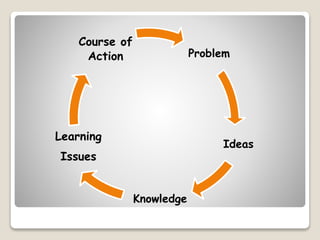
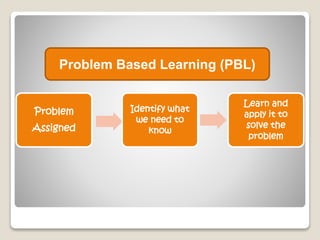
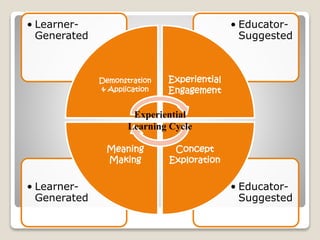
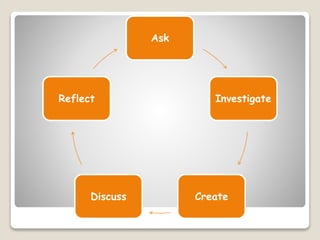
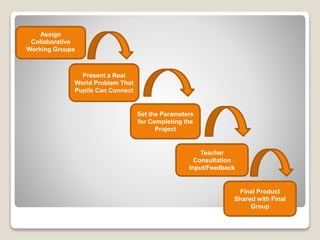
The document discusses several pedagogical approaches to enhance learning including problem-based learning, collaborative learning, authentic learning, inquiry learning, project-based learning, problem-solving approaches, and differentiated instruction. Problem-based learning uses ill-structured problems to develop problem solving skills and knowledge. Collaborative learning involves students working in groups toward a common goal to promote critical thinking. Authentic learning focuses on real-world problems and roles to bring in multiple perspectives.










![Know the Learner
Questioning
Strategies
Adjustable
Assignments
]
Assess the Learner
Curriculum
Approaches](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enhancepedadogies-sirec-150301040258-conversion-gate01/85/Enhance-Pedadogies-16-320.jpg)
