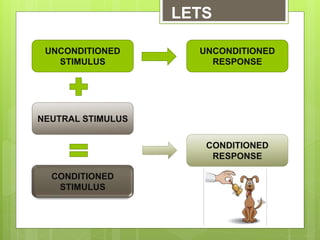
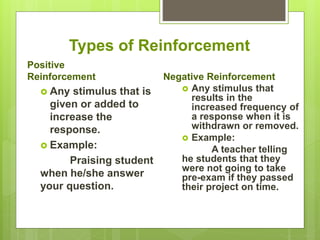
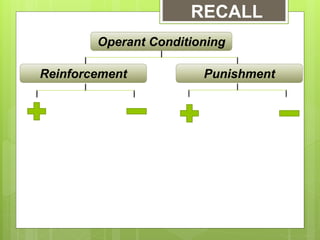
This document discusses classical and operant conditioning theories. It provides biographical information on Ivan Pavlov and B.F. Skinner, who discovered classical and operant conditioning, respectively. Classical conditioning involves associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response. Operant conditioning is learning through rewards and punishments that reinforce or reduce behaviors. The document explains the key components of each theory, including unconditioned/conditioned stimuli and responses, reinforcement, and punishment.