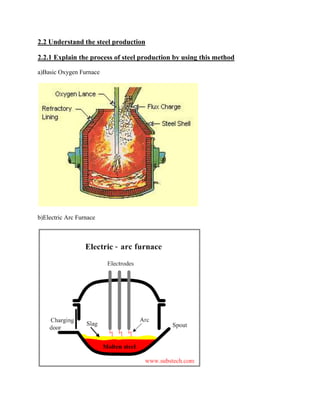
The document discusses ferrous material structure and binary alloy systems. It provides information on:
1) Metal production industries such as automated welding equipment, metal cleaning equipment, foundry equipment, CNC machine refit, plasma and laser cutting, press room equipment, die monitoring and control, spin forming, precision winding, and remote control systems.
2) The content of iron ore, which is usually rich in iron oxides and includes magnetite, hematite, goethite, limonite, and siderite.
3) The process of iron production using a blast furnace, where iron oxide, limestone, coke, and oxygen are injected and react to produce pure liquid iron and slag