
in mmolL) is just over 20:1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-26-2048.jpg)
![The kidneys
Two renal mechanism control [HCO3
-]in the
extracellular fluid:
Bicarbonate reclamation (reabsorption)
The CO2 driving in renal tubular cells is derived
from filtered bicarbonate, after action of the
carbonate dehydratase.
There is no correct to an acidosis but can
maintain a steady state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-29-2048.jpg)



![Bicarbonate generation
A very important mechanism for correcting acidosis,
in which the levels of CO2 or [HCO3
-] affecting the
carbonate dehydratase reaction in tubular cells
reflect those in the extracellular fluid, there is a net
loss of H+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-150602065351-lva1-app6892/75/Buffers-in-the-body-33-2048.jpg)