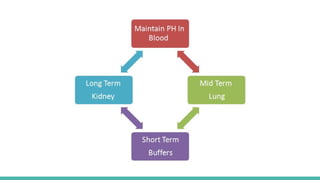
The document discusses acidity, basicity, pH, and buffer systems in the human body. It defines acids as having a high hydrogen ion concentration and bases as having a low hydrogen ion concentration. The blood needs to maintain its pH between 7.35-7.45. The lungs and kidneys help regulate pH through exchanging carbon dioxide and excreting acids and bases. The bicarbonate buffer system uses dissolved carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, and bicarbonate ions to neutralize changes in blood pH. Too much acid in the body leads to acidosis and symptoms like fatigue, while too much base causes alkalosis and issues like arrhythmias.





![What is pH?
The concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution is usually denoted by the
term pH, which is the negative log10
of the hydrogen ion concentration
expressed in moles per liter (mol/L)
pH = -log[H+
]
The pH value is an expression of the ratio of [H+ ] to [OH‐] (hydroxide ion
concentration). Hence, if the [H+ ] is greater than [OH‐ ], the solution is acidic.
Conversely, if the [OH‐ ] is greater than the [H+ ], the solution is basic.
Since pH is a logarithmic value, it doesn’t have any unit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thebiochemistryblock3case2-170513140215/85/BUFFER-SYSTEM-6-320.jpg)

![Calculate pH
To calculate the pH of an aqueous solution you need to know the
concentration of the hydronium ion in moles per liter (molarity). The pH
is then calculated using the expression:
pH = - log [HзO ].
similarly, pOH is the negative of the logarithm of the OH-
ion
concentration.
pOH = - log [OH-
]
pH + pOH = 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thebiochemistryblock3case2-170513140215/85/BUFFER-SYSTEM-8-320.jpg)
![Examples:
Example1: Calculate the pH of 0.06 mol/L HCl.
pH = − log0.06 = 1.22
Example 2: Calculate the pH of 0.02 mol/L H2SO4 .
pH = − log0.04 = 1.3979 = ~ 1.4
What is the pOH of a solution that has a hydroxide ion concentration of
4.82 x 10-5
M?
pOH = - log [4.82 x 10-5
] = - ( - 4.32) = 4.32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thebiochemistryblock3case2-170513140215/85/BUFFER-SYSTEM-9-320.jpg)
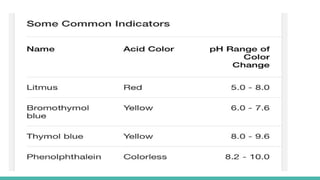
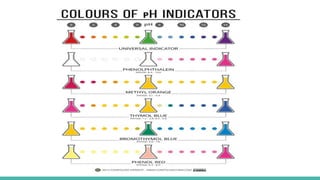
![PH SCALE
The ion product of water,is the basis for
the pH scale .It is a convenient means of
designating the actual concentration of
H+ (and thus of OH− ) in any aqueous
solution in the range between 1.0 M H+
and 1.0 M OH−
Because pH is equal to –log [H+], the
greater the [H+], the lower the pH. A
solution with a pH of 7 is neutral, a
solution with a pH <7 is acidic, and a
solution with a pH >7 is basic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thebiochemistryblock3case2-170513140215/85/BUFFER-SYSTEM-12-320.jpg)