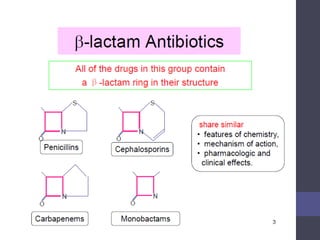
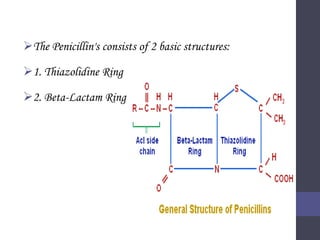
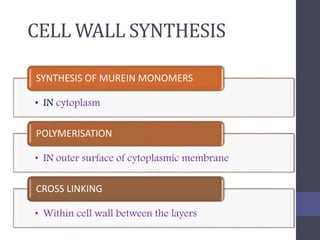
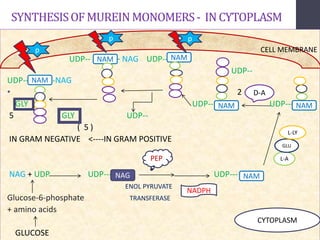
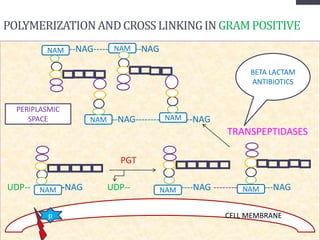
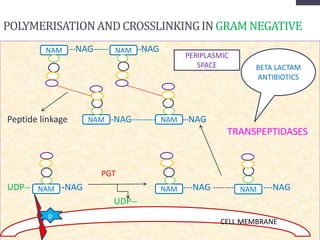
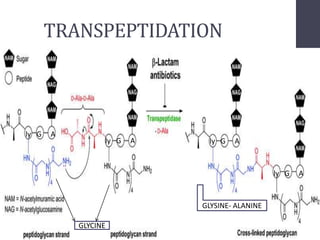
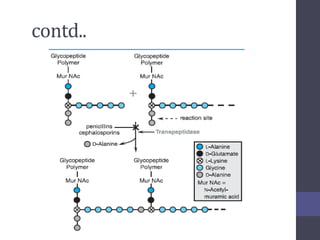
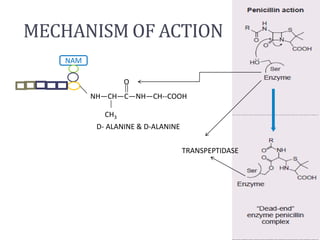
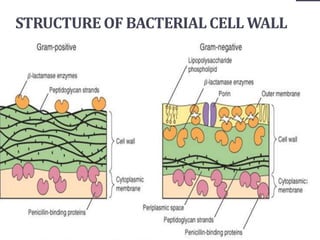
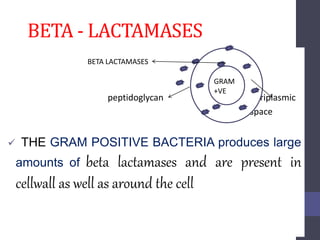
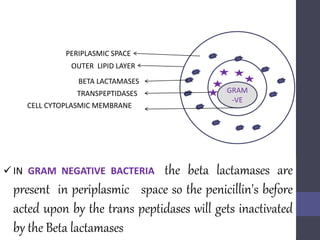
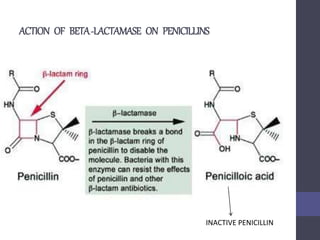
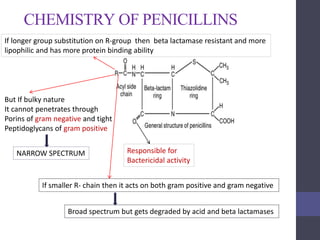
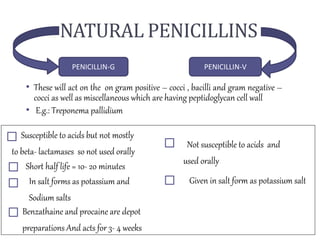
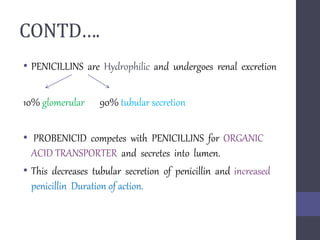
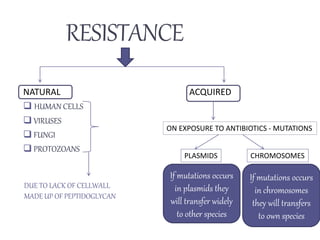
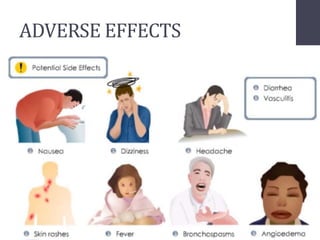
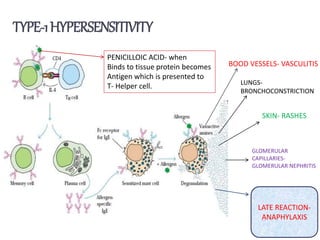
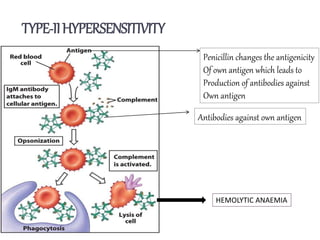
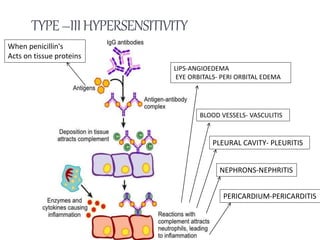
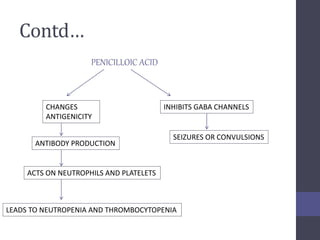
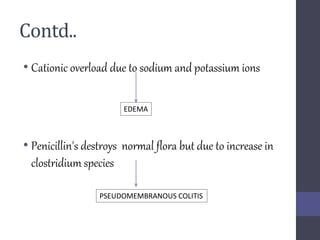
Penicillins are beta-lactam antibiotics that were discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming. They work by inhibiting the final step of peptidoglycan synthesis in bacterial cell walls. There are several classes of penicillins including natural penicillins, anti-staphylococcal penicillins, and extended spectrum penicillins. They are generally well-absorbed, have varying spectra of activity, and can cause allergic reactions ranging from mild rashes to anaphylaxis. Common adverse effects include hypersensitivity reactions, neutropenia, seizures, and pseudomembranous colitis.