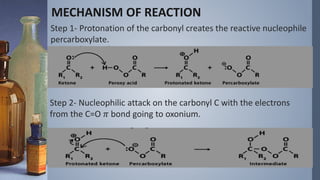
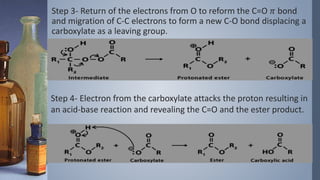
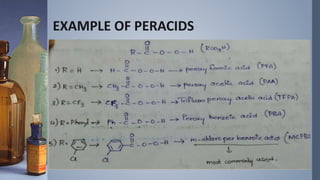
This document discusses the Vilsmeyer-Haack reaction, which involves the oxidation and rearrangement of ketones to produce esters. It first reported the reaction, which uses peroxy acids or compounds to add an oxygen atom to the carbonyl group of a ketone. The reaction proceeds through a mechanism of protonation, nucleophilic attack, carbon-carbon electron migration, and formation of an ester product. The migratory aptitude of groups during the reaction follows a general order. Common reagents include peracids, hydrogen peroxide, and bis(trimethylsilyl)peroxide. An example application is the conversion of cyclohexanone to caprolactone.