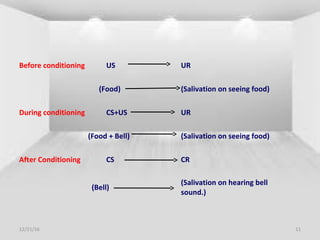
The document defines learning as a permanent change in behavior resulting from experience or practice, and details various paradigms of learning, including classical conditioning, which was famously demonstrated by Ivan Pavlov. It describes the concepts of unconditioned and conditioned stimuli and responses, along with factors influencing classical conditioning such as time relations and the type of stimuli. Applications of classical conditioning principles in treating phobias, addictions, and hypertension are also discussed.