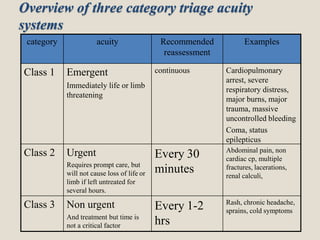
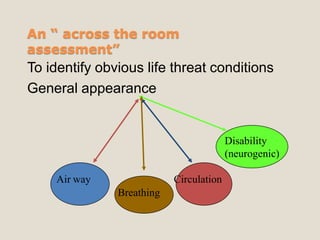
Triage is the process of sorting patients based on the urgency of their condition to determine priority of treatment. The goal is to provide the right care to the right patient at the right time. There are different categories for triage, such as immediate, urgent, less urgent and non-urgent. The triage nurse conducts an initial assessment of the patient's airway, breathing, circulation and disability level to identify life-threatening issues and assign an acuity level for treatment. Re-triage is important as a patient's condition may deteriorate while waiting. The triage nurse plays a key role in efficiently sorting and treating patients based on need.