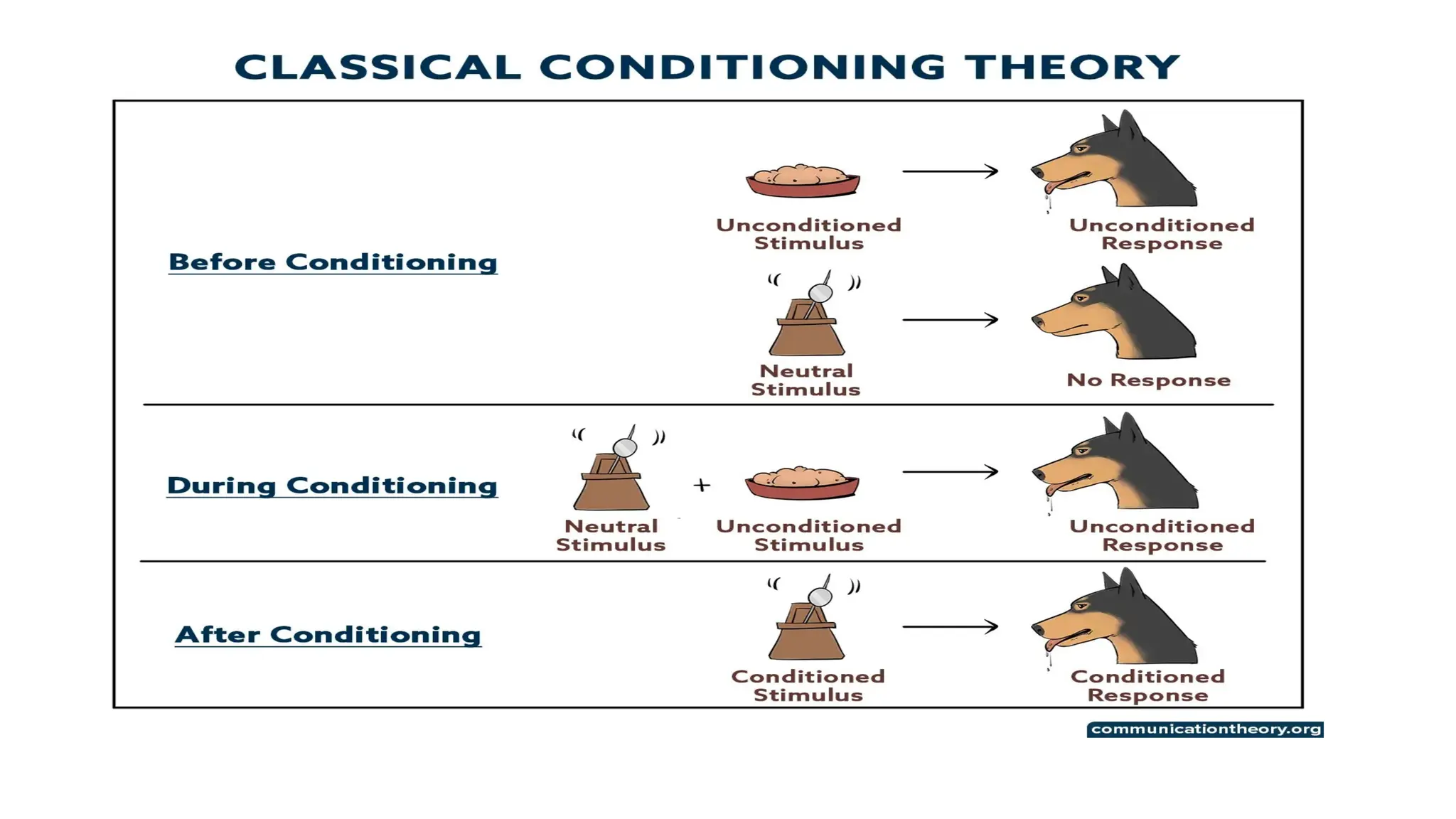
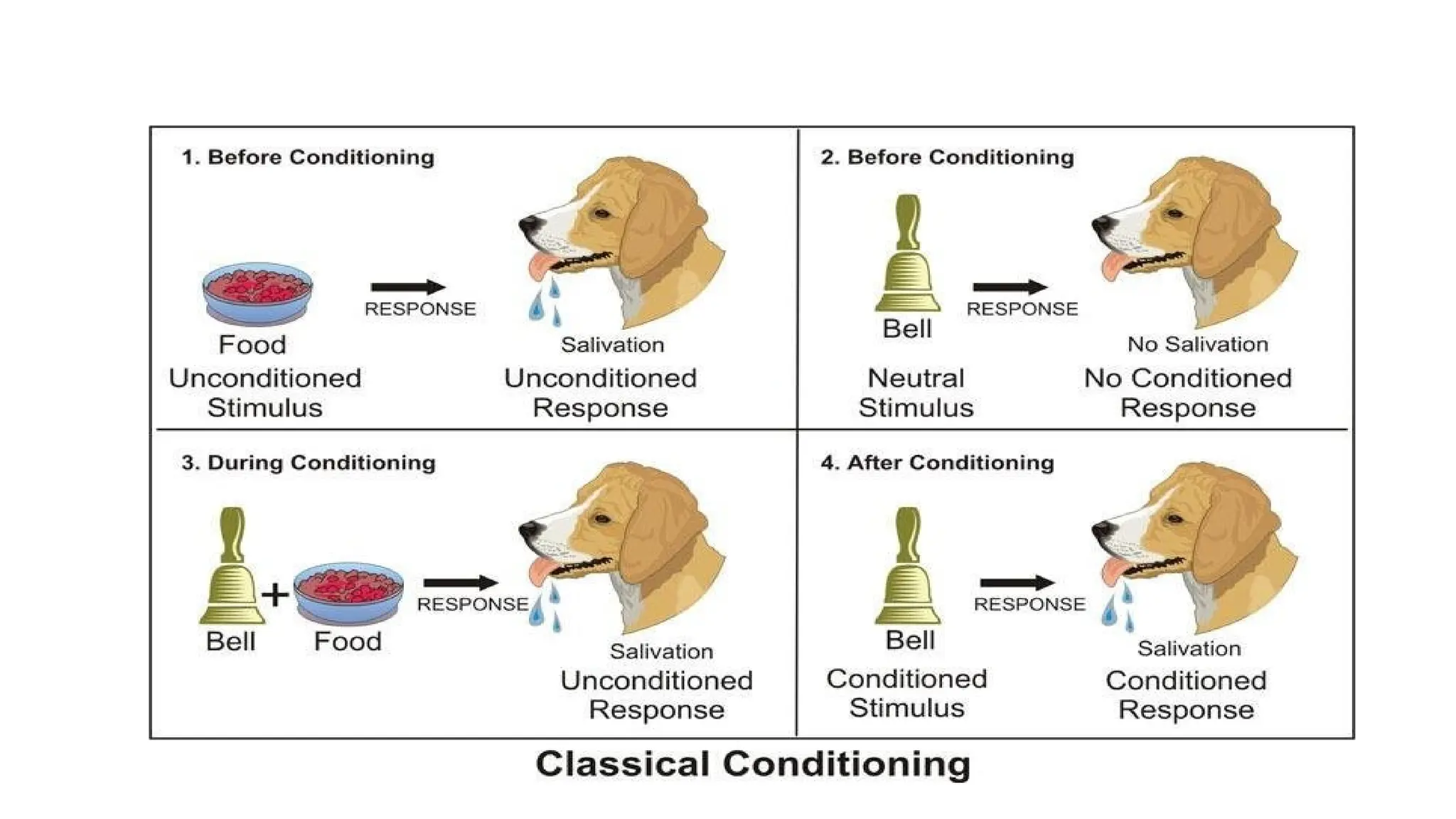
Classical conditioning is a learning process where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a natural stimulus, leading to a conditioned response. This method was first studied by Ivan Pavlov, who observed that dogs would salivate in response to a bell after being repeatedly paired with food. The key concepts include unconditioned stimulus (UCS), unconditioned response (UCR), conditioned stimulus (CS), and conditioned response (CR).