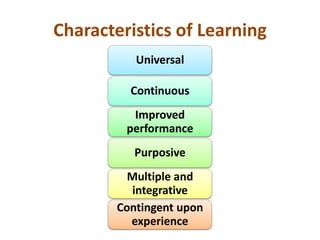
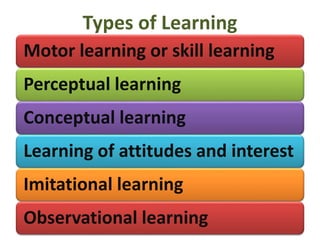
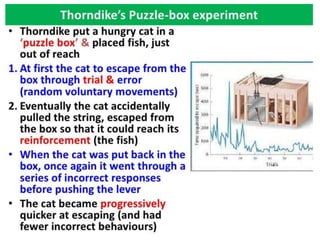
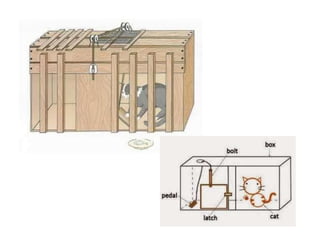
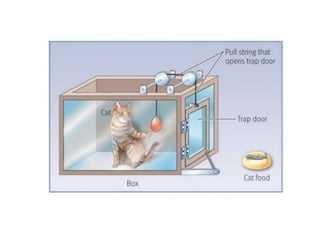
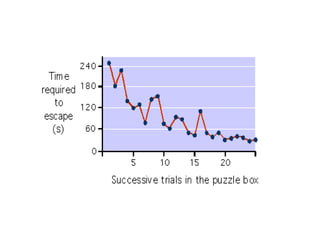
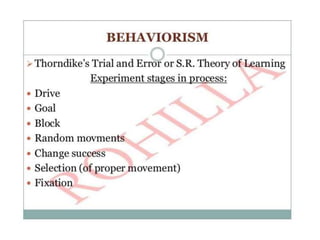
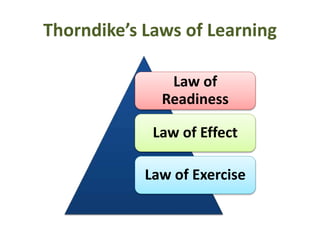
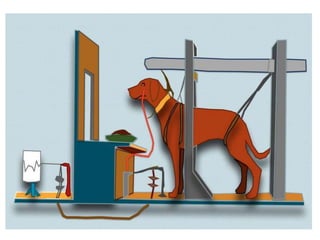
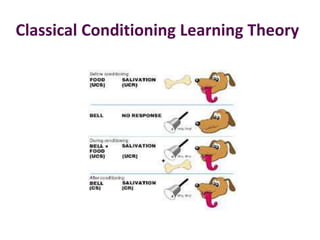
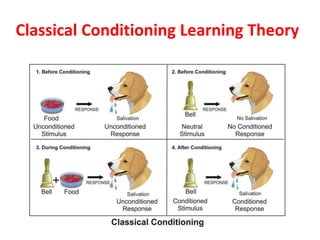
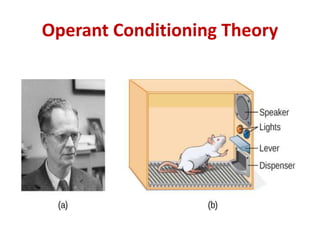
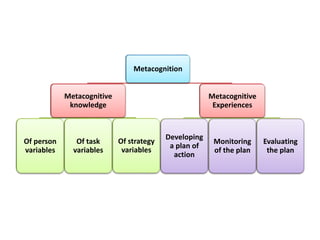
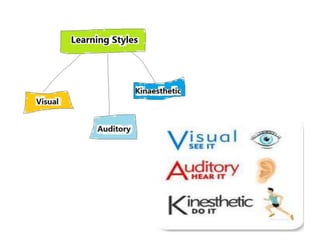
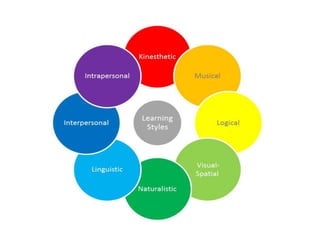
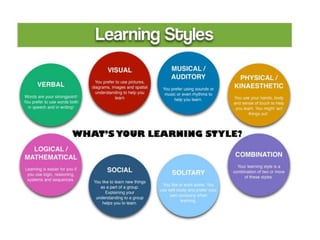
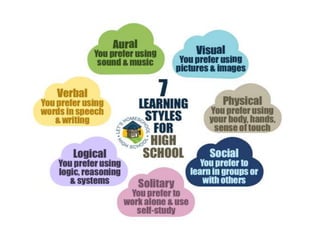
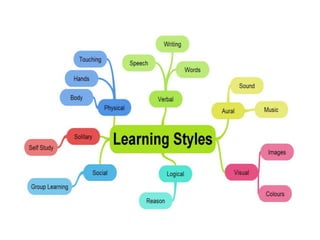
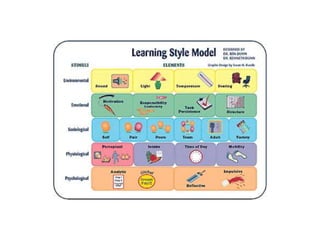
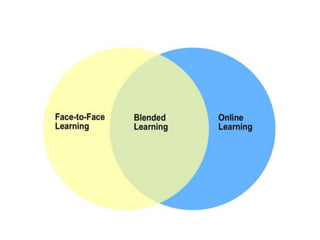
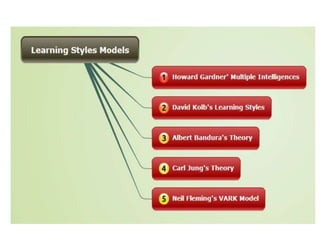
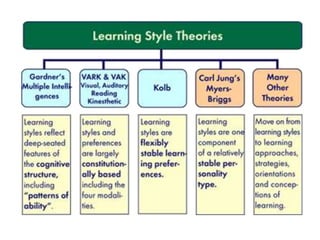
This document discusses various theories of learning including Thorndike's connectionism, Pavlov's classical conditioning, Skinner's operant conditioning, and Hull's reinforcement theory. It also covers concepts like transfer of training, learning styles, and metacognition. The key points are:
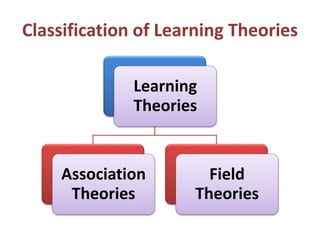
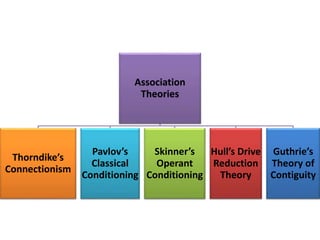
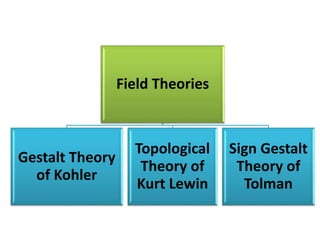
1) Several theories of learning are presented including association theories like Thorndike's connectionism and Pavlov's classical conditioning, as well as field theories like Gestalt psychology.
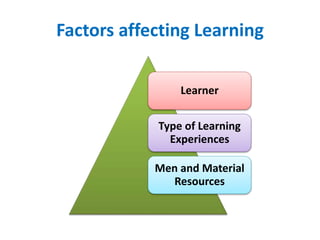
2) Factors that influence learning include characteristics of the learner, the learning experiences, resources available, and motivation.
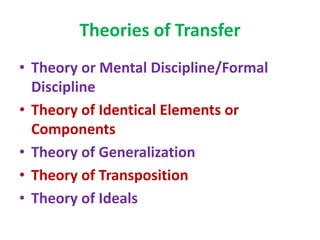
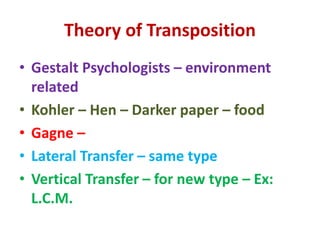
3) Transfer of training refers to applying what is learned in one context to another context. Several theories attempt to explain how and why