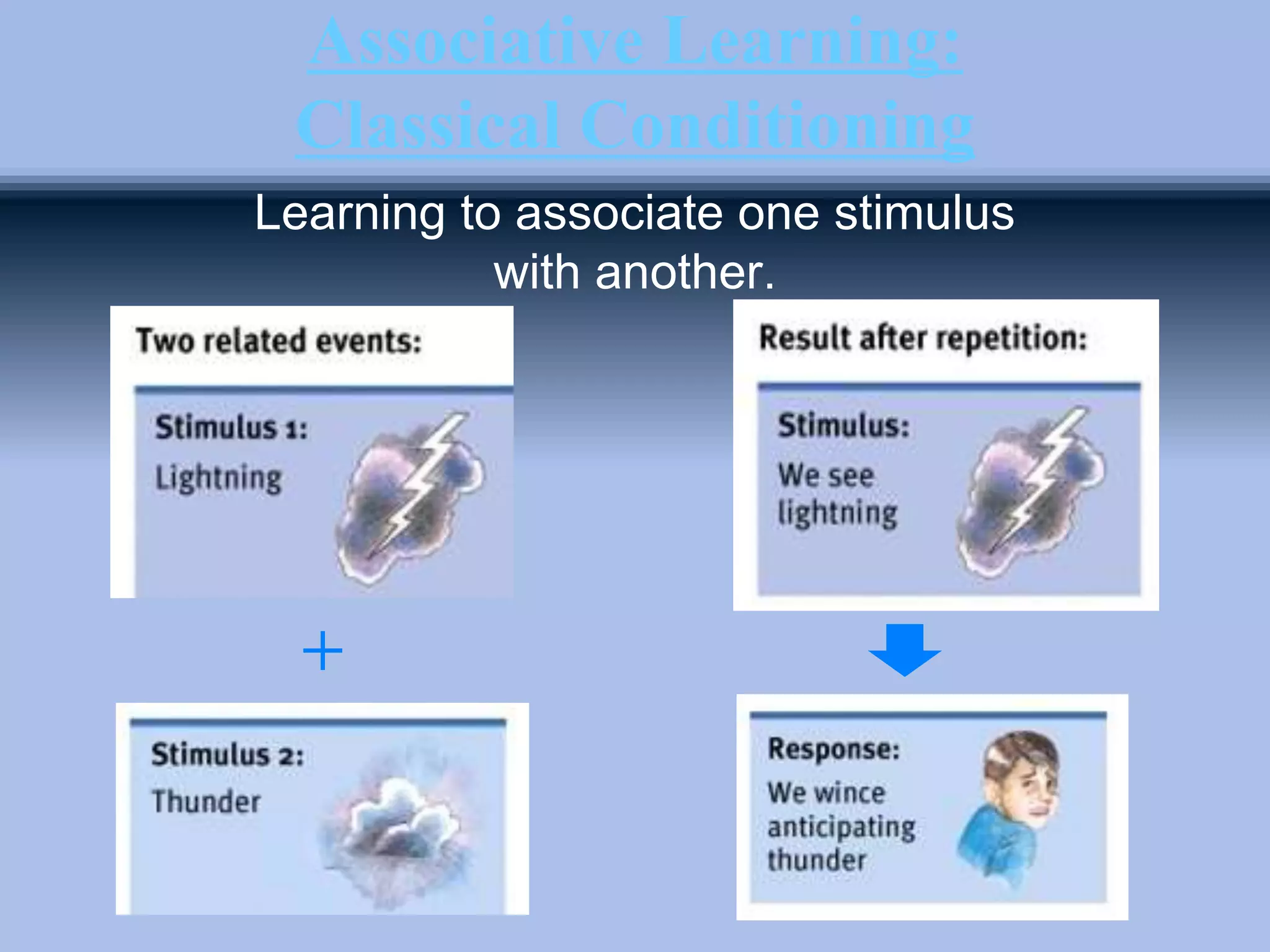
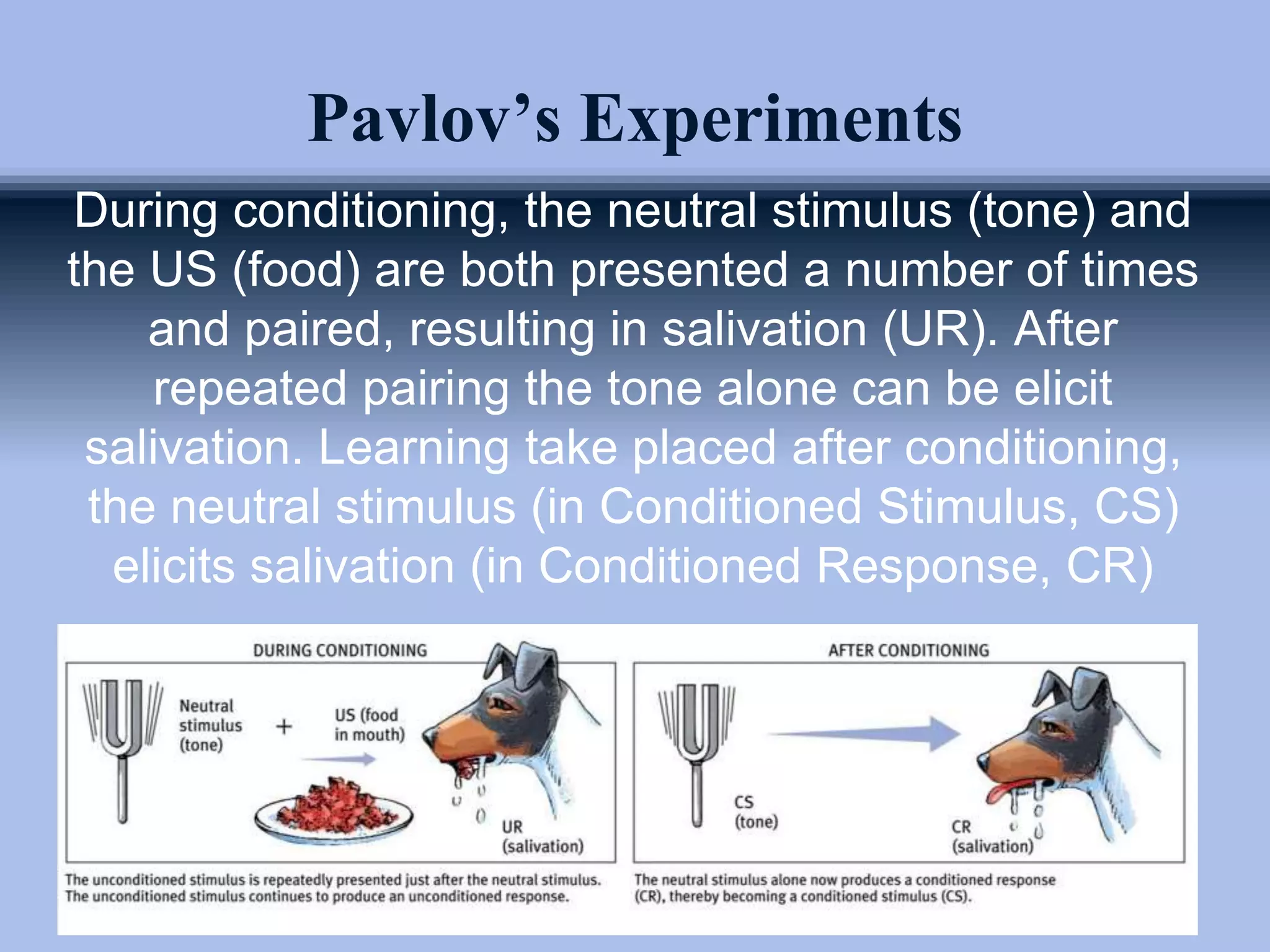
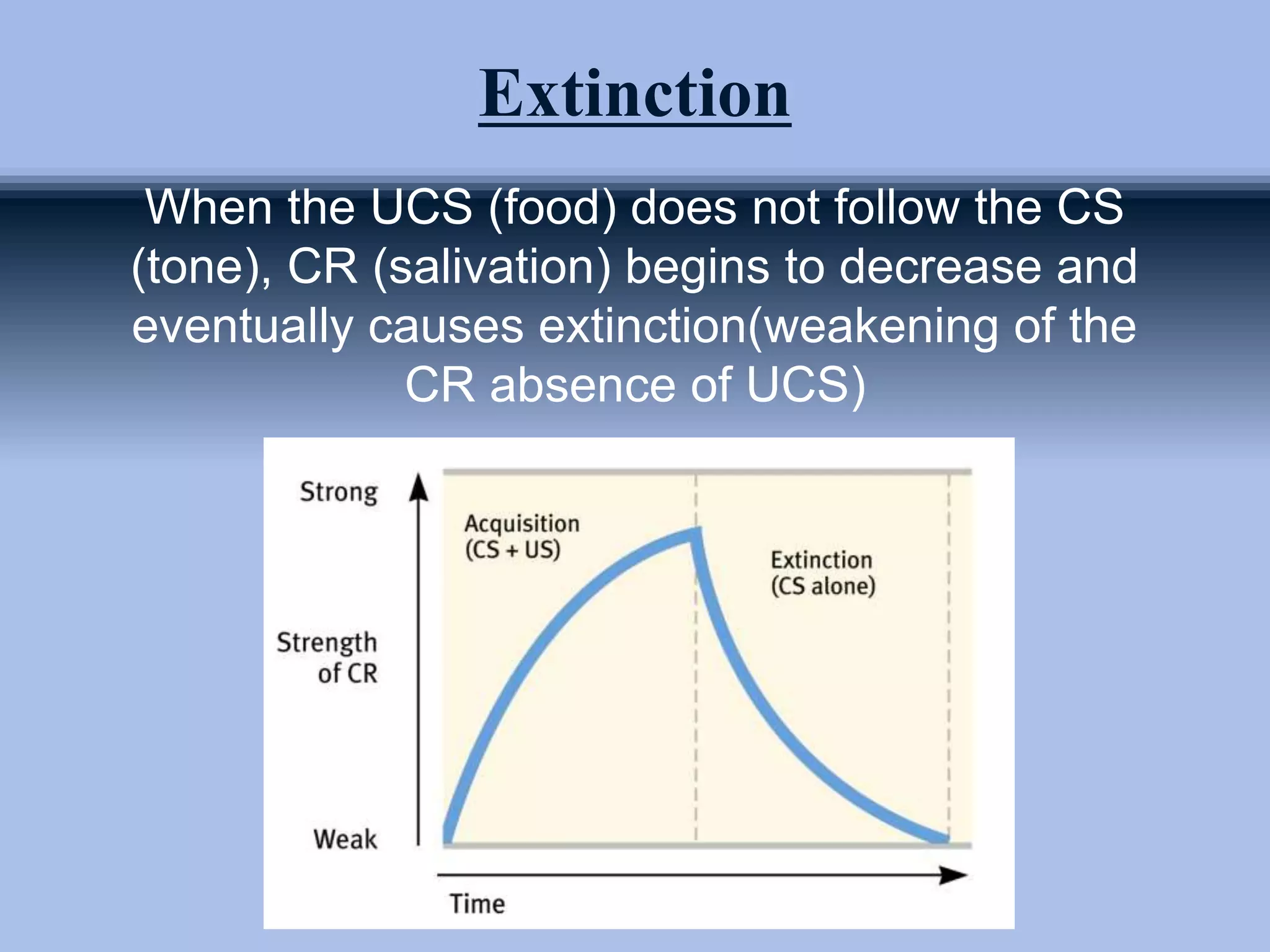
