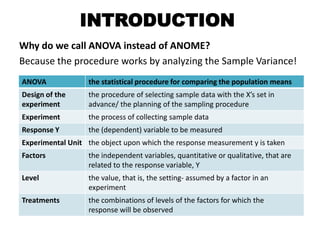
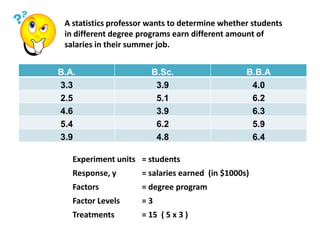
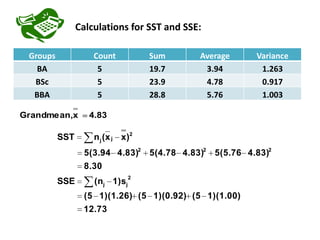
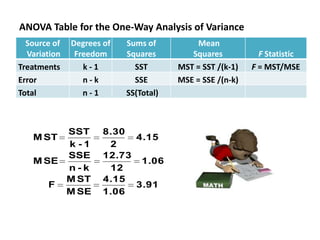
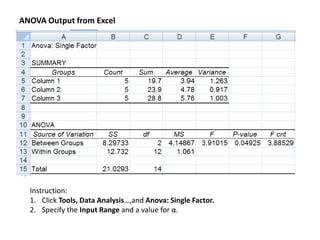
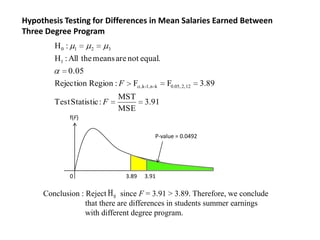
This document provides information about analysis of variance (ANOVA). It begins by explaining why ANOVA is called ANOVA and defines key terms related to experimental design and ANOVA. It then discusses the advantages of using ANOVA, describes three common experimental designs (completely randomized design, randomized block design, and two-factorial design), and provides an example of a completely randomized design (CRD) to compare mean salaries earned by students in different degree programs over the summer. The example calculates sums of squares, conducts an ANOVA test, and concludes that there are statistically significant differences in mean salaries earned between the three degree programs.