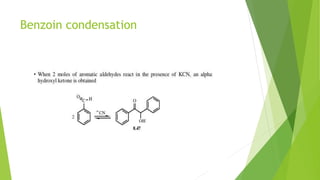
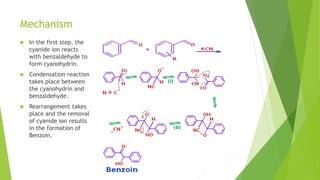
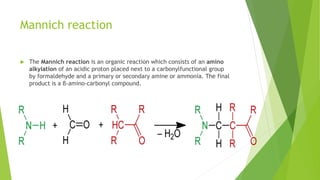
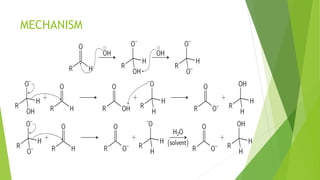
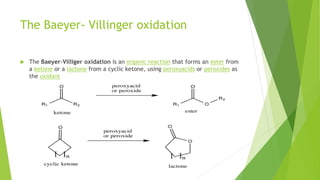
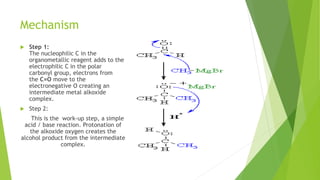
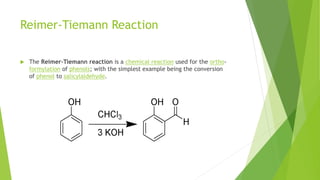
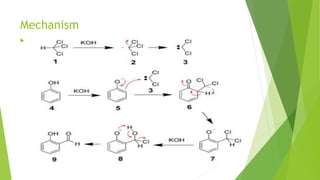
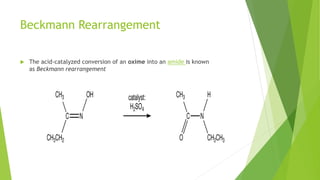
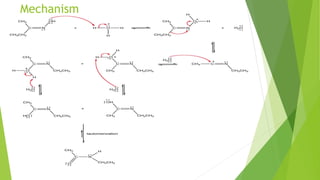
Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (>C=O) and can undergo numerous reactions. In aldehydes, the carbonyl is bonded to one alkyl group and one hydrogen. In ketones, it is bonded to two alkyl groups. Common reactions include reduction to alcohols using LiAlH4 or NaBH4, addition of Grignard reagents, and reactions involving the acidic alpha-hydrogens like benzoin condensation, Cannizzaro reaction, and Clemmenson reduction. Other important reactions are the Wittig reaction, Knoevenagel condensation, Wolf-Kishner reduction, and Baeyer-Villiger oxidation.