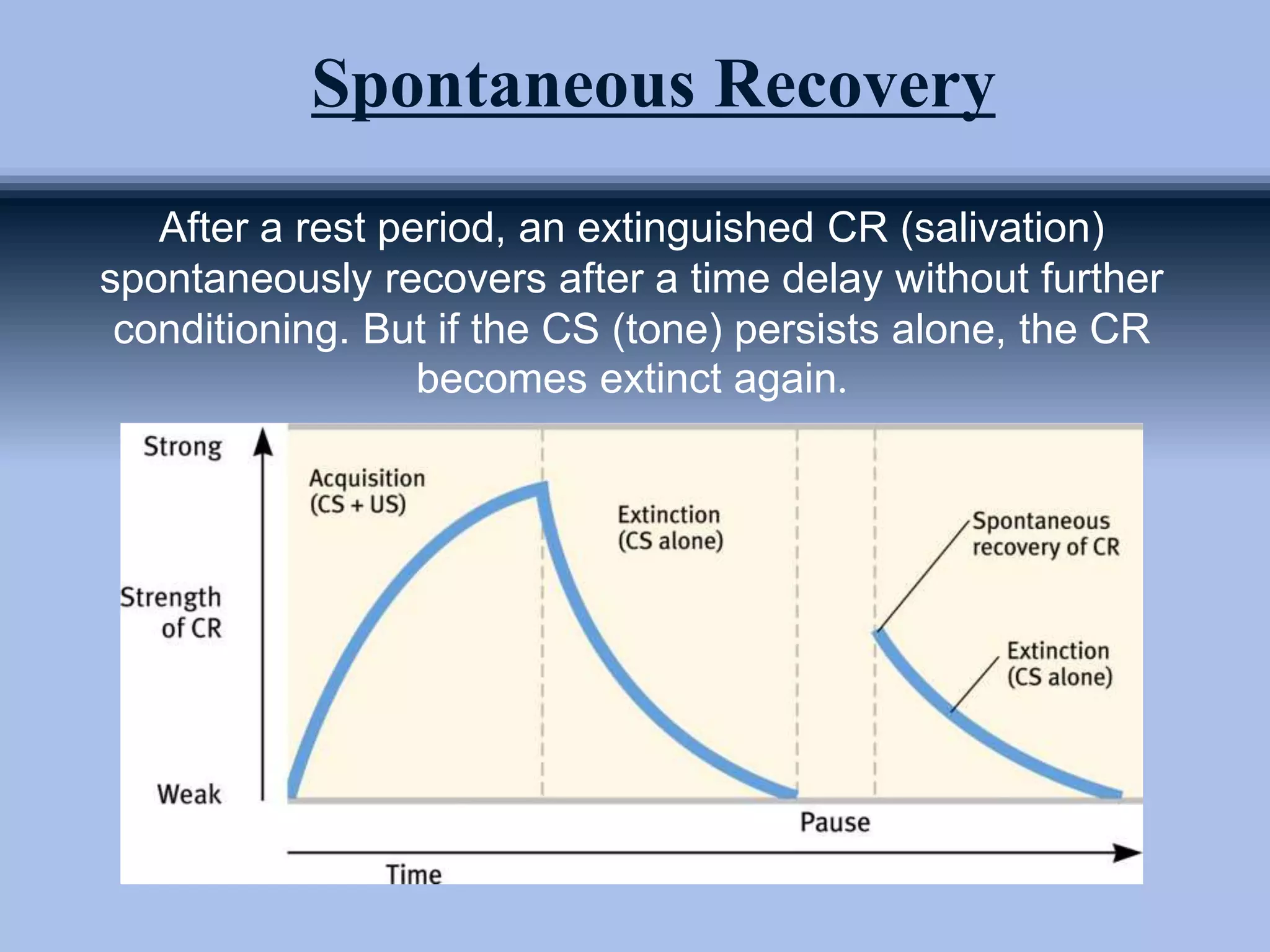
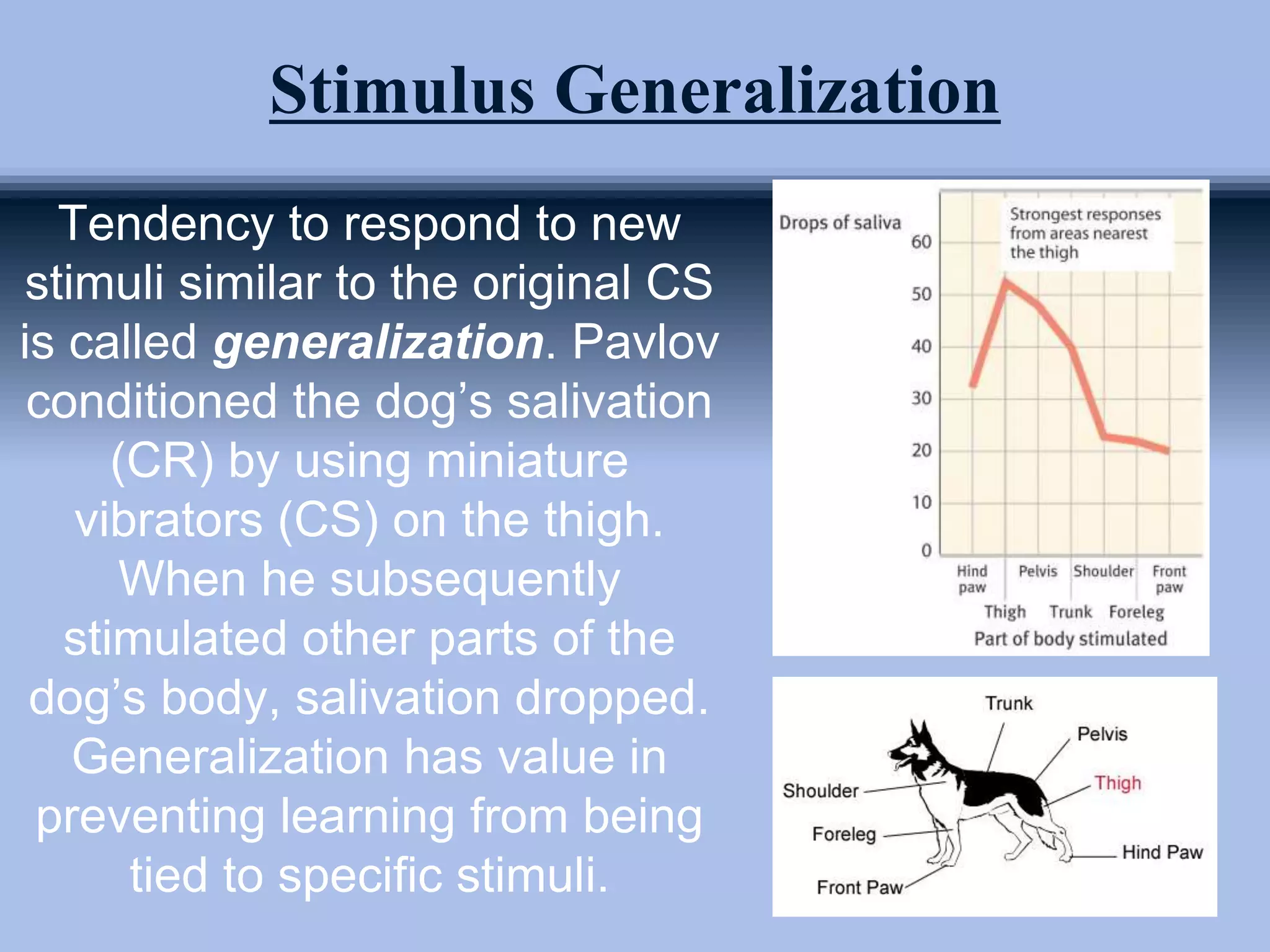
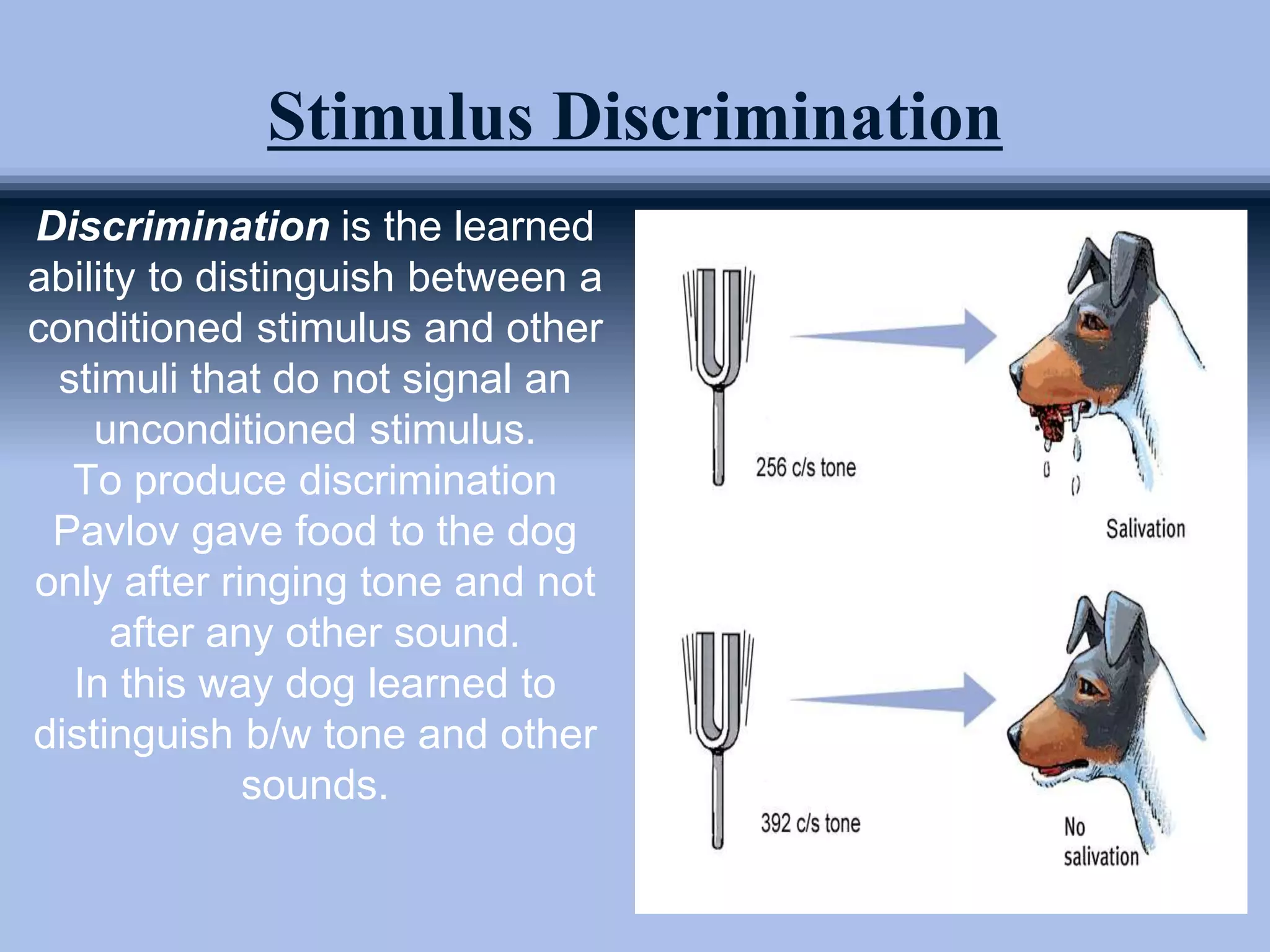
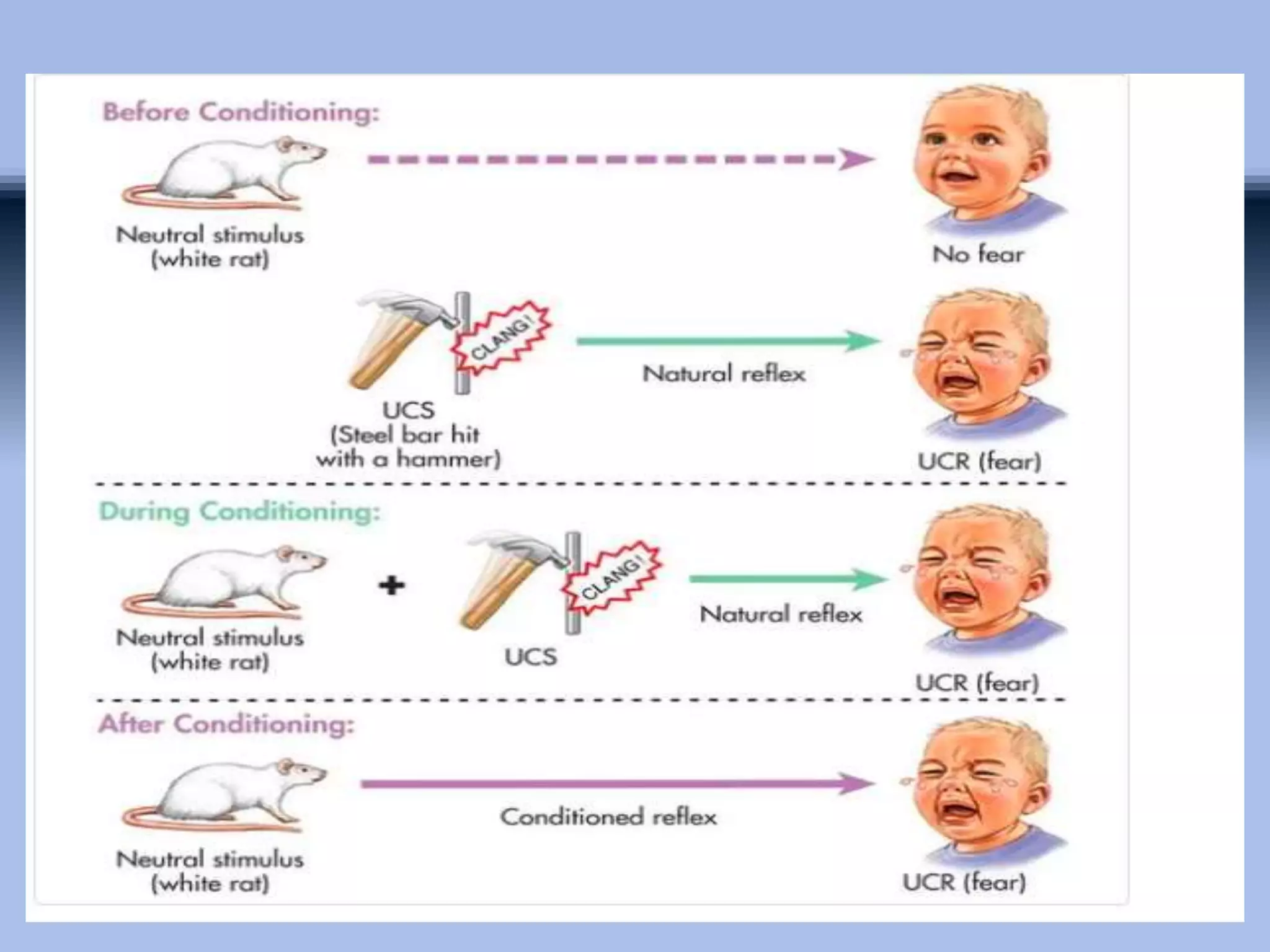
The document outlines principles of classical conditioning within the context of educational psychology, highlighting concepts, key figures like Ivan Pavlov and John B. Watson, and their experiments. It explores how behaviors can be learned through conditioning, emphasizing the importance of environmental factors over innate traits. Applications of these principles in education and therapy for issues like anxiety, phobias, and addiction are also discussed.