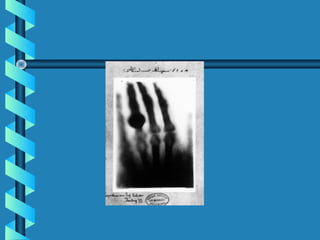
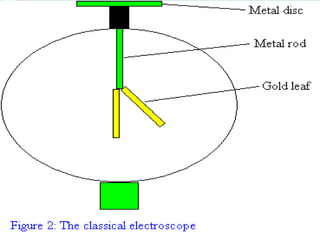
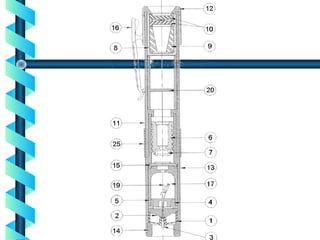
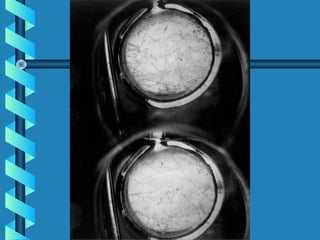
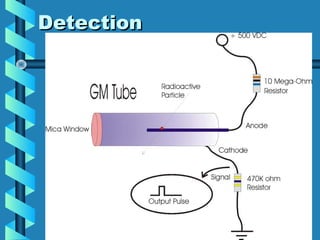
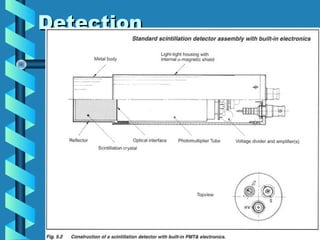
This document discusses various methods for detecting radiation. It outlines passive detectors like photographic film, electroscopes, dosimeters, and thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLDs) which do not require a power source. Active detectors mentioned include Geiger-Muller tubes and scintillation detectors, which need a constant energy supply. Both types detect radiation indirectly by ionizing matter and detecting the ions produced, though active detectors provide more information about the radiation type and energy.