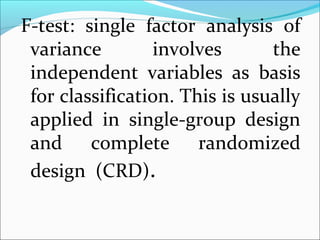
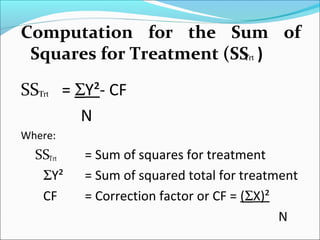
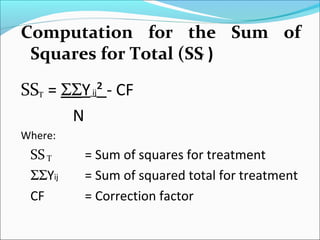
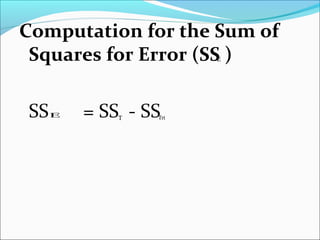
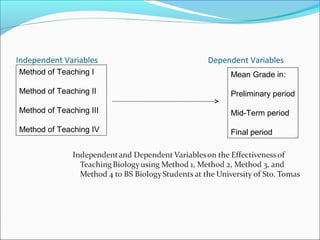
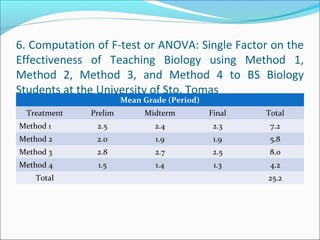
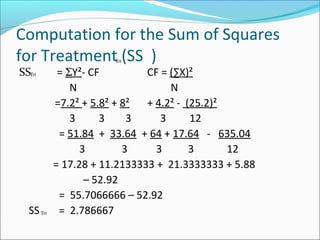
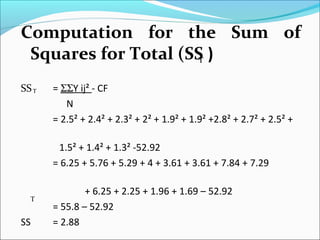
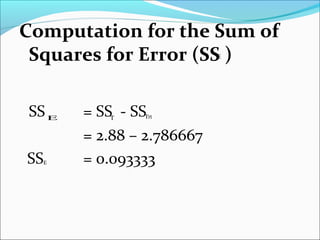
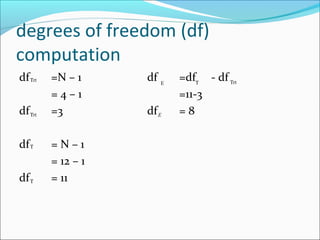
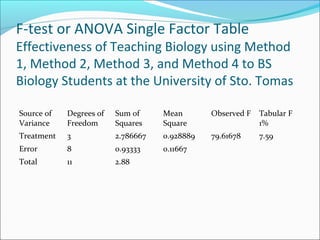
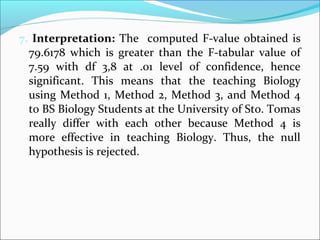
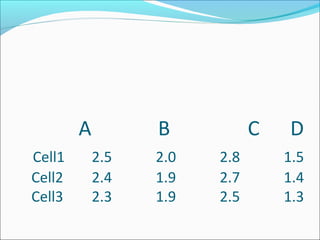
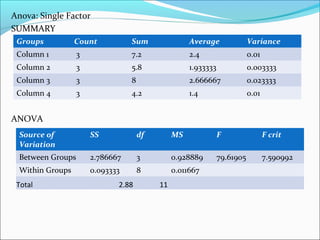
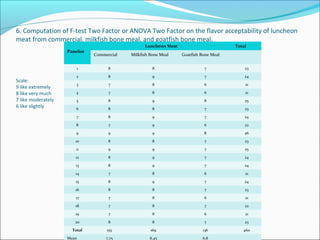
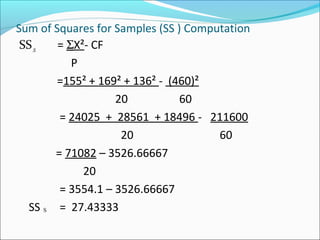
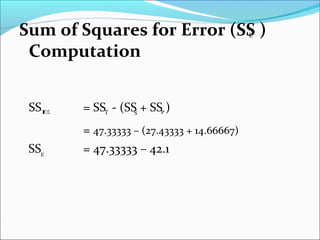
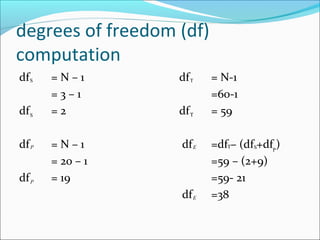
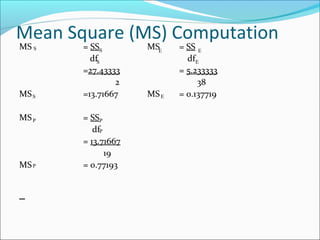
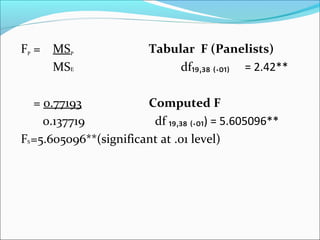
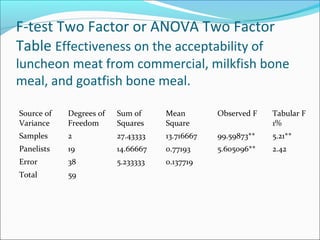
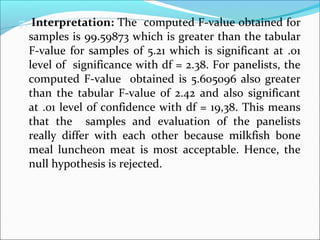
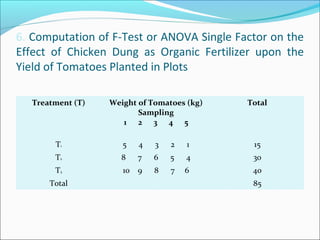
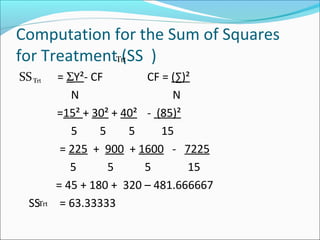
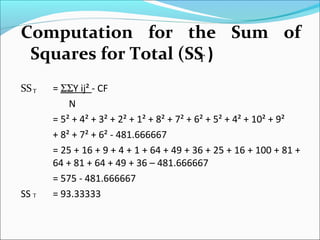
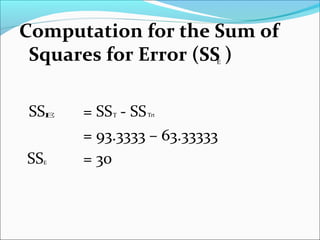
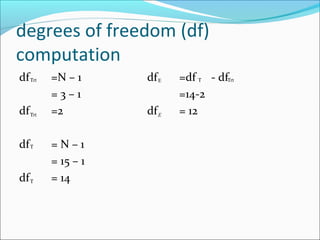
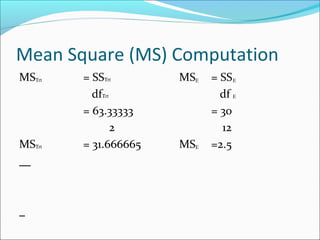
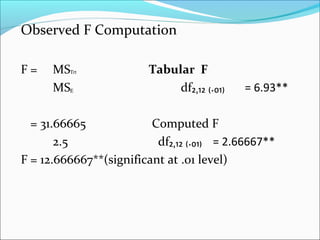
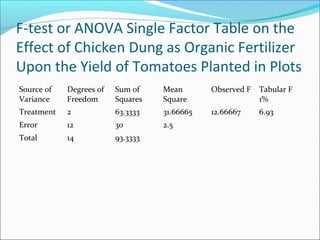
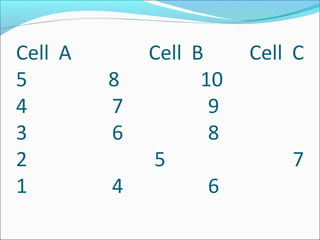
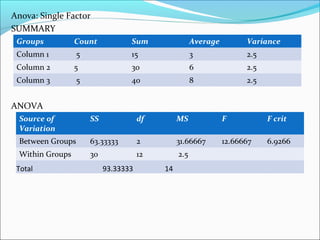
ANOVA analysis was conducted to compare the effectiveness of 4 teaching methods on student grades. The analysis found a significant difference between the methods (F=79.61678, p<0.01), with Method 4 being most effective. A second ANOVA compared acceptability of luncheon meat from 3 sources using 20 panelists, finding significant differences between sources (F=99.59873, p<0.01) and panelists (F=5.605096, p<0.01).