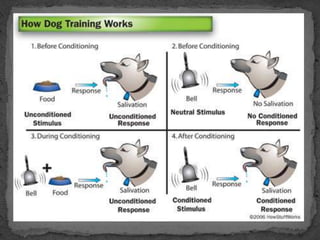
The document discusses behavioral learning theories, highlighting key figures such as Ivan Pavlov, B.F. Skinner, and Albert Bandura. It explains classical conditioning as a learning process through associations between stimuli, illustrated by the famous Little Albert experiment, which conditioned a fear response to a white rat. The document emphasizes that behaviors can be influenced by antecedents and consequences, shaping learning and responses in various environments.