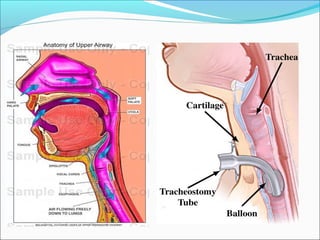
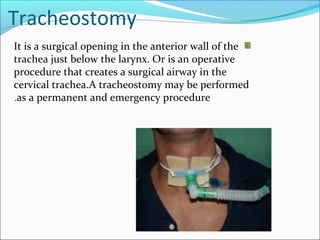
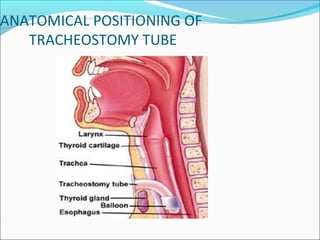
1. Tracheostomy is a surgical opening in the front of the trachea below the larynx that creates an airway. It is performed to maintain a clear airway, remove secretions, and enable ventilation.
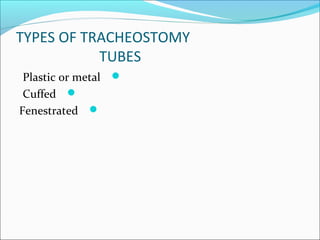
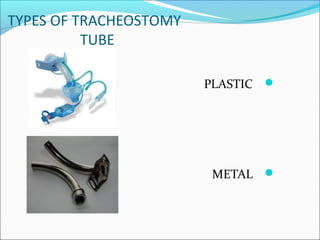
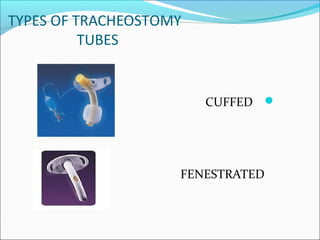
2. Tracheostomy tubes can be plastic, metal, cuffed, or fenestrated. Speaking valves allow vocalization without finger occlusion using a silicone diaphragm that opens for inhalation and closes for exhalation.
3. Complications include bleeding, infection, tube obstruction, aspiration, and tracheal stenosis. Care involves cleaning the stoma and tube, suctioning secretions, providing humidification, and assessing for ineffective airway clearance or