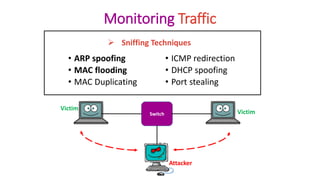
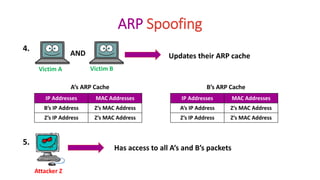
Packet sniffing involves monitoring network traffic by capturing and analyzing data packets as they flow through a network interface. It can be performed using packet sniffers, which are programs that can intercept and read all network traffic passing through a device's network interface card or wireless adapter. While packet sniffers can be used for troubleshooting network issues, they can also be used maliciously by hackers to intercept sensitive information like usernames and passwords by using techniques like ARP spoofing to fool devices into thinking the hacker's machine has the IP address of another machine on the network. Network administrators can use tools to detect the presence of packet sniffers operating in promiscuous mode and monitor ARP caches for signs of spoofing.