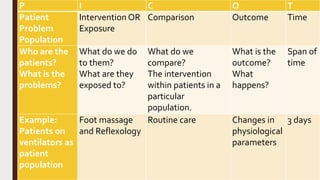
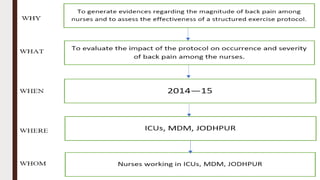
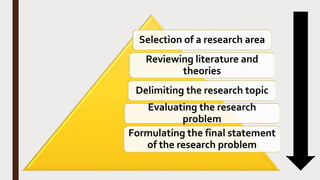
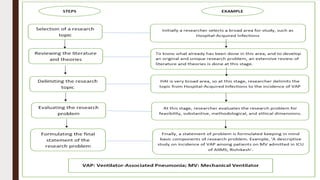
This document discusses formulating a research problem. It defines a research problem, outlines the key elements including objectives, topics, time dimensions, locations, and populations. It also discusses criteria for selecting a good research problem such as feasibility, novelty, ethics, and relevance. Sources of research problems and the phases of establishing a problem statement are described. An example of a well-formulated research problem is provided.