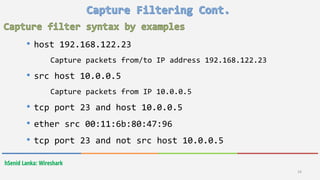
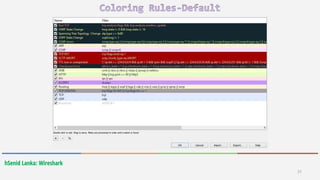
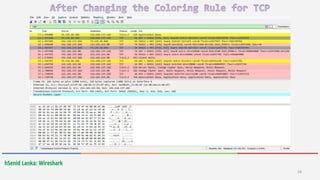
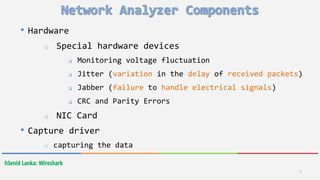
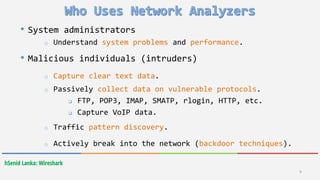
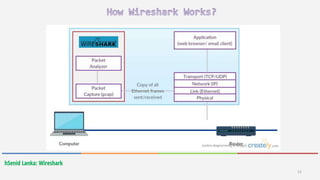
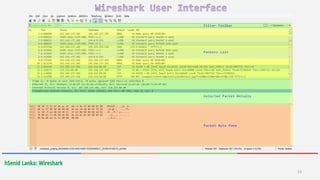
Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer that allows users to capture and analyze network traffic. It can be used to troubleshoot network problems, analyze network security issues, and debug protocol implementations. Wireshark has both a graphical user interface and command line interface and supports filtering, sorting, and color-coding packets to help users analyze network traffic.














![hSenid Lanka: Wireshark
22
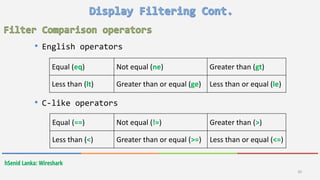
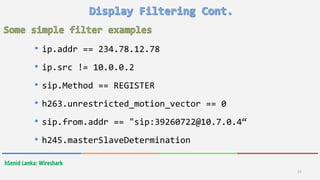
and && Logical and
or || Logical or
xor ^^ Logical XOR
not ! Logical Not
[…] Substring operator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wireshark-160421065958/85/Wireshark-22-320.jpg)