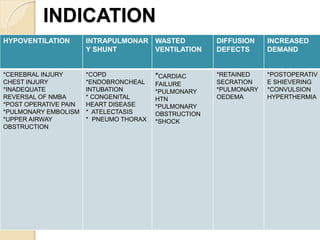
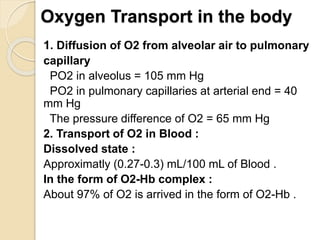
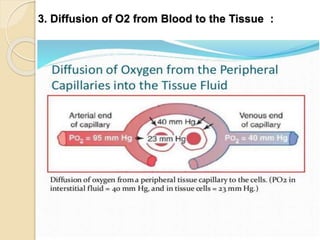
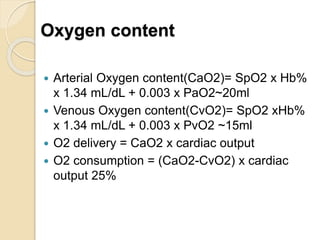
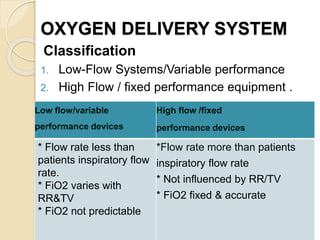
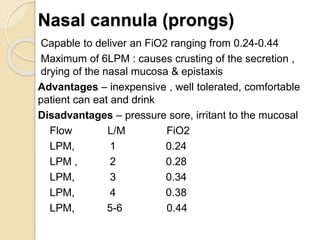
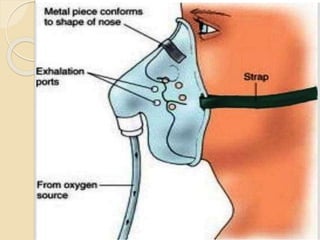
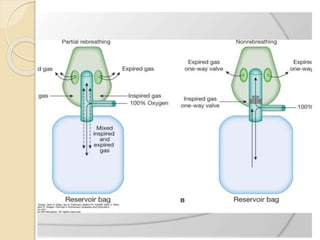
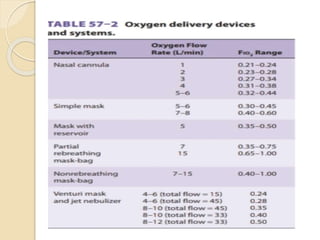
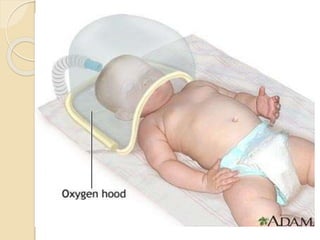
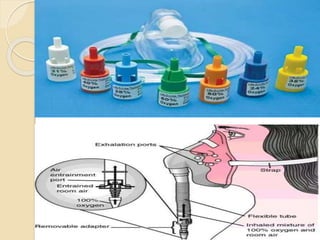
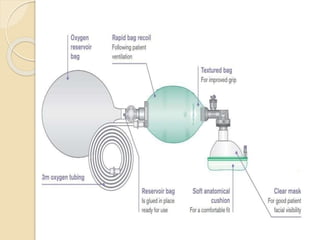
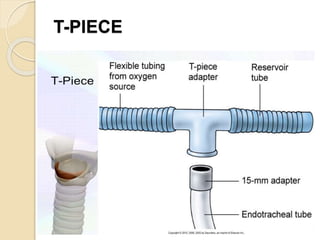
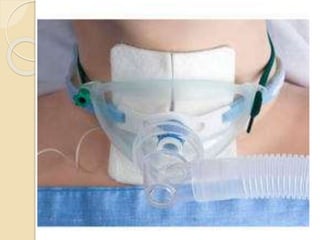
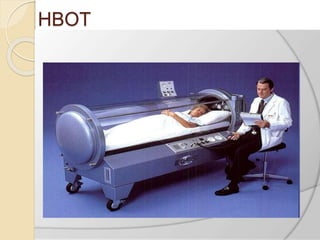
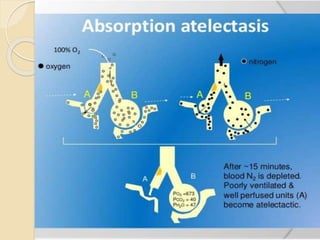
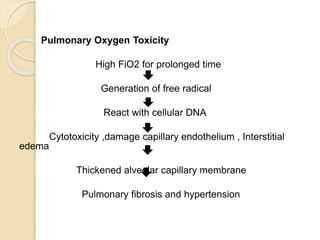
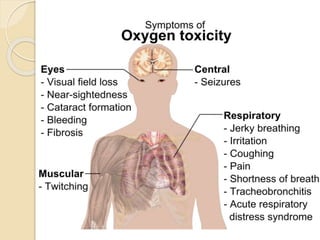
Oxygen therapy involves administering oxygen at concentrations greater than in ambient air to treat hypoxia and reduce work of breathing and myocardial work. It can be delivered via low-flow nasal cannulas or high-flow face masks, hoods, and tents. Precautions must be taken when using oxygen to avoid drying tissues, hypoventilation, absorption atelectasis, oxygen toxicity, and fire hazards. Clinical assessment and arterial blood gases are used to monitor patients and determine appropriate oxygen concentrations and durations of therapy.