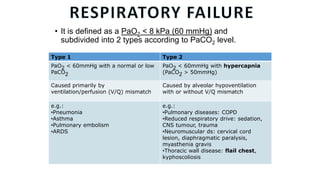
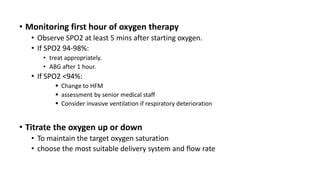
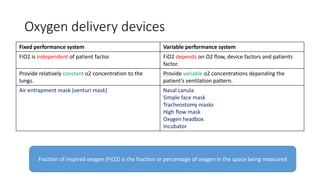
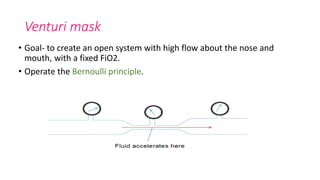
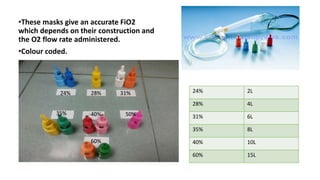
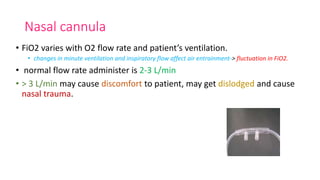
This document discusses oxygen therapy, including its indications, principles, devices, hazards, and key takeaways. Oxygen therapy aims to correct hypoxemia by raising oxygen levels in the alveoli and blood. Different oxygen delivery devices provide either fixed or variable concentrations of oxygen depending on factors like flow rate and patient breathing. Positive pressure ventilation like CPAP and BiPAP help keep alveoli open to improve gas exchange. Hazards include oxygen toxicity from prolonged high concentrations and carbon dioxide narcosis in patients with respiratory failure. Monitoring is important when starting and adjusting oxygen therapy.