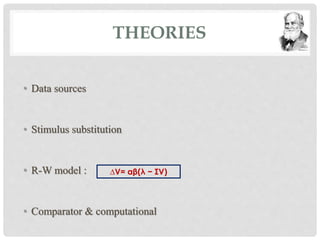
This document summarizes Ivan Pavlov's classical conditioning experiment. It explains that classical conditioning is a type of learning where a stimulus acquires the ability to elicit a reflexive response through repeated association with another stimulus. Pavlov demonstrated this by pairing food with a stimulus to condition dogs to salivate upon hearing the stimulus alone. The document then discusses various concepts of classical conditioning like unconditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus and conditioned response. It also covers applications of classical conditioning principles in behavior therapy and influencing emotional responses.