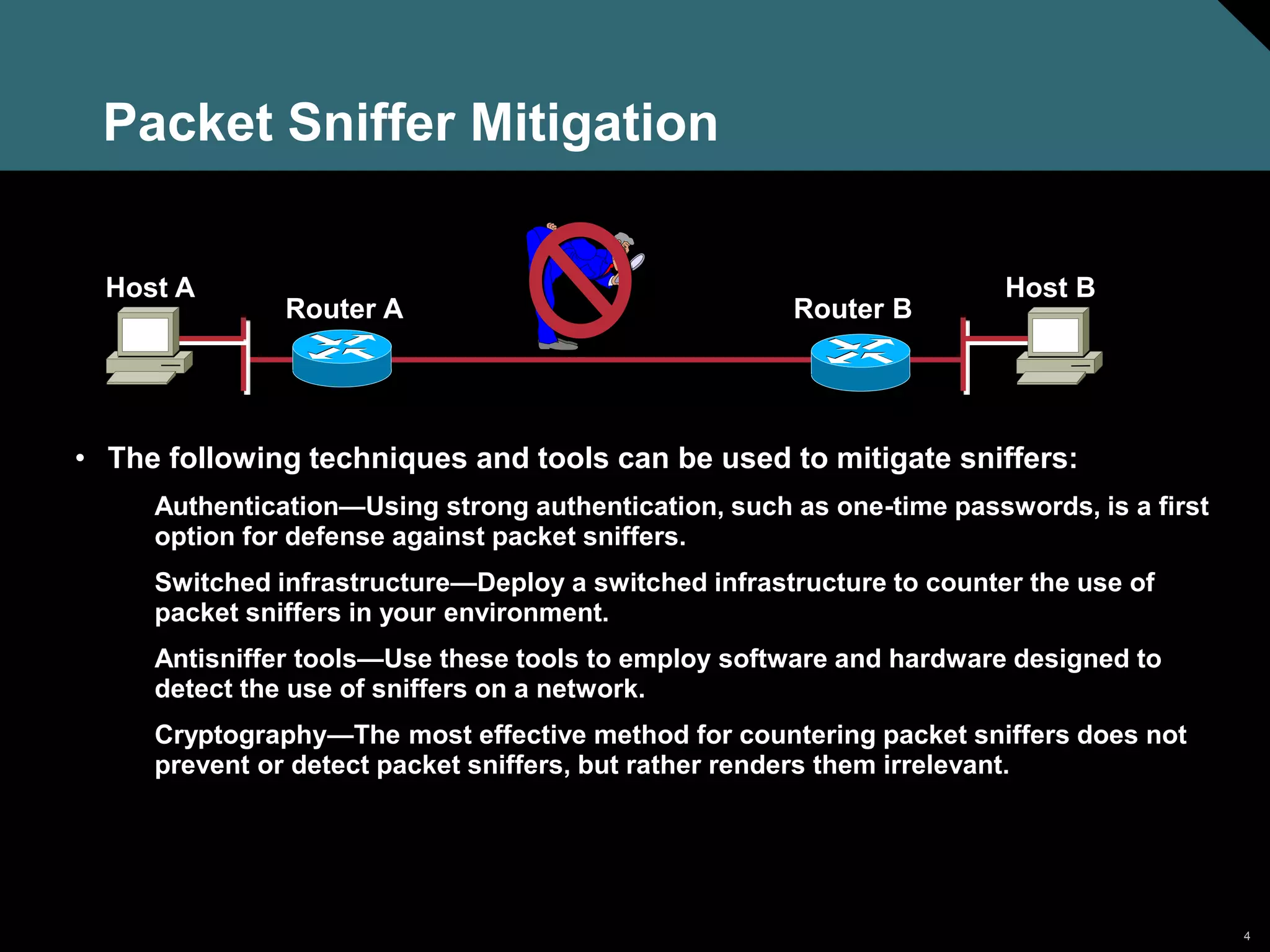
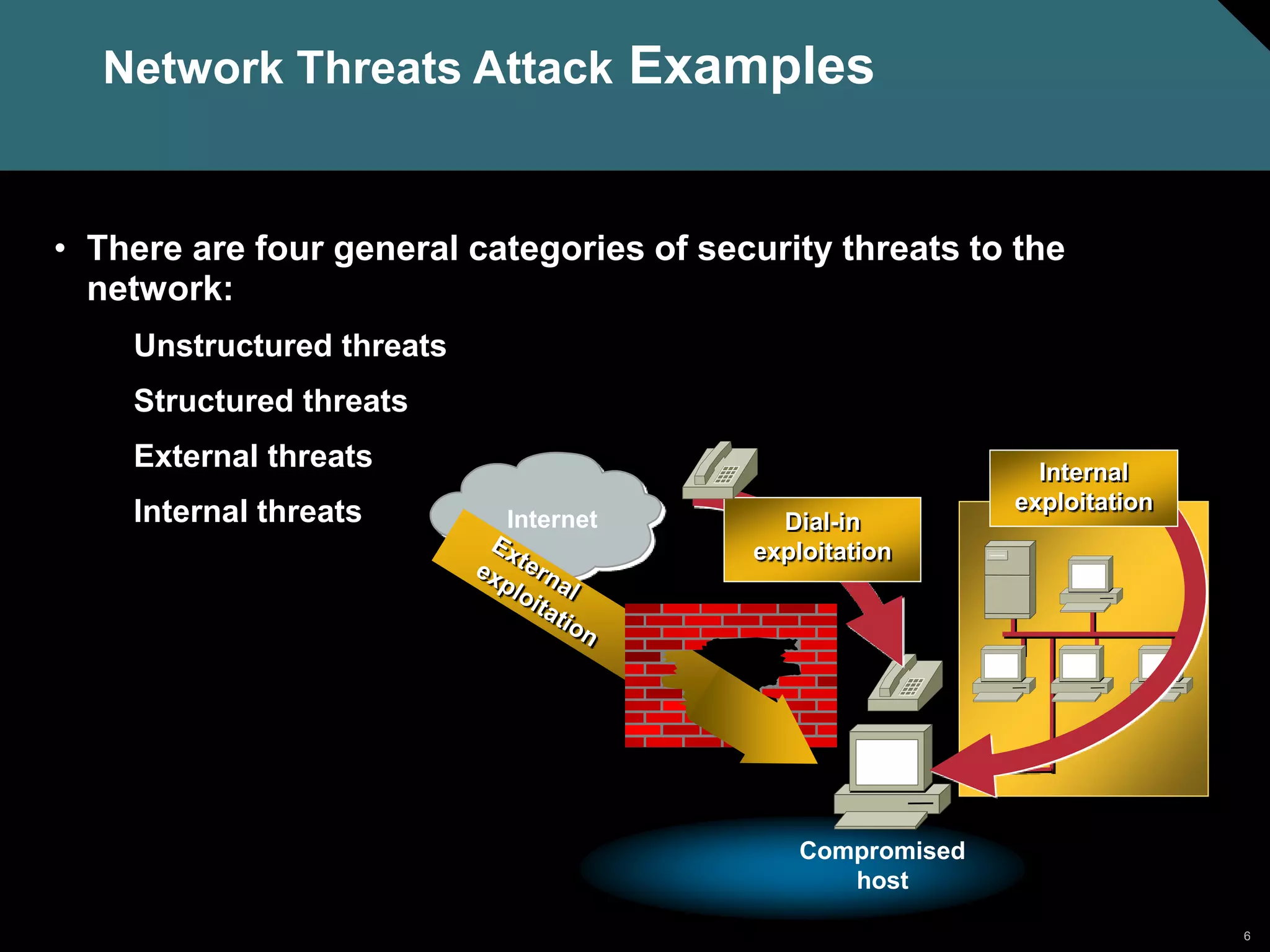
Packet sniffers are software applications that can capture all network packets by using a network adapter card in promiscuous mode. They exploit information passed in clear text protocols like Telnet, FTP, SNMP, and POP. To be effective, packet sniffers must be on the same collision domain as the target network traffic. Authentication, switched infrastructure, antisniffer tools, and cryptography can be used to mitigate packet sniffers.