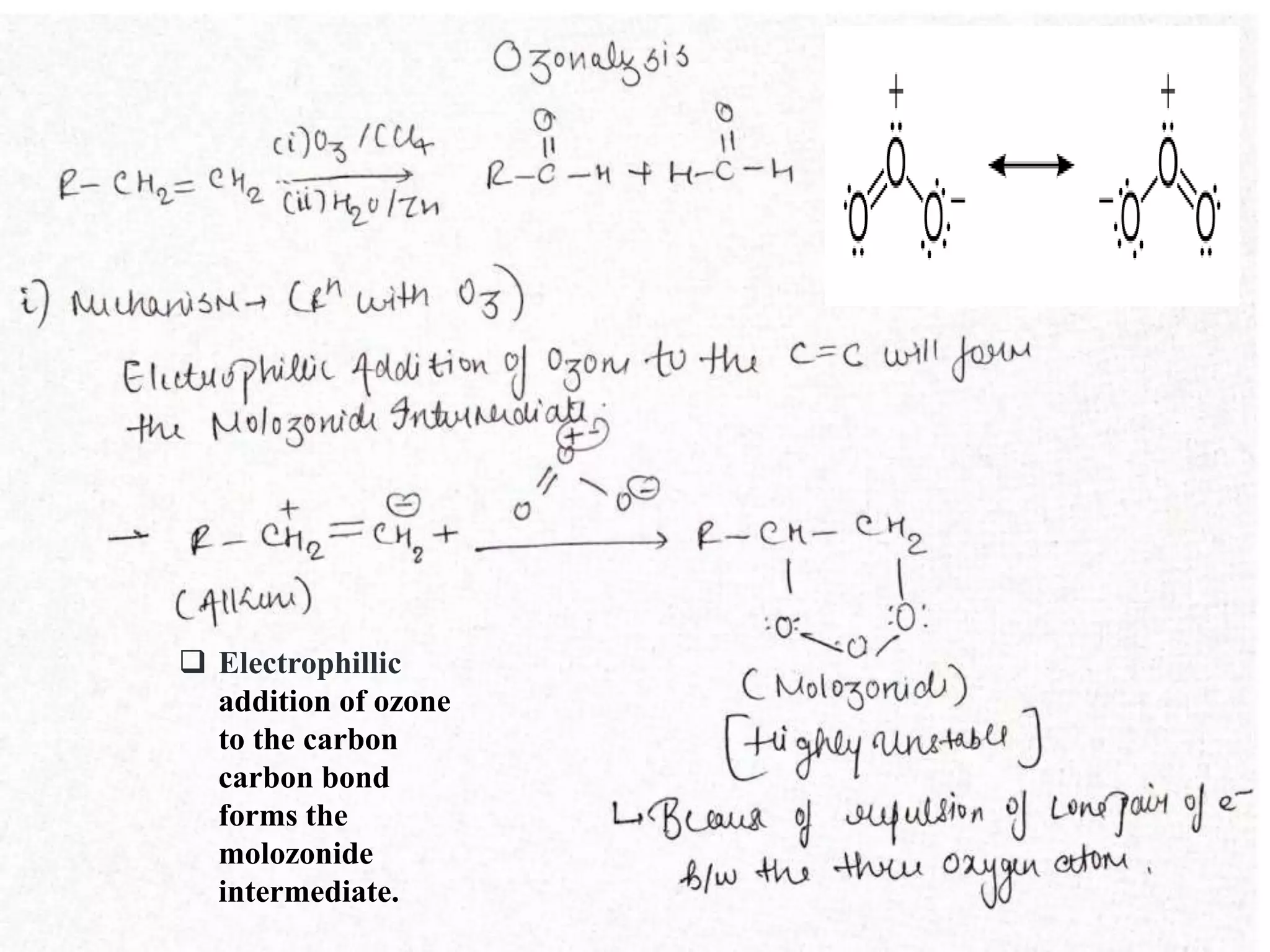
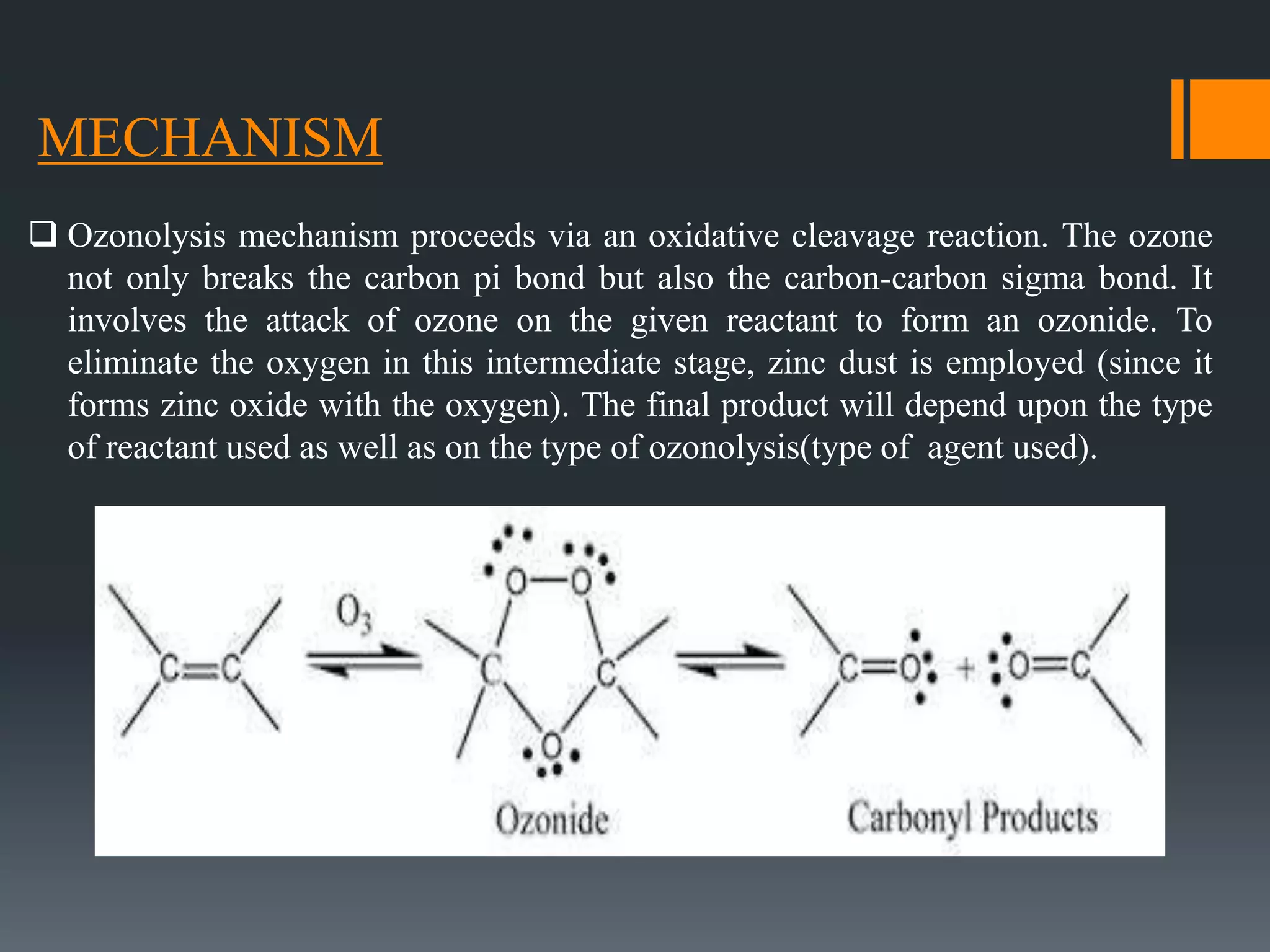
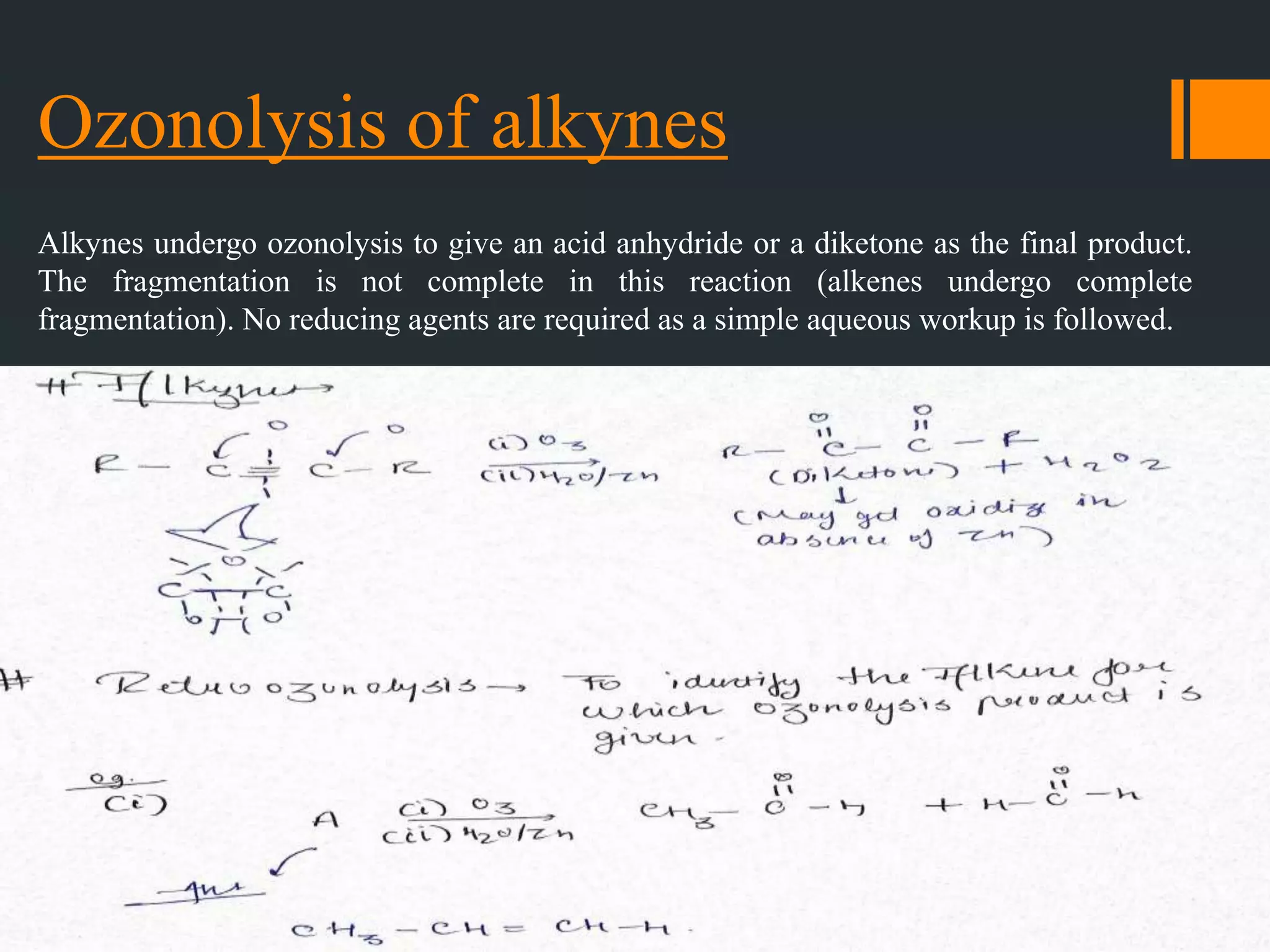
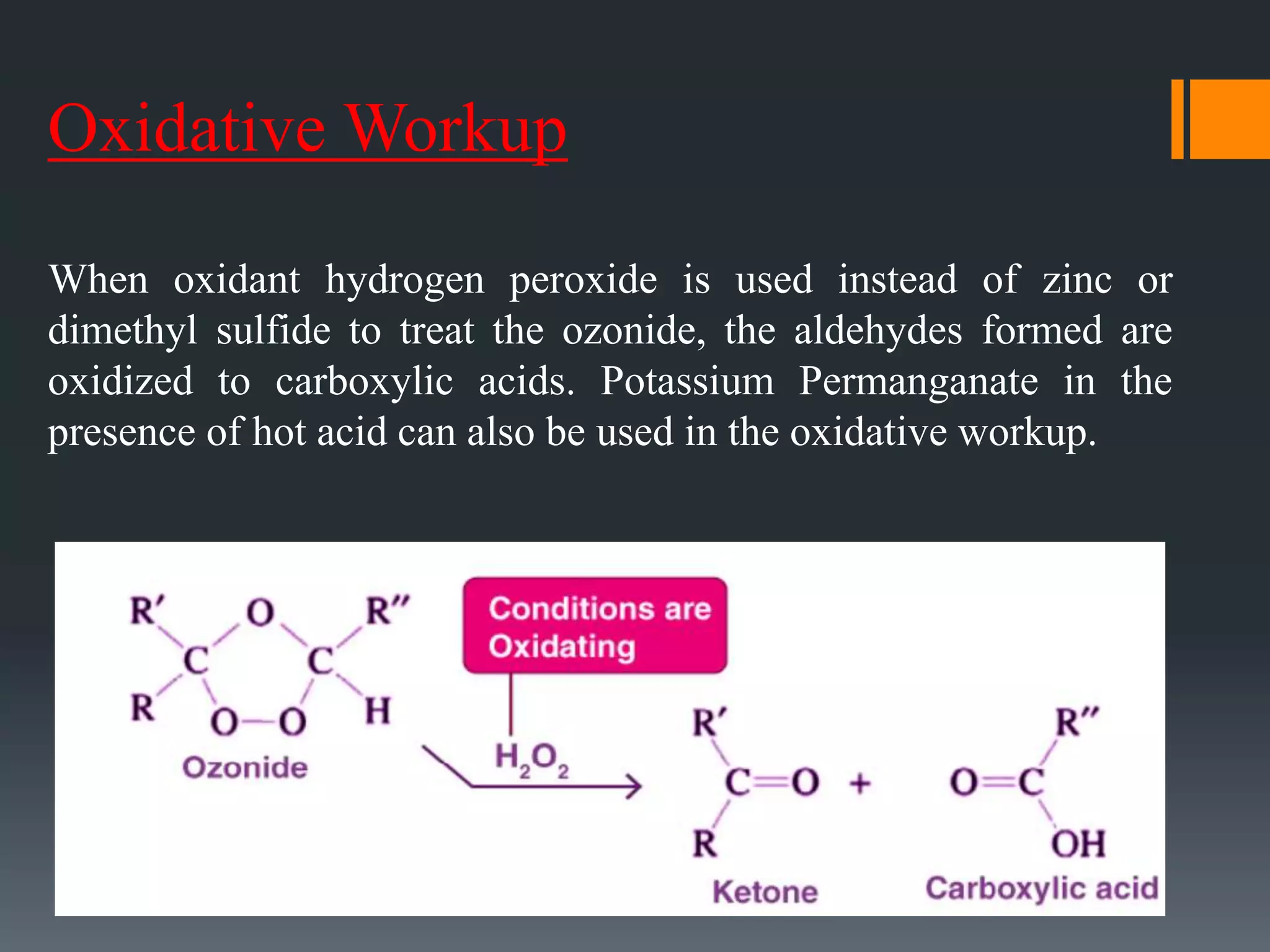
The document summarizes ozonolysis, which is the reaction of ozone with alkenes, alkynes, and azo compounds. Ozonolysis of alkenes forms an ozonide intermediate that can be converted to alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids depending on the workup. Alkynes undergo ozonolysis to form diketones or carboxylic acids. Ozonolysis has applications in synthesizing aldehydes, ketones, and drugs, and can be used to determine double bond locations in unknown alkenes.