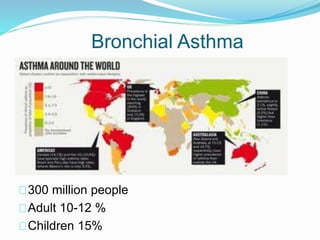
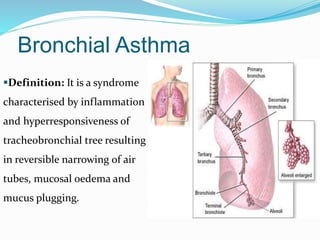
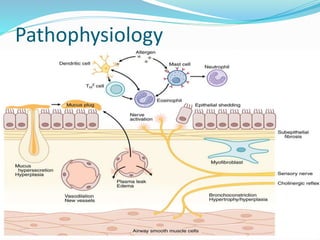
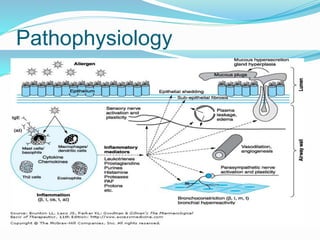
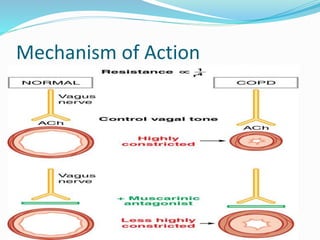
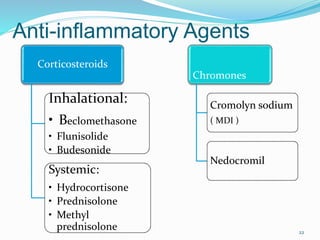
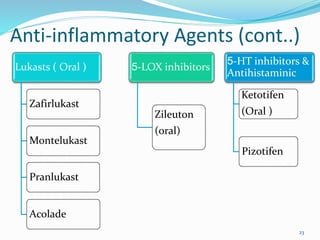
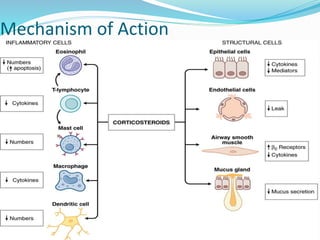
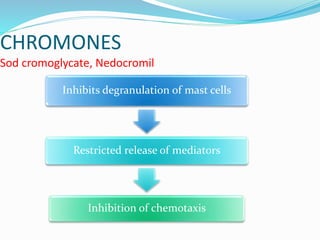
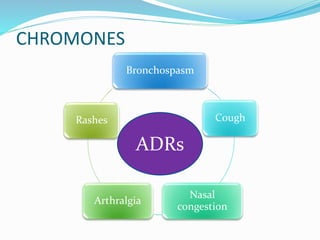
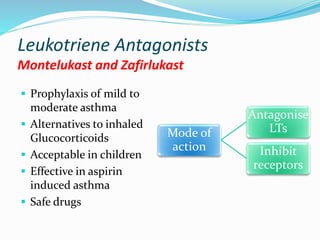
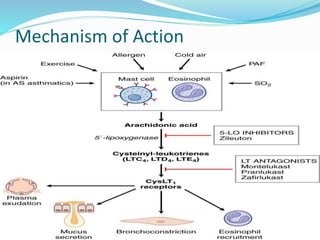
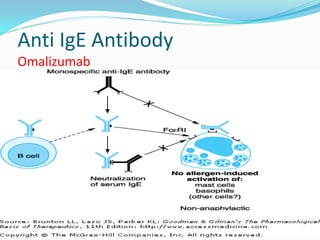
This document discusses bronchial asthma, including its definition, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, and various treatment approaches. It notes that asthma affects 300 million people worldwide and is characterized by inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness. Treatment involves preventing antigen reactions, suppressing inflammation, blocking mediators, and using bronchodilators such as beta-2 agonists, methylxanthines, corticosteroids, and leukotriene antagonists to relax airway smooth muscle. Status asthmaticus, a severe life-threatening form of asthma, requires aggressive treatment including nebulized bronchodilators, steroids, oxygen, and potentially intubation.

















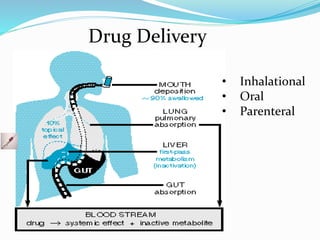
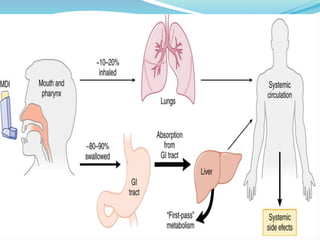
![Inhalational Drug Delivery Systems
MDI Dischalers Spacer
Rotahalers Nebulizer
37
Green
[Salmeterol]
Orange
[Fluticasone]
Blue
[SABA]
Brown
[budesonide]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchialasthma-140830103728-phpapp01/85/Bronchial-asthma-pharmacology-37-320.jpg)

