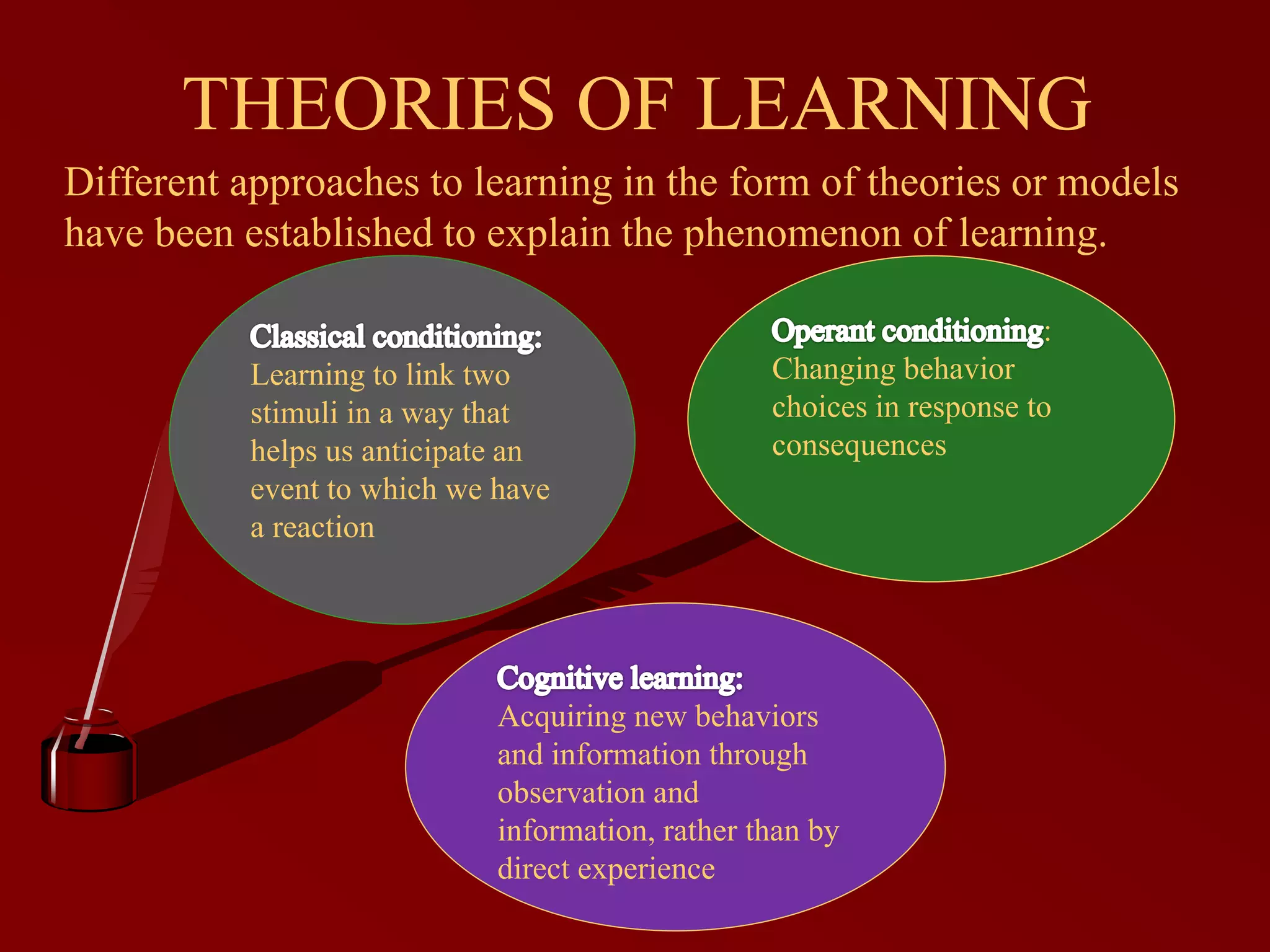
Ivan Pavlov was a Russian physiologist known for his discovery of classical conditioning, which involves linking stimuli to evoke responses, demonstrated in his experiments with dogs. Learning is a process of acquiring behaviors and modifying responses through experiences, while classical conditioning has implications in psychology, though it is deemed ineffective for classroom instruction. In conclusion, while Pavlov saw conditioned reflexes as unstable, classical conditioning can still be beneficial in maintaining positive classroom authority if applied correctly.