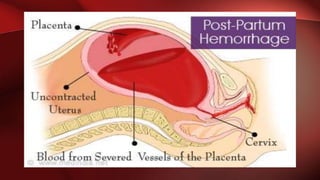
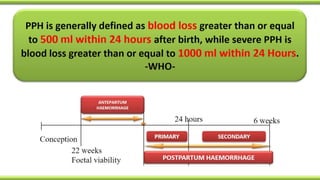
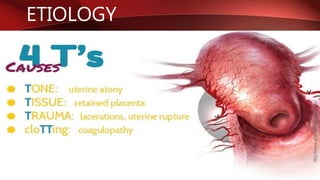
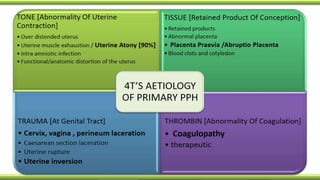
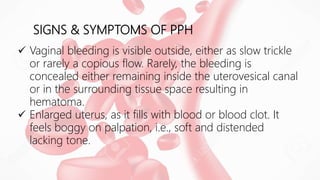
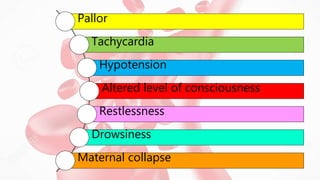
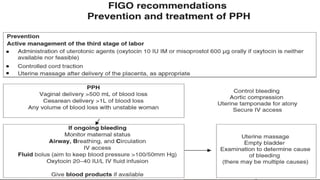
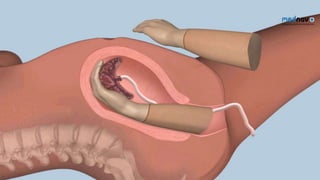
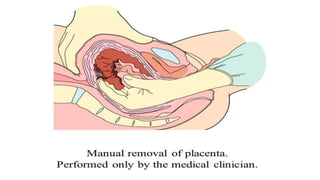
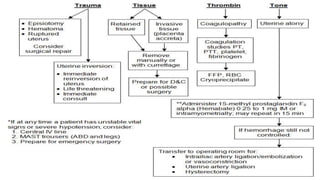
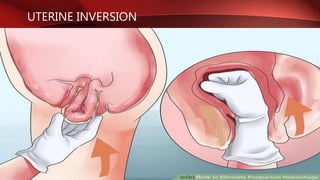
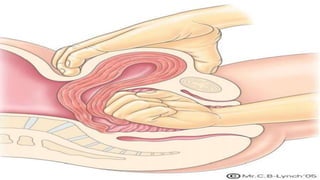
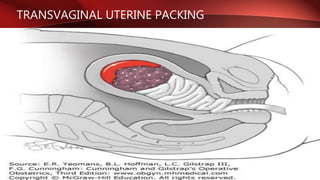
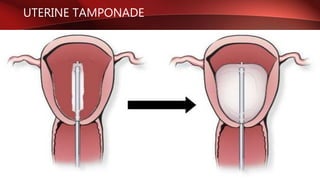
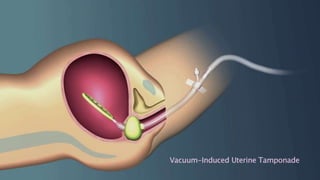
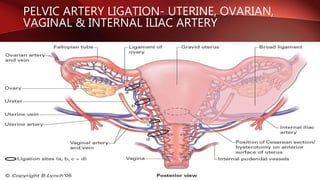
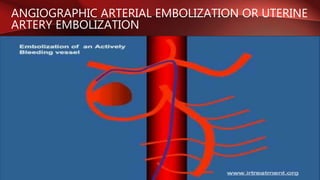
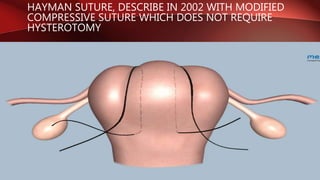
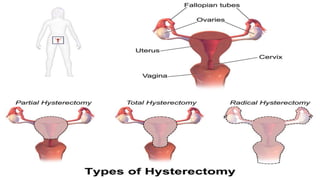
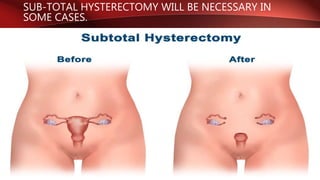
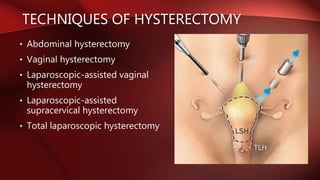
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is excessive bleeding following childbirth. It is a leading cause of maternal mortality, accounting for nearly one quarter of maternal deaths worldwide. The most common cause is uterine atony, or failure of the uterus to contract after delivery. Other causes include retained placenta, trauma during delivery, coagulation disorders, and issues like placenta previa. Risk factors include previous PPH, macrosomia, multiple pregnancy, and uterine overdistention. Prevention focuses on risk assessment and active management of the third stage of labor. Treatment depends on the severity but may include uterine massage, uterotonic drugs, uterine packing, arterial ligation, embolization, compression sutures,