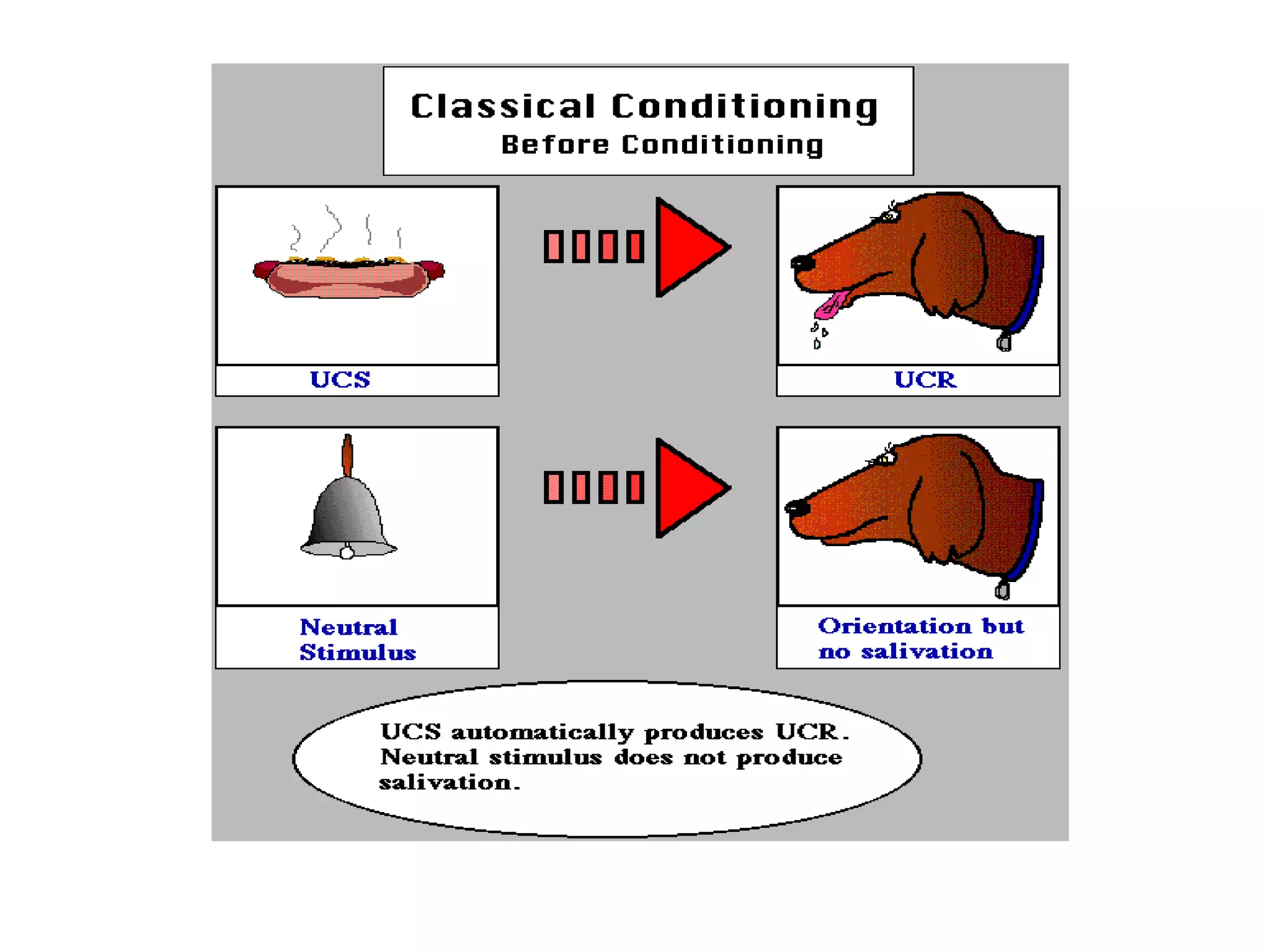
Classical conditioning is a learning process where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with an unconditioned stimulus to produce a conditioned response. Ivan Pavlov studied classical conditioning in dogs, finding that he could elicit salivation by pairing a neutral stimulus like a bell with the unconditioned stimulus of food. His work established the concepts of the unconditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response that form the basis of classical conditioning theory. Classical conditioning explains how emotions and behaviors can become associated with previously neutral stimuli through repeated pairings in the environment.