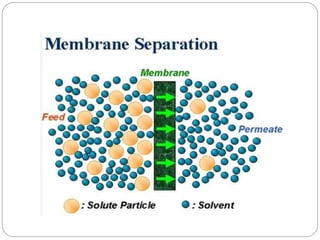
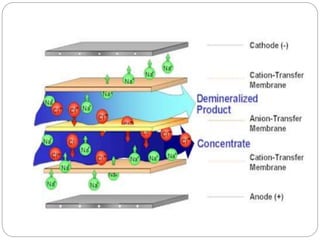
This document discusses different membrane separation techniques including reverse osmosis, dialysis, and electrodialysis. Reverse osmosis uses pressure to force purified water through a semi-permeable membrane, leaving dissolved ions behind. Dialysis relies on diffusion across a semi-permeable membrane to remove low molecular weight solutes from fluids. Electrodialysis transports ions through ion exchange membranes under an applied electric potential to purify solutions.