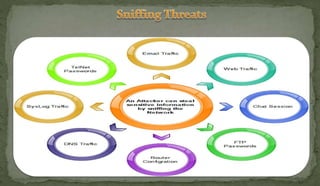
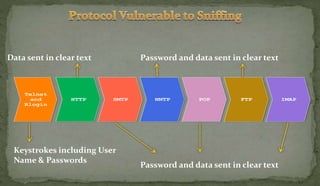
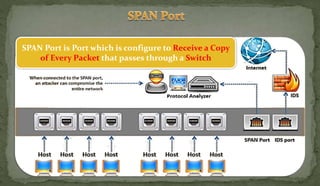
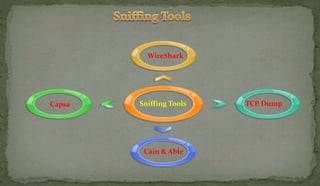
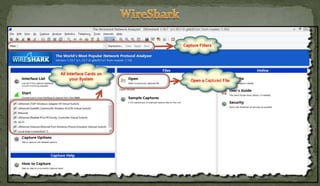
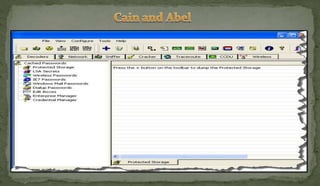
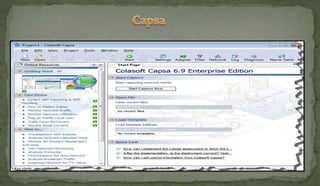
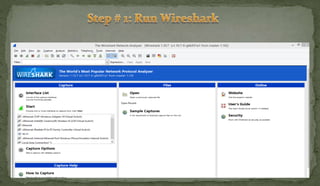
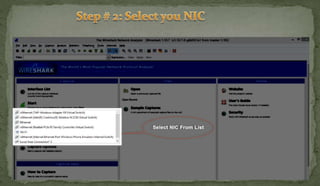
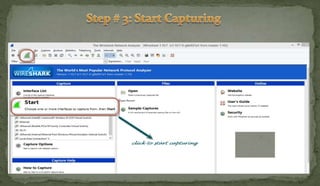
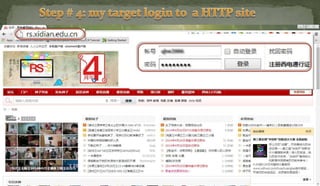
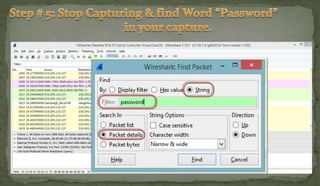
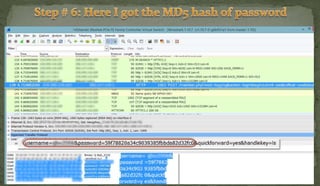
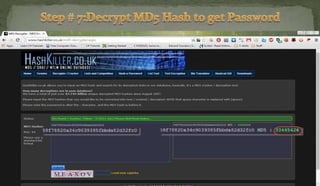
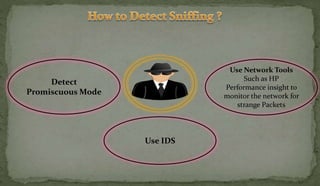
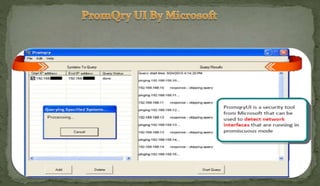
This document discusses packet sniffing and network monitoring. It defines a sniffer as a tool that can capture and display network data in transit. It explains that sniffers work by putting network adapters in promiscuous mode to listen to all traffic, not just traffic addressed to that system. The document outlines different types of sniffing attacks and protocols that are vulnerable when not encrypted. It also provides examples of sniffer tools and ways to detect and protect against sniffing on a network, such as using encryption, static configurations, and intrusion detection systems.