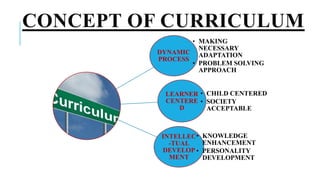
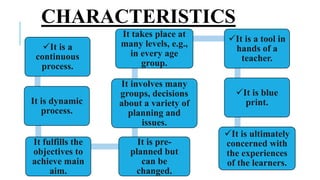
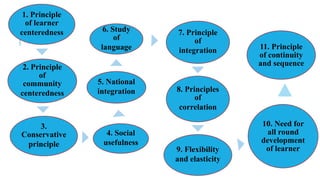
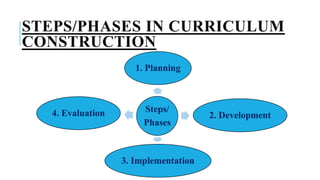
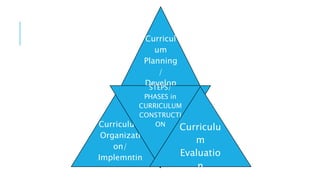
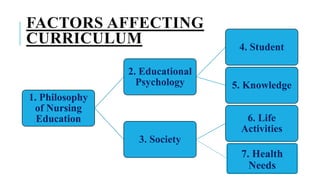
The document discusses the key aspects of curriculum development for nursing education programs. It defines curriculum and provides principles and factors to consider in curriculum planning, development, implementation and evaluation. The summary should include the purpose of the curriculum, the main phases of development, and that it aims to equip students with the necessary knowledge, skills and attitudes for their professional roles.