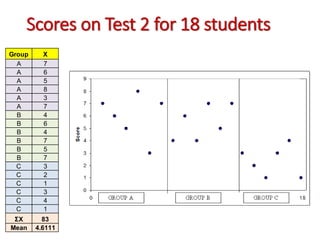
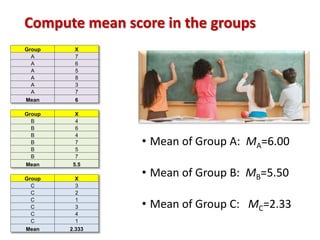
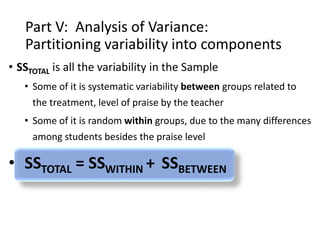
1. Students were randomly assigned to one of three groups and given a math test. The teacher then provided different levels of praise to each group: high praise to Group A, moderate praise to Group B, and no praise to Group C.
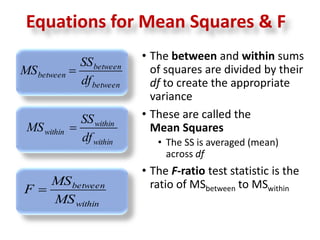
2. The next day, all students took another math test, and their scores were analyzed using ANOVA to determine if the different levels of praise had an effect.
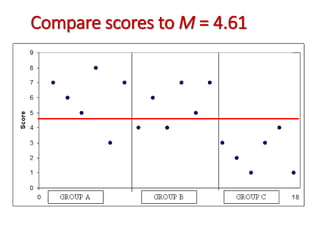
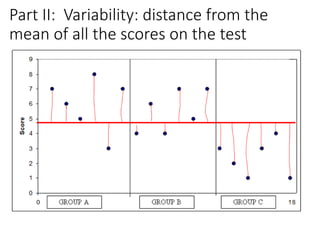
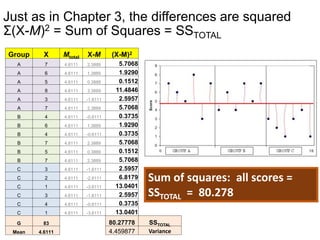
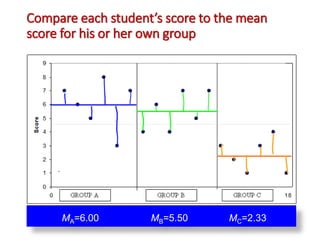
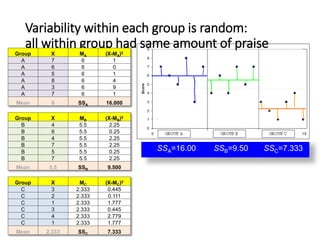
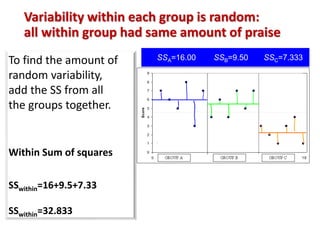
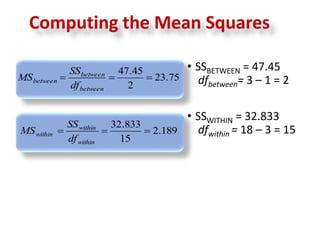
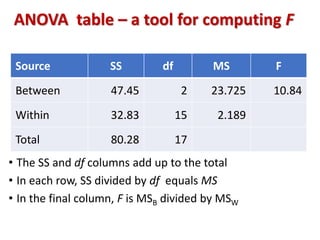
3. The ANOVA analysis found a significant difference between the group means, with Group A scoring highest and Group C scoring lowest. This led to a rejection of the null hypothesis that the praise had no impact on test scores.