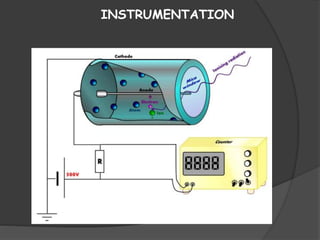
1) A Geiger-Muller counter detects ionizing radiation by measuring the pulses produced when radiation particles pass through a gas-filled tube and cause ionization.
2) It consists of a copper cylinder containing an inert gas at low pressure, with electrodes to collect ions produced and measure the resulting pulse.
3) Geiger counters are useful for detecting beta particles and low-energy photons, and have applications in radiation dosimetry, health physics, and other fields where radiation detection is needed.