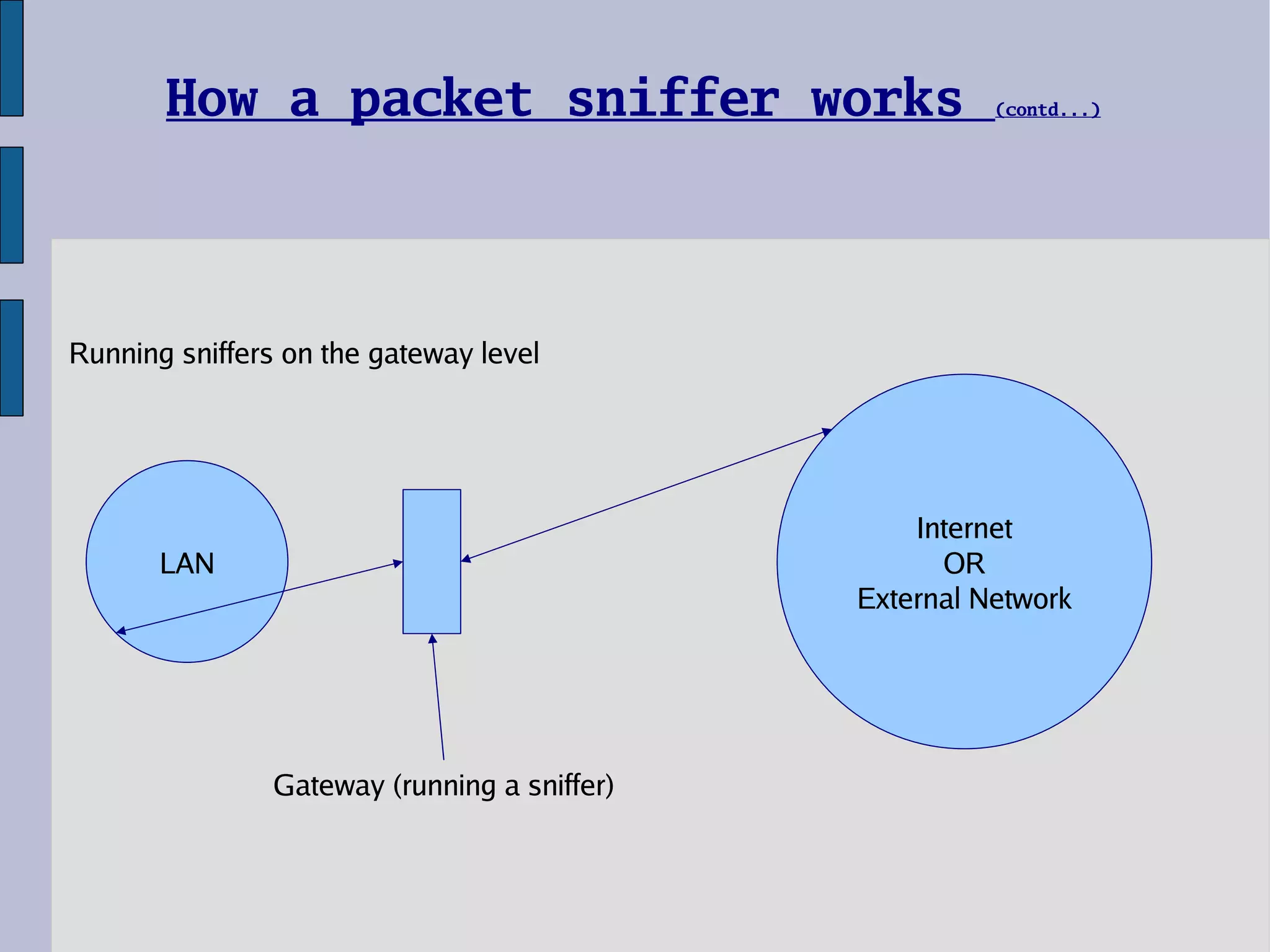
A packet sniffer is a program that intercepts and monitors network traffic by capturing packets in promiscuous mode. There are two main network environments where a sniffer can operate: a shared Ethernet and a switched Ethernet. In a shared Ethernet, all systems are connected to the same bus and broadcast domain, allowing a sniffer to easily capture all traffic. In a switched Ethernet, packets are specifically sent to intended machines, but a sniffer can still operate using techniques like ARP spoofing to intercept traffic. Common sniffer programs include Ethereal, Tcpdump, and Ettercap, while AntiSniff and ARP Watch can detect sniffing activities on a network.