1) Shock is a life-threatening condition where tissue perfusion is inadequate, preventing delivery of oxygen and nutrients to vital organs and cells.
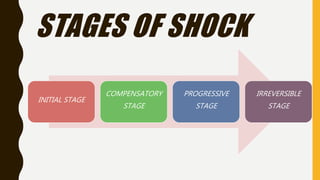
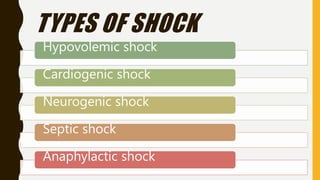
2) Shock progresses through initial, compensatory, progressive, and irreversible stages and can be caused by hypovolemia, heart problems, neurologic issues, sepsis, or allergic reactions.
3) Nursing management of shock involves rapid assessment of circulation, breathing, level of consciousness and skin signs; providing immediate care like oxygen, IV fluids, medications; and identifying and treating the underlying cause.