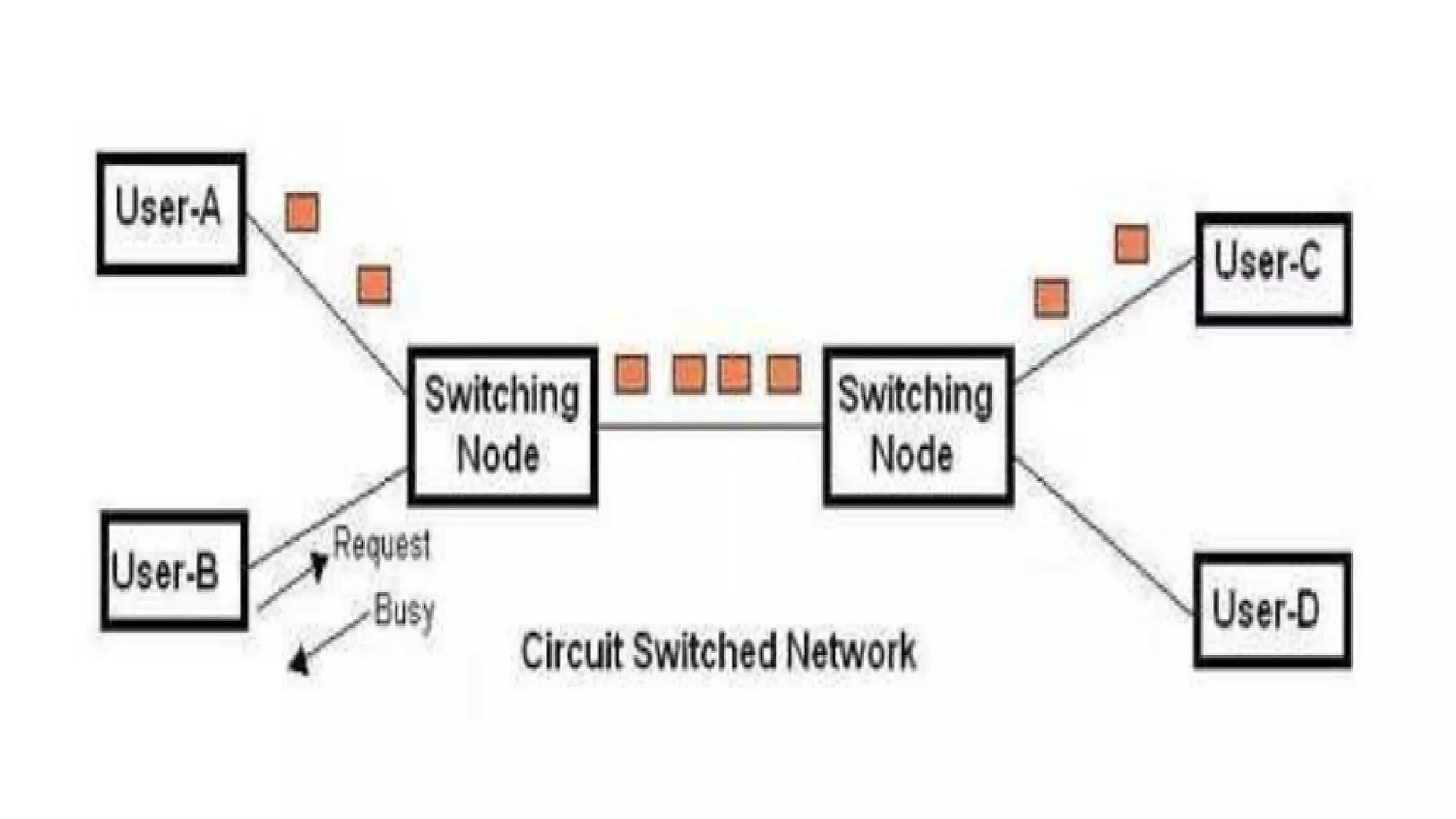
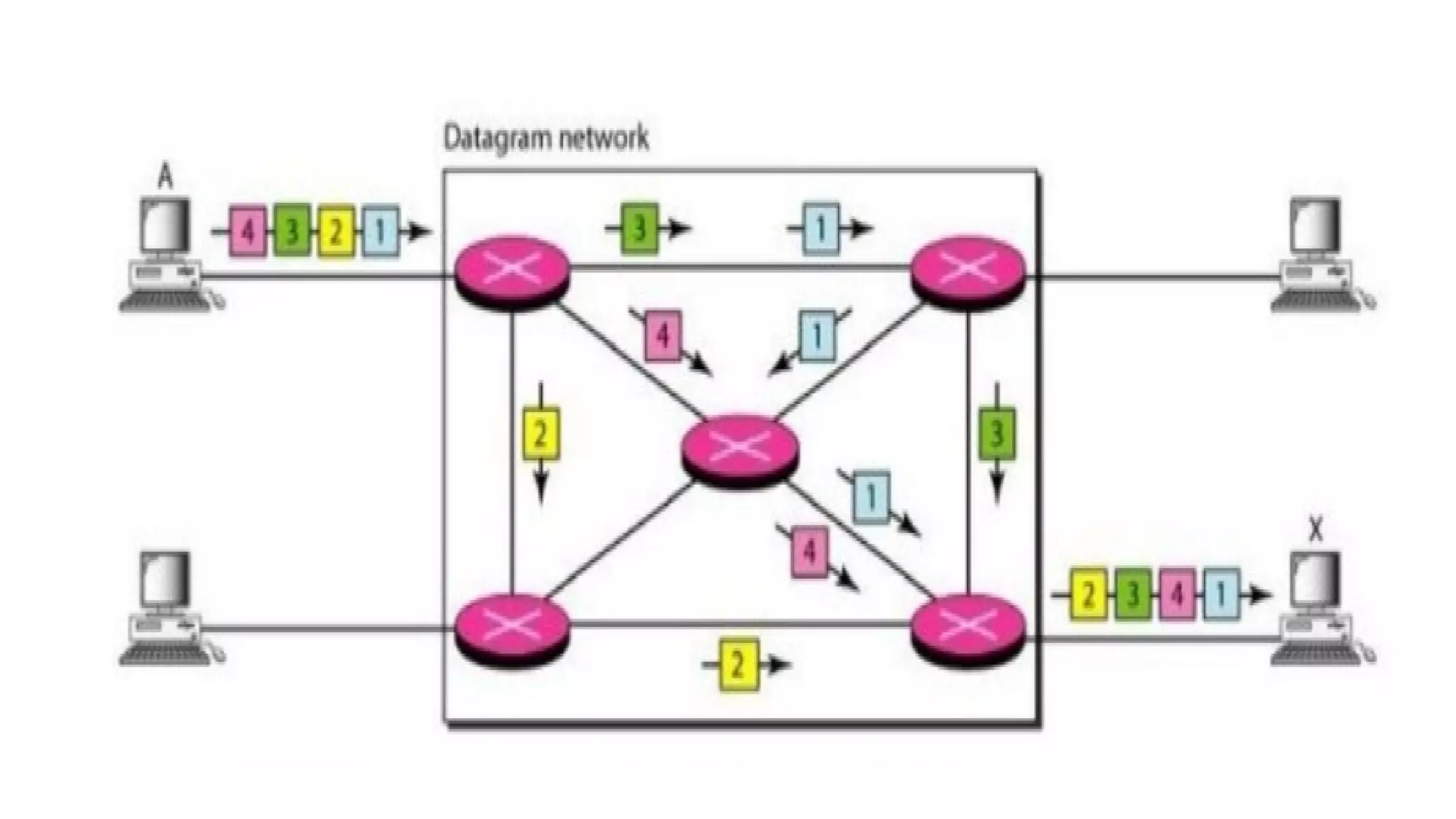
The document compares circuit switching and packet switching in computer networks. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated path for data that guarantees delivery but can waste bandwidth, while packet switching divides messages into packets that travel independently without setting up a connection, allowing for faster data transmission but at the cost of reliability. It also covers virtual circuit networks, which combine aspects of both methodologies, and datagram networks, which are connectionless with independent packet treatment